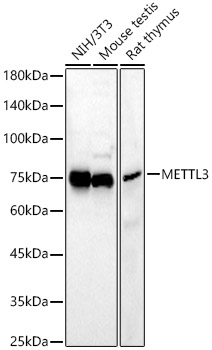
![Various whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 7.5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with METTL3 antibody [N2C2], Internal (GTX105037) diluted at 1:10000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody, and the signal was developed with Trident ECL plus-Enhanced. Various whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 7.5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with METTL3 antibody [N2C2], Internal (GTX105037) diluted at 1:10000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody, and the signal was developed with Trident ECL plus-Enhanced.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX105037/GTX105037_40044_20191227_WB_R_w_23060120_981.webp)
Various whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 7.5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with METTL3 antibody [N2C2], Internal (GTX105037) diluted at 1:10000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody, and the signal was developed with Trident ECL plus-Enhanced.
METTL3 antibody [N2C2], Internal
GTX105037
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Rat
TargetMETTL3
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameMETTL3 antibody [N2C2], Internal
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:5000-1:20000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.54 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID56339
- Target nameMETTL3
- Target descriptionmethyltransferase 3, N6-adenosine-methyltransferase complex catalytic subunit
- Target synonymsIME4, M6A, MT-A70, Spo8, hMETTL3, N(6)-adenosine-methyltransferase catalytic subunit METTL3, N(6)-adenosine-methyltransferase 70 kDa subunit, N6-adenosine-methyltransferase 70 kDa subunit, N6-adenosine-methyltransferase catalytic subunit, adoMet-binding subunit of the human mRNA (N6-adenosine)-methyltransferase, mRNA (2'-O-methyladenosine-N(6)-)-methyltransferase, mRNA m(6)A methyltransferase, methyltransferase like 3, methyltransferase-like protein 3
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ86U44
- Protein NameN(6)-adenosine-methyltransferase catalytic subunit METTL3
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes the 70 kDa subunit of MT-A which is part of N6-adenosine-methyltransferase. This enzyme is involved in the posttranscriptional methylation of internal adenosine residues in eukaryotic mRNAs, forming N6-methyladenosine. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161

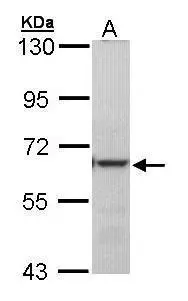
![Various whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 7.5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with METTL3 antibody [N2C2], Internal (GTX105037) diluted at 1:10000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Corresponding RNA expression data for the same cell lines are based on Human Protein Atlas program. Various whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 7.5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with METTL3 antibody [N2C2], Internal (GTX105037) diluted at 1:10000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Corresponding RNA expression data for the same cell lines are based on Human Protein Atlas program.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX105037/GTX105037_45385_20240419_WB_TPM_watermark_24043002_369.webp)