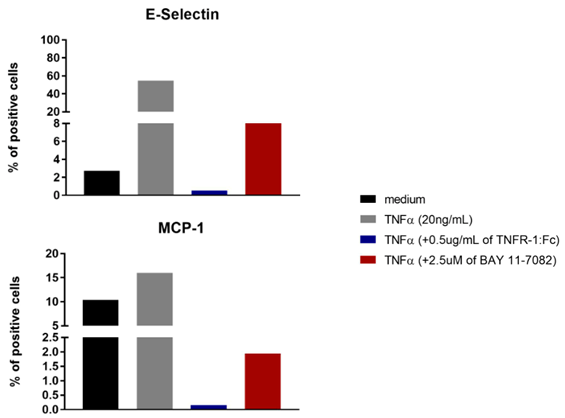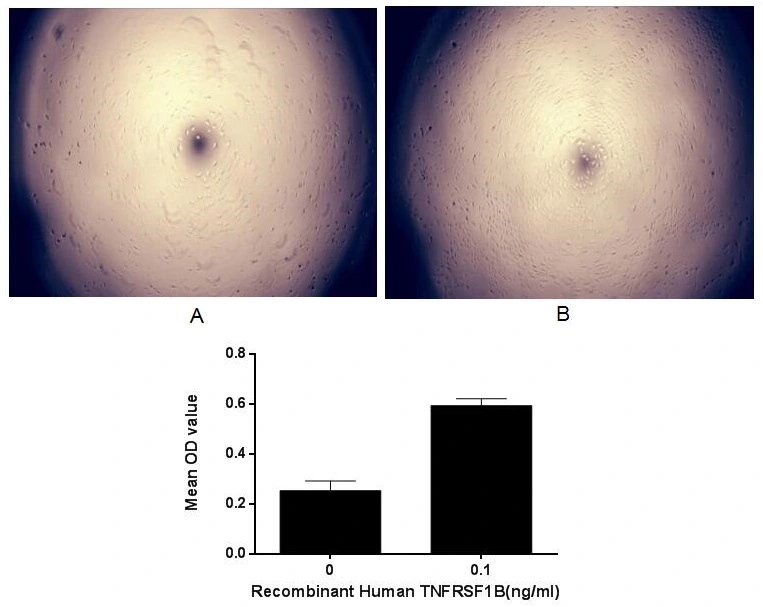
The suppression effect of GTX00234-pro Human TNF Receptor I protein (active) on TNF-alpha induced apoptosis. Cell viability was measured by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8). (A) A549 cells cultured in DMEM only contain 1 μg/ml TNFα for 96hrs. (B) A549 cells cultured in DMEM contain 1 μg/ml TNF alpha and 0.1 ng/ml TNFRSF1B for 96hrs.
Human TNF Receptor I protein, His and GST tag (active)
GTX00234-PRO
ApplicationsFunctional Assay
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Protein IDP19438
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameHuman TNF Receptor I protein, His and GST tag (active)
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteTumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 1B (TNFRSF1B), also known as tumor necrosis factor receptor 2 (TNFR2) and CD120b, is a membrane receptor that binds tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFalpha). This protein and TNF-receptor 1 form a heterocomplex that mediates the recruitment of two anti-apoptotic proteins, c-IAP1 and c-IAP2, which possess E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. TNFRSF1B can inhibit cell apoptosis which induced by TNFalpha. Briefly, A549 cells were seeded into triplicate wells of 96-well plates at a density of 2000 cells/well and allowed to attach, replaced with serum-free overnight, then the medium was replaced with 2% serum standard DMEM including 1microg/ml TNFalpha and various concentrations of recombinant human TNFRSF1B. After incubated for 96h, cells were observed by inverted microscope and cell proliferation was measured by Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8). Briefly, 10 microl of CCK-8 solution was added to each well of the plate, then the absorbance at 450nm was measured using a microplate reader after incubating the plate at 37C for 1-4 hours. Apoptosis of A549 cells had been inhibit after incubation with TNFRSF1B for 96h observed by inverted microscope.
- ApplicationsFunctional Assay
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID7132
- Target nameTNFRSF1A
- Target descriptionTNF receptor superfamily member 1A
- Target synonymsCD120a, FPF, TBP1, TNF-R, TNF-R-I, TNF-R55, TNFAR, TNFR1, TNFR55, TNFR60, p55, p55-R, p60, tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 1A, TNF-R1, TNF-RI, TNFR-I, tumor necrosis factor binding protein 1, tumor necrosis factor receptor type 1, tumor necrosis factor-alpha receptor
- Protein IDP19438
- Protein NameTumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 1A
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a member of the TNF receptor superfamily of proteins. The encoded receptor is found in membrane-bound and soluble forms that interact with membrane-bound and soluble forms, respectively, of its ligand, tumor necrosis factor alpha. Binding of membrane-bound tumor necrosis factor alpha to the membrane-bound receptor induces receptor trimerization and activation, which plays a role in cell survival, apoptosis, and inflammation. Proteolytic processing of the encoded receptor results in release of the soluble form of the receptor, which can interact with free tumor necrosis factor alpha to inhibit inflammation. Mutations in this gene underlie tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated periodic syndrome (TRAPS), characterized by fever, abdominal pain and other features. Mutations in this gene may also be associated with multiple sclerosis in human patients. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2016]
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116100
- SpeciesHuman