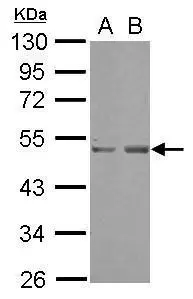
Sample (30 ug of whole cell lysate) A: A549 B: HeLa 10% SDS PAGE GTX117333 diluted at 1:1000
SETD7 antibody [N1C1]
GTX117333
ApplicationsWestern Blot
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetSETD7
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameSETD7 antibody [N1C1]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID80854
- Target nameSETD7
- Target descriptionSET domain containing 7, histone lysine methyltransferase
- Target synonymsKMT7, SET7, SET7/9, SET9, histone-lysine N-methyltransferase SETD7, H3-K4-HMTase SETD7, SET domain containing 7, lysine methyltransferase, SET domain containing lysine methyltransferase 7, SET domain-containing protein 7, histone H3-K4 methyltransferase SETD7, histone H3-lysine 4-specific methyltransferase, lysine N-methyltransferase 7
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ8WTS6
- Protein NameHistone-lysine N-methyltransferase SETD7
- Scientific DescriptionHistone methyltransferase that specifically monomethylates Lys-4 of histone H3. H3 Lys-4 methylation represents a specific tag for epigenetic transcriptional activation. Plays a central role in the transcriptional activation of genes such as collagenase or insulin. Recruited by IPF1/PDX-1 to the insulin promoter, leading to activate transcription. Has also methyltransferase activity toward non-histone proteins such as p53/TP53, TAF10, and possibly TAF7 by recognizing and binding the [KR]-[STA]-K in substrate proteins. Monomethylates Lys-189 of TAF10, leading to increase the affinity of TAF10 for RNA polymerase II. Monomethylates Lys-372 of p53/TP53, stabilizing p53/TP53 and increasing p53/TP53-mediated transcriptional activation. Also able to demethylated Lys-372 of p53/TP53 in vitro.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161