![ELISA analysis of antigen using GTX60523 NQO1 antibody [4D12]. Black : Control antigen 100ng Purple : Antigen 10ng Blue : Antigen 50ng Red : Antigen 100ng ELISA analysis of antigen using GTX60523 NQO1 antibody [4D12]. Black : Control antigen 100ng Purple : Antigen 10ng Blue : Antigen 50ng Red : Antigen 100ng](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX60523/GTX60523_20170912_ELISA_w_23061123_645.webp)
ELISA analysis of antigen using GTX60523 NQO1 antibody [4D12]. Black : Control antigen 100ng Purple : Antigen 10ng Blue : Antigen 50ng Red : Antigen 100ng
NQO1 antibody [4D12]
GTX60523
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetNQO1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameNQO1 antibody [4D12]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1/500 - 1/2000. IHC-P: 1/200 - 1/1000. FACS: 1/200 - 1/400. ELISA: 1/10000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone ID4D12
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID1728
- Target nameNQO1
- Target descriptionNAD(P)H quinone dehydrogenase 1
- Target synonymsDHQU, DIA4, DTD, NMOR1, NMORI, QR1, NAD(P)H dehydrogenase [quinone] 1, DT-diaphorase, NAD(P)H dehydrogenase, quinone 1, NAD(P)H-quinone oxidoreductase, NAD(P)H:Quinone acceptor oxidoreductase type 1, NAD(P)H:menadione oxidoreductase 1, NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1, NAD(P)H:quinone oxireductase, azoreductase, diaphorase (NADH/NADPH) (cytochrome b-5 reductase), diaphorase-4, dioxin-inducible 1, menadione reductase, phylloquinone reductase, quinone reductase 1
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG1
- Protein IDP15559
- Protein NameNAD(P)H dehydrogenase [quinone] 1
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene is a member of the NAD(P)H dehydrogenase (quinone) family and encodes a cytoplasmic 2-electron reductase. This FAD-binding protein forms homodimers and reduces quinones to hydroquinones. This proteins enzymatic activity prevents the one electron reduction of quinones that results in the production of radical species. Mutations in this gene have been associated with tardive dyskinesia (TD), an increased risk of hematotoxicity after exposure to benzene, and susceptibility to various forms of cancer. Altered expression of this protein has been seen in many tumors and is also associated with Alzheimers disease (AD). Alternate transcriptional splice variants, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203

![FACS analysis of NIH3T3 cells using GTX60523 NQO1 antibody [4D12]. Green : NQO1 Red : negative control FACS analysis of NIH3T3 cells using GTX60523 NQO1 antibody [4D12]. Green : NQO1 Red : negative control](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX60523/GTX60523_20170912_FACS_w_23061123_474.webp)
![IHC-P analysis of human testis tissue using GTX60523 NQO1 antibody [4D12]. IHC-P analysis of human testis tissue using GTX60523 NQO1 antibody [4D12].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX60523/GTX60523_20170912_IHC-P_1_w_23061123_738.webp)
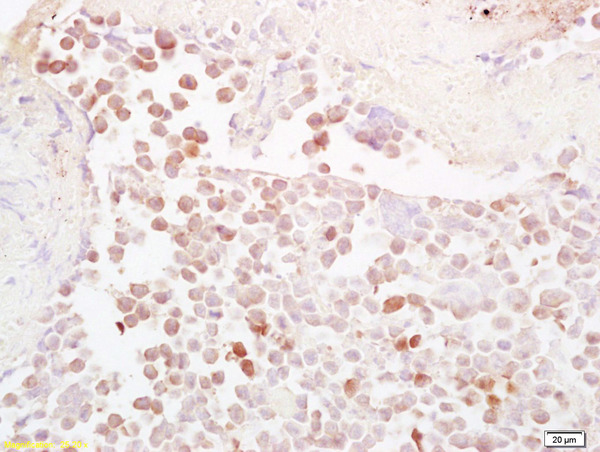
![IHC-P analysis of ovarian cancer tissue using GTX60523 NQO1 antibody [4D12]. IHC-P analysis of ovarian cancer tissue using GTX60523 NQO1 antibody [4D12].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX60523/GTX60523_20170912_IHC-P_w_23061123_846.webp)
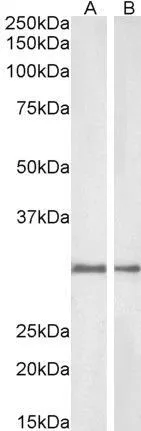
![WB analysis of human NQO1 (AA: 134-274) recombinant protein using GTX60523 NQO1 antibody [4D12]. WB analysis of human NQO1 (AA: 134-274) recombinant protein using GTX60523 NQO1 antibody [4D12].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX60523/GTX60523_20170912_WB_1_w_23061123_186.webp)
![WB analysis of A549 (1), SKNES (2), HepG2 (3), MCF-7 (4) and HeLa (5) cell lysate using GTX60523 NQO1 antibody [4D12]. WB analysis of A549 (1), SKNES (2), HepG2 (3), MCF-7 (4) and HeLa (5) cell lysate using GTX60523 NQO1 antibody [4D12].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX60523/GTX60523_20170912_WB_w_23061123_748.webp)

![ELISA analysis of antigen using GTX60524 NQO1 antibody [1A11]. Black : Control antigen 100ng Purple : Antigen 10ng Blue : Antigen 50ng Red : Antigen 100ng](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX60524/GTX60524_20170912_ELISA_w_23061123_544.webp)

![IHC-P analysis of mouse kidney tissue section using GTX09504 NQO1 antibody [GT1171]. Dlution : 1:100](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX09504/GTX09504_20191101_AP_003_107_w_23053123_659.webp)