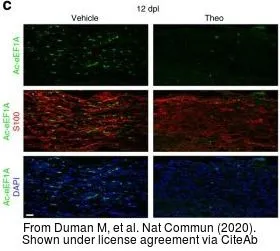
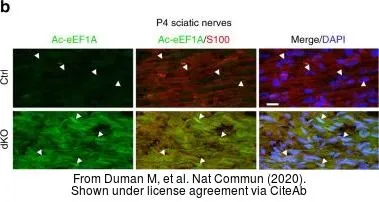
The data was published in the journal Nat Commun in 2020.
S100 beta antibody [SH-B4]
GTX11179
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityBovine, Canine, Feline, Goat, Human, Mouse, Porcine, Rabbit, Rat, Sheep
TargetS100B
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameS100 beta antibody [SH-B4]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteIHC-P: 1:100. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDSH-B4
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID6285
- Target nameS100B
- Target descriptionS100 calcium binding protein B
- Target synonymsNEF, S100, S100-B, S100beta, protein S100-B, S-100 calcium-binding protein, beta chain, S-100 protein subunit beta, S100 calcium-binding protein, beta (neural)
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG1
- Protein IDP04271
- Protein NameProtein S100-B
- Scientific DescriptionS100 is a set of small, thermolabile, highly acidic dimer proteins, of approx. 20 kDa, widely distributed in different tissues. Dimeric combinations of two chains; the alpha chain (93 a.a. 10.4 kDa) and the beta chain (91 a.a. 10.5 kDa), form the three known subtypes of S100 [S100ao (alpha alpha), S100a (alpha beta) and S100b (beta beta). Although there is slight variation in the primary structure in different species, the S100 molecule is markedly conserved in the amino acid sequence, and the protein extracted from different organs of the same species is identical. The alpha and beta chains are 58% homologous (54 a.a.) and both have divalent cation binding sites situated toward the carboxy terminus and apparently similar functional features. S100 can be grouped with other calcium binding proteins, to which it has a significant sequence homology, particularly around the calcium binding domain, such as calmodulin, parvalbumin, intestinal calcium binding protein, myosin light chain, and troponin-C. Hence, S100 is a calcium modulated protein that binds calcium and zinc ions reversibly at physiologic pH and ionic strength, followed by a conformational change in the molecule. S100 is considered to be a cell-growth regulator, but other functions have been suggested, e.g., increasing the membrane permeability to cations under physiologic conditions, stimulation of nucleolar RNA polymerase activity, interaction with the tumor suppressor protein p53 and as a carrier of proteins and free fatty acids in adipocytes. Human S100 containing cells are subdivided to three groups, S100b containing cells (such as Schwann cells, pituicytes of the neurohypophysis, Langerhanis cells, and interdigitating cells), S100a containing cells (such as glial cells and melanocytes) and S100ao containing cells (such as neurons, ganglion cells, slow skeletal muscle cells, cardiac cells, monocytes and some macrophages). Although the tissue distribution of S100 is too broad to conform to a single histogenetic pattern, it is sufficiently restricted that the localization of this protein is useful in the differential diagnosis of neoplasms and proliferative processes. Monoclonal antibody reacting specifically with the beta subunit of S100 may be use to distinguish malignant melanoma from undifferentiated carcinoma or lymphoma, and to distinguish leiomyomas from schwannomas and their counterparts in the gastrointestinal tract.
- ReactivityBovine, Canine, Feline, Goat, Human, Mouse, Porcine, Rabbit, Rat, Sheep
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Duman M, Vaquié A, Nocera G, et al. EEF1A1 deacetylation enables transcriptional activation of remyelination. Nat Commun. 2020,11(1):3420. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17243-zRead this paper
- Mikawa S, Sato K. Chordin expression in the adult rat brain. Neuroscience. 2014,258:16-33. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.11.006Read this paper
- Sango K, Yanagisawa H, Kawakami E, et al. Spontaneously immortalized Schwann cells from adult Fischer rat as a valuable tool for exploring neuron-Schwann cell interactions. J Neurosci Res. 2011,89(6):898-908. doi: 10.1002/jnr.22605Read this paper



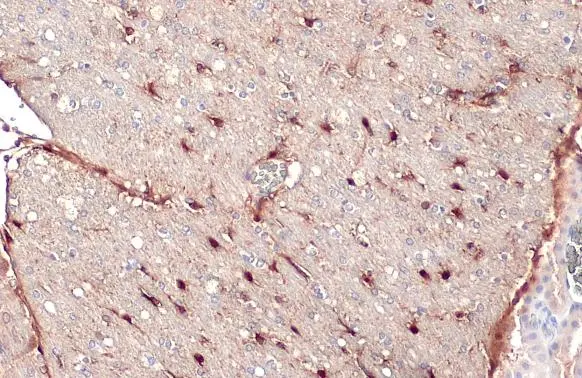
![IHC-P analysis of human cerebrum (grey matter) tissue using GTX04404 S100 beta antibody [MSVA-490R] HistoMAX?. Strong ubiquitous S100 beta staining, except neirons.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX04404/GTX04404_20230728_IHC-P_107_23072722_172.webp)
![SDS-PAGE analysis of GTX04511 S100 beta antibody [4C4.9].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX04511/GTX04511_20230802_Image_23080120_268.webp)
![Various tissue extracts (50 μg) were separated by 15% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with S100 beta antibody [HL2228] (GTX638273) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX638273/GTX638273_T-44956_20230217_WB_M_R_23022022_230.webp)
![WB analysis of full-length S100B recombinant protein using GTX83327 S100 beta antibody [9A11B9].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX83327/GTX83327_20170912_WB_w_23061322_321.webp)