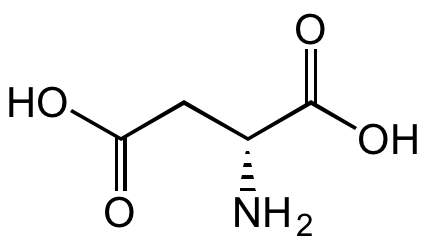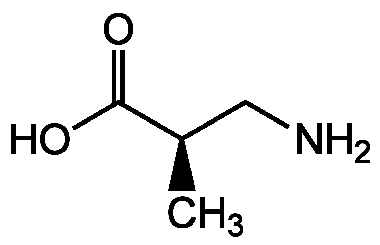
Chemical Structure
R-BAIBA [2140-95-6] [2140-95-6]
CDX-A0148
CAS Number2140-95-6
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>99%
Molecular Weight103.12
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product NameR-BAIBA [2140-95-6] [2140-95-6]
- Delivery Days Customer2
- CAS Number2140-95-6
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>99%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC4H9NO2
- Molecular Weight103.12
- Scientific DescriptionBeta-Aminoisobutyric acid is a non-protein amino acid originating from the catabolism of thymine and valine. beta-Aminoisobutyric acid occurs in two isomeric forms and both enantiomers of beta-Aminoisobutyric acid can be detected in human urine and plasma. In plasma, the S-enantiomer is the predominant type due to active renal reabsorption. In contrast, urine almost exclusively contains the R-enantiomer of beta-Aminoisobutyric acid, which is eliminated both by filtration and tubular secretion. The S-enantiomer of beta-Aminoisobutyric acid is predominantly derived from the catabolism of valine, the R-enantiomer is the product of the catabolism of the pyrimidine bases uracil and thymine by the enzyme dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD), in what constitutes the first step of the pyrimidine degradation pathway. Transient high levels of beta-Aminoisobutyric acid have been observed under a variety of pathological conditions such as lead poisoning, starvation, in total body irradiation and in a number of malignancies. Recently R-/S-enantiomer mixtures have been shown to be browning inducer of white adipose tissue. - Chemical. CAS: 2140-95-6. Formula: C4H9NO2. MW: 103.12. Synthetic Beta-Aminoisobutyric acid is a non-protein amino acid originating from the catabolism of thymine and valine. beta-Aminoisobutyric acid occurs in two isomeric forms and both enantiomers of beta-Aminoisobutyric acid can be detected in human urine and plasma. In plasma, the S-enantiomer is the predominant type due to active renal reabsorption. In contrast, urine almost exclusively contains the R-enantiomer of beta-Aminoisobutyric acid, which is eliminated both by filtration and tubular secretion. The S-enantiomer of beta-Aminoisobutyric acid is predominantly derived from the catabolism of valine, the R-enantiomer is the product of the catabolism of the pyrimidine bases uracil and thymine by the enzyme dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (DPD), in what constitutes the first step of the pyrimidine degradation pathway. Transient high levels of beta-Aminoisobutyric acid have been observed under a variety of pathological conditions such as lead poisoning, starvation, in total body irradiation and in a number of malignancies. Recently R-/S-enantiomer mixtures have been shown to be browning inducer of white adipose tissue.
- SMILESC[C@H](CN)C(O)=O
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200