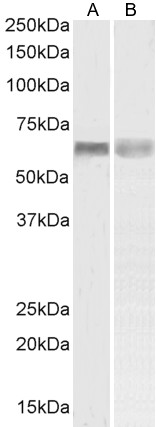
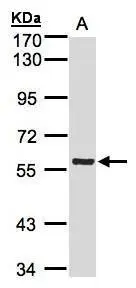
Rabbit anti Human PINK1 (G309D Mutant)
X2761P
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetPINK1
Product X2761P is not available
Product not available
There may be an alternative product available, please contact our technical support team.
Overview
- SupplierNordic-MUbio
- Product NameRabbit anti Human PINK1 (G309D Mutant)
- Delivery Days Customer7
- Application Supplier NoteOptimal concentration should be evaluated by serial dilutions.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- Applications SupplierWestern Blotting;Enzyme Immunoassay;Western Blotting;Immunohistochemistry;Enzyme Immunoassay
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Gene ID65018
- Target namePINK1
- Target descriptionPTEN induced kinase 1
- Target synonymsBRPK, PARK6, serine/threonine-protein kinase PINK1, mitochondrial, PTEN induced putative kinase 1, PTEN-induced putative kinase protein 1, protein kinase BRPK
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ9BXM7
- Protein NameSerine/threonine-protein kinase PINK1, mitochondrial
- Scientific DescriptionPTEN-induced putative kinase protein 1
- Shelf life instructionSee expiration date on vial
- ReactivityHuman
- Reactivity SupplierHuman
- Reactivity Supplier NoteSynthetic peptide derived from a mutant form of the human PINK1 protein
- UNSPSC12352203