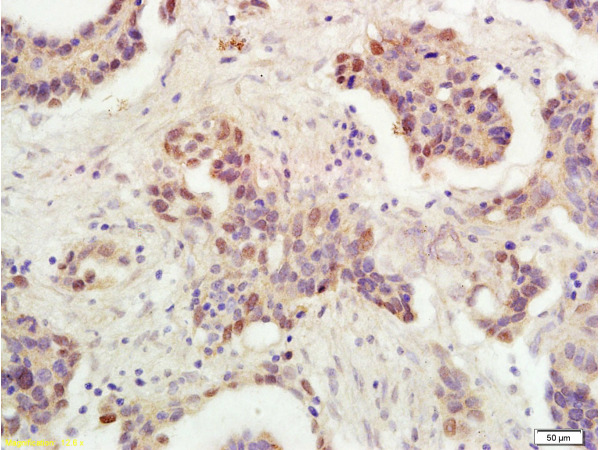
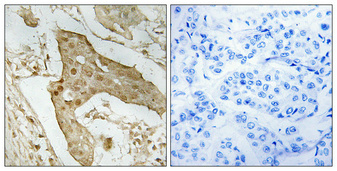
p53 antibody [DO1]
GTX70214
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetTP53
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product Namep53 antibody [DO1]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:10000. IHC-P: 1:1000. IP: 1:100-1:500. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDDO1
- Concentration0.25 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID7157
- Target nameTP53
- Target descriptiontumor protein p53
- Target synonymsBCC7, BMFS5, LFS1, P53, TRP53, cellular tumor antigen p53, antigen NY-CO-13, mutant tumor protein 53, phosphoprotein p53, transformation-related protein 53, tumor protein 53, tumor supressor p53
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG2a
- Protein IDP04637
- Protein NameCellular tumor antigen p53
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a tumor suppressor protein containing transcriptional activation, DNA binding, and oligomerization domains. The encoded protein responds to diverse cellular stresses to regulate expression of target genes, thereby inducing cell cycle arrest, apoptosis, senescence, DNA repair, or changes in metabolism. Mutations in this gene are associated with a variety of human cancers, including hereditary cancers such as Li-Fraumeni syndrome. Alternative splicing of this gene and the use of alternate promoters result in multiple transcript variants and isoforms. Additional isoforms have also been shown to result from the use of alternate translation initiation codons from identical transcript variants (PMIDs: 12032546, 20937277). [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2016]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Phan TTT, Truong NV, Wu WG, et al. Tumor suppressor p53 mediates interleukin-6 expression to enable cancer cell evasion of genotoxic stress. Cell Death Discov. 2023,9(1):340. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01638-0Read this paper
- Lin RC, Chao YY, Lien WC, et al. Polo‑like kinase 1 selective inhibitor BI2536 (dihydropteridinone) disrupts centrosome homeostasis via ATM‑ERK cascade in adrenocortical carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 2023,50(3):pii: 167. doi: 10.3892/or.2023.8604.Read this paper
- Xu P, Zheng Y, Liao J, et al. AMPK regulates homeostasis of invasion and viability in trophoblasts by redirecting glucose metabolism: Implications for pre-eclampsia. Cell Prolif. 2023,56(2):e13358. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13358Read this paper
- Leu JD, Lin ST, Chen CT, et al. BPR0C261, An Analogous of Microtubule Disrupting Agent D-24851 Enhances the Radiosensitivity of Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells via p53-Dependent and p53-Independent Pathways. Int J Mol Sci. 2022,23(22). doi: 10.3390/ijms232214083Read this paper
- Li J, Ding R, Gao H, et al. New spirobisnaphthalenes from an endolichenic fungus strain CGMCC 3.15192 and their anticancer effects through the P53-P21 pathway. RSC Adv. 2019,9(67):39082-39089. doi: 10.1039/c9ra07917cRead this paper
- Yang C, Zhang X, Gao C, et al. NRBP1 negatively regulates SALL4 to reduce the invasion and migration, promote apoptosis and increase the sensitivity to chemotherapy drugs of breast cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 2022,23(4):139. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13259Read this paper
- Wang LY, Yeh SL, Hsu ST, et al. The Anti-Proliferative and Apoptotic Effects of Rutaecarpine on Human Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cell Line CE81T/VGH In Vitro and In Vivo. Int J Mol Sci. 2022,23(5). doi: 10.3390/ijms23052843Read this paper
- Lee CW, Huang CC, Chi MC, et al. Naringenin Induces ROS-Mediated ER Stress, Autophagy, and Apoptosis in Human Osteosarcoma Cell Lines. Molecules. 2022,27(2). doi: 10.3390/molecules27020373Read this paper
- Li R, Qu Y, Li X, et al. Molecular Hydrogen Attenuated N-methyl-N-Nitrosourea Induced Corneal Endothelial Injury by Upregulating Anti-Apoptotic Pathway. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021,62(9):2. doi: 10.1167/iovs.62.9.2Read this paper
- Wang Y, Zhu S, Wei W, et al. Interleukin-6 knockout reverses macrophage differentiation imbalance and alleviates cardiac dysfunction in aging mice. Aging (Albany NY). 2020,12(20):20184-20197. doi: 10.18632/aging.103749Read this paper





![ICC/IF analysis of HeLa cells treated with 100 nM Doxorubicin for 24 hrs using GTX00675 p53 (Acetyl Lys120) antibody [10E5]. Red : Primary antibody Green : DAPI Dilution : 1:1000 Fixation : 4% PFA, overnight Permeabilization : 0.25% Triton X-100 in PBS for 10 min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX00675/GTX00675_20191104_ICC-IF_w_23053121_863.webp)