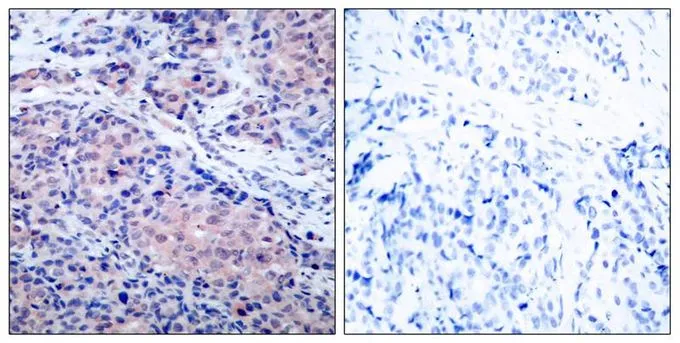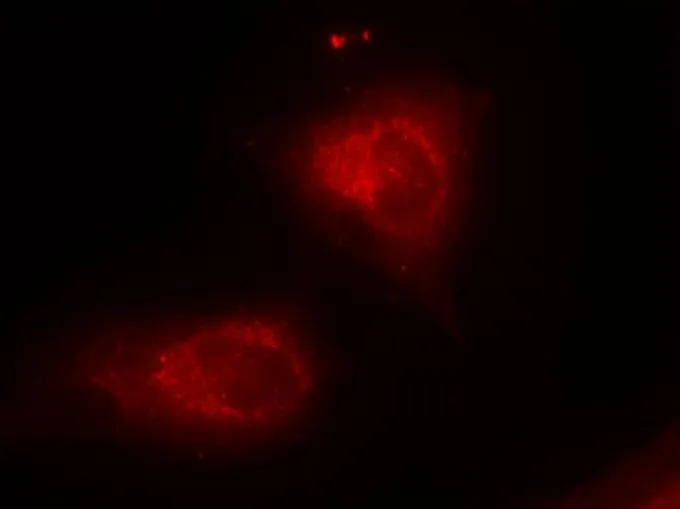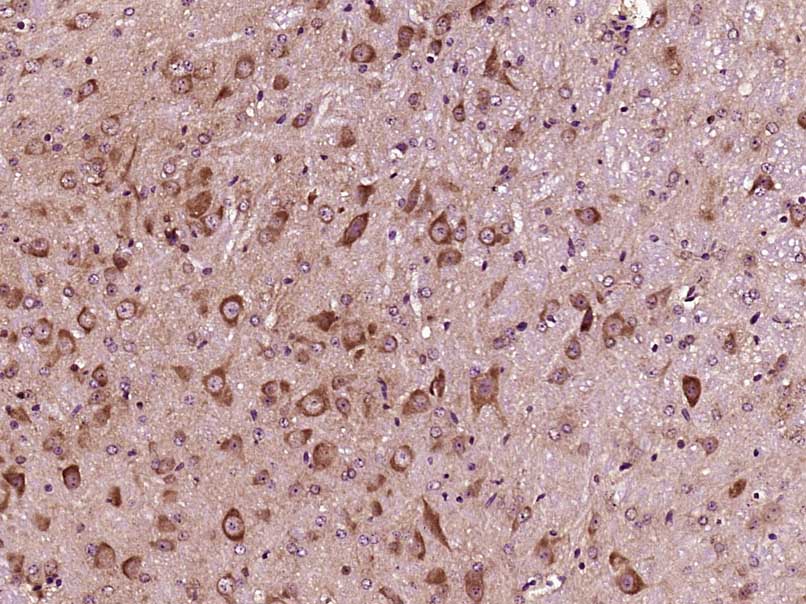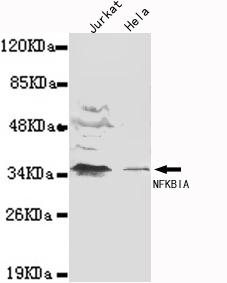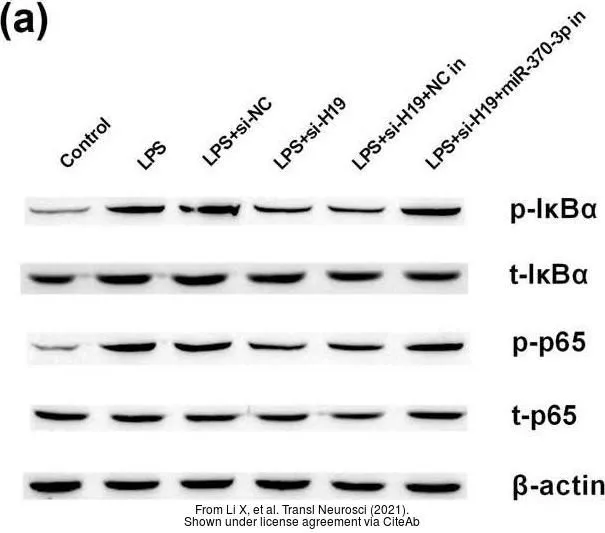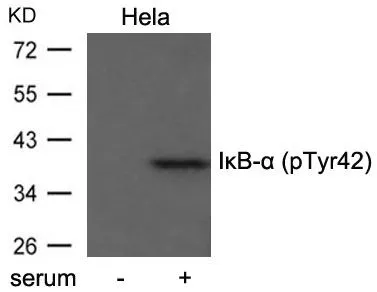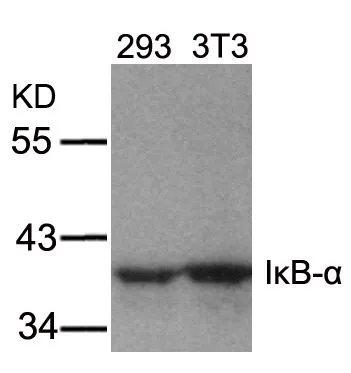
WB analysis of extracts from 293 and 3T3 cells using GTX50468 IKB alpha antibody.
IKB alpha antibody
GTX50468
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetNFKBIA
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameIKB alpha antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:1000. ICC/IF: 1:100-1:200. IHC-P: 1:50-1:100. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID4792
- Target nameNFKBIA
- Target descriptionNFKB inhibitor alpha
- Target synonymsEDAID2, IKBA, MAD-3, NFKBI, NF-kappa-B inhibitor alpha, I-kappa-B-alpha, IkappaBalpha, ikB-alpha, major histocompatibility complex enhancer-binding protein MAD3, nuclear factor of kappa light chain gene enhancer in B-cells, nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, alpha
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP25963
- Protein NameNF-kappa-B inhibitor alpha
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a member of the NF-kappa-B inhibitor family, which contain multiple ankrin repeat domains. The encoded protein interacts with REL dimers to inhibit NF-kappa-B/REL complexes which are involved in inflammatory responses. The encoded protein moves between the cytoplasm and the nucleus via a nuclear localization signal and CRM1-mediated nuclear export. Mutations in this gene have been found in ectodermal dysplasia anhidrotic with T-cell immunodeficiency autosomal dominant disease. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2011]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Wei CC, Kung YJ, Chen CS, et al. Allergic Conjunctivitis-induced Retinal Inflammation Promotes Myopia Progression. EBioMedicine. 2018,28:274-286. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.01.024Read this paper