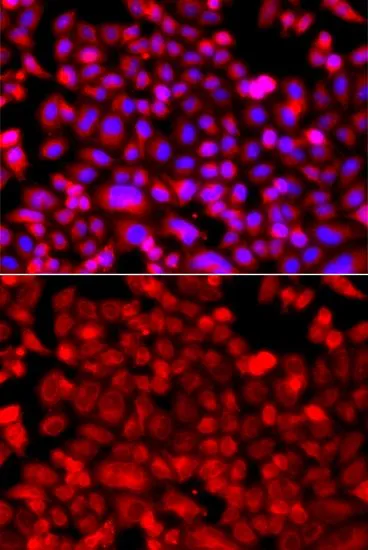
ICC/IF analysis of A549 cells using GTX33351 NDUFV1 antibody. Blue : DAPI
NDUFV1 antibody
GTX33351
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetNDUFV1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameNDUFV1 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500 - 1:2000. ICC/IF: 1:50 - 1:100. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID4723
- Target nameNDUFV1
- Target descriptionNADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase core subunit V1
- Target synonymsCI-51K, CI51KD, MC1DN4, UQOR1, NADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] flavoprotein 1, mitochondrial, NADH dehydrogenase (ubiquinone) flavoprotein 1, 51kDa, NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase 51 kDa subunit, complex I 51 kda subunit, complex I 51kDa subunit, complex I, mitochondrial respiratory chain, mitochondrial NADH dehydrogenase ubiquinone flavoprotein 1, mitochondrial NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase 51 kda subunit
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP49821
- Protein NameNADH dehydrogenase [ubiquinone] flavoprotein 1, mitochondrial
- Scientific DescriptionThe mitochondrial respiratory chain provides energy to cells via oxidative phosphorylation and consists of four membrane-bound electron-transporting protein complexes (I-IV) and an ATP synthase (complex V). This gene encodes a 51 kDa subunit of the NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase complex I; a large complex with at least 45 nuclear and mitochondrial encoded subunits that liberates electrons from NADH and channels them to ubiquinone. This subunit carries the NADH-binding site as well as flavin mononucleotide (FMN)- and Fe-S-biding sites. Defects in complex I are a common cause of mitochondrial dysfunction; a syndrome that occurs in approximately 1 in 10,000 live births. Mitochondrial complex I deficiency is linked to myopathies, encephalomyopathies, and neurodegenerative disorders such as Parkinsons disease and Leigh syndrome. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms.[provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161

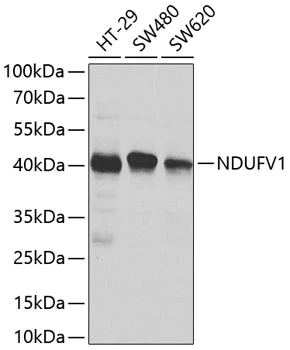




![Wild-type (WT) and NDUFV1 knockout (KO) 293T cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with NDUFV1 antibody [HL1600] (GTX637079) diluted at 1:5000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX637079/GTX637079_T-44725_20220819_WB_KO_watermark_22082402_548.webp)
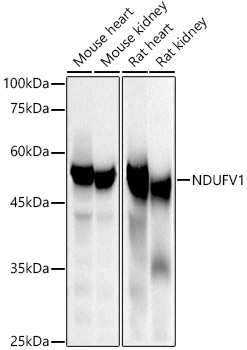
![Immunohistochemical analysis of paraffin-embedded zebrafish tissue, using NDUFV1 antibody [N3C3] (GTX102209) at 1:300 dilution.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX102209/GTX102209_40073_IHC_Z_22111423_752.webp)