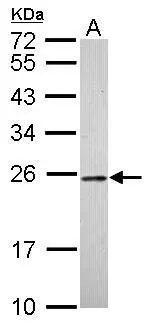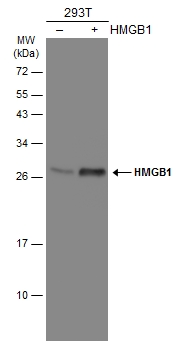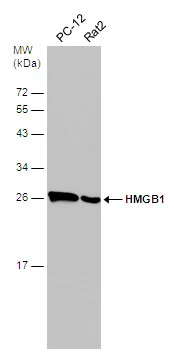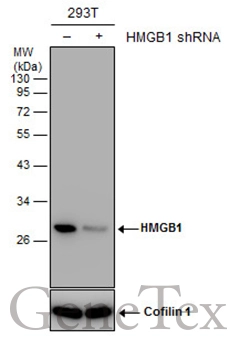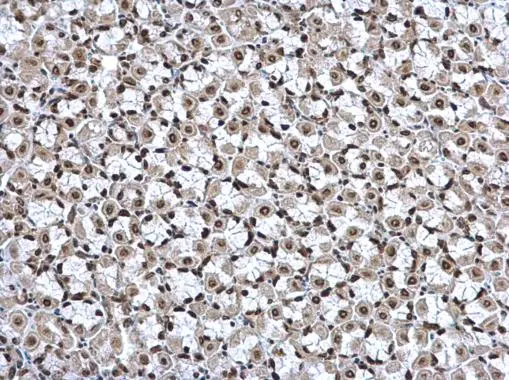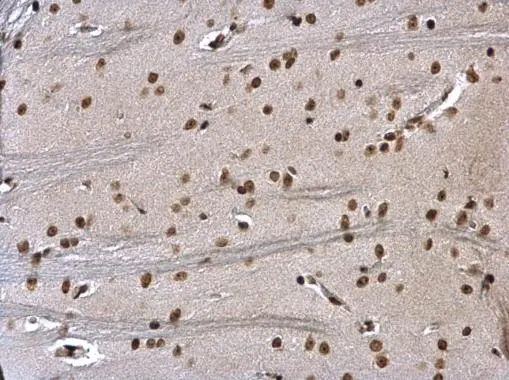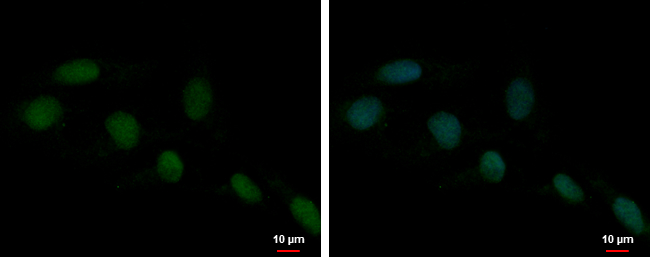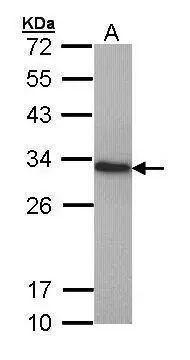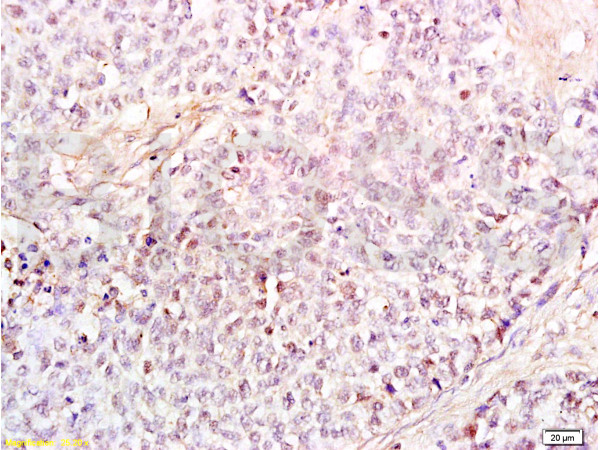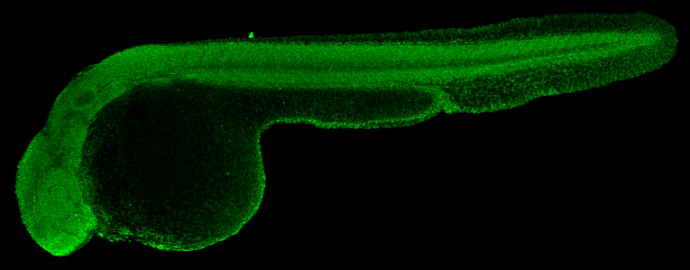
HMGB1 antibody detects Hmgb1 protein on zebrafish by whole mount immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: 2 days-post-fertilization zebrafish embryo. HMGB1 antibody (GTX112959) dilution: 1:100.
HMGB1 antibody
GTX112959
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat, Zebra Fish
TargetHMGB1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameHMGB1 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. ICC/IF: 1:100-1:1000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.53 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID3146
- Target nameHMGB1
- Target descriptionhigh mobility group box 1
- Target synonymsHMG-1, HMG1, HMG3, SBP-1, high mobility group protein B1, Amphoterin, Sulfoglucuronyl carbohydrate binding protein, high-mobility group (nonhistone chromosomal) protein 1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP09429
- Protein NameHigh mobility group protein B1
- Scientific DescriptionDNA binding proteins that associates with chromatin and has the ability to bend DNA. Binds preferentially single-stranded DNA. Involved in V(D)J recombination by acting as a cofactor of the RAG complex. Acts by stimulating cleavage and RAG protein binding at the 23 bp spacer of conserved recombination signal sequences (RSS). Heparin-binding protein that has a role in the extension of neurite-type cytoplasmic processes in developing cells.
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat, Zebra Fish
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Yang C, Kim SH, Bianco NR, et al. Tumor-derived exosomes confer antigen-specific immunosuppression in a murine delayed-type hypersensitivity model. PLoS One. 2011,6(8):e22517. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0022517Read this paper