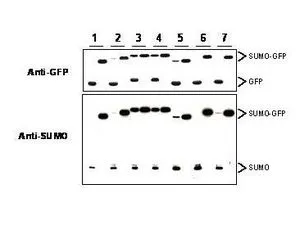
Western blot of SUMO-GFP fusion proteins cleaved by insect cell protein extracts.
Anti-SUMO antibody, generated by immunization with recombinant yeast SUMO, was tested by western blot against several constructs of SUMO-GFP fusion proteins after cleavage by proteases in insect cell protein extracts. These constructs contained various linkers between the SUMO and GFP portion of the fusion proteins. Each sample was run twice. The left lanes each contain 2 μg E.coli expressed and purified SUMO-GFP fusion proteins after incubation with lysed cells (50 μg total protein) for 1 h. The right lanes contain the same fusion proteins incubated with the lysate in the presence of 2% SDS. After probing with anti-GFP antibodies the membranes were stripped of antibody using SDS-DTT solution for 30 m at 60o C and were then re-probed using the anti-SUMO antibody at a 1:1000 dilution incubated overnight at 4o C in 5% non-fat dry milk in TBST. Detection occurred using a 1:2000 dilution of HRP-labeled Donkey anti-Rabbit IgG.
Sumo antibody
GTX48822
ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ChIP Chromatin ImmunoPrecipitation, ELISA
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityYeast
TargetSMT3
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameSumo antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. ELISA: 1:5000-1:25000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ChIP Chromatin ImmunoPrecipitation, ELISA
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID852122
- Target nameSMT3
- Target descriptionSUMO family protein SMT3
- Target synonymsYDR510W, SUMO family protein SMT3
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ12306
- Protein NameUbiquitin-like protein SMT3
- Scientific DescriptionCovalent modification of cellular proteins by the ubiquitin-like modifier SUMO (small ubiquitin-like modifier) regulates various cellular processes, such as nuclear transport, signal transduction, stress responses and cell cycle progression. But, in contrast to ubiquination, sumoylation does not tag proteins for degradation by the 26S proteasome, but rather seems to enhance stability or modulate their subcellular compartmentalization. Ubiquitin-like proteins fall into two classes: the first class, ubiquitin-like modifiers (UBLs) function as modifiers in a manner analogous to that of ubiquitin. Examples of UBLs are SUMO, Rub1 (also called Nedd8), Apg8 and Apg12. Proteins of the second class include parkin, RAD23 and DSK2, are designated ubiquitin-domain proteins (UDPs). These proteins contain domains that are related to ubiquitin but are otherwise unrelated to each other. In contrast to UBLs, UDPs are not conjugated to other proteins. Once covalently attached to cellular targets, SUMO regulates protein:protein and protein:DNA interactions, as well as localization and stability of the target protein. Sumoylation occurs in most eukaryotic systems, and SUMO is highly conserved from yeast to humans. Where invertebrates have only a single SUMO gene termed SMT3, three members of the SUMO family have been identified in vertebrates: SUMO-1 and the close homologues SUMO-2 and SUMO-3. SUMO has been called SMT3 (yeast), sentrin, PIC1, GMP1 and UBL1. SUMO has been shown to bind and regulate mammalian SP-RINGs (such as Mdm2, PIAS and PML), RanGAP1, RanBP2, p53, p73, HIPK2, TEL, c-Jun, Fas, Daxx, TNFRI, Topo-I, Topo-II, WRN, Sp100, IkB-a, Androgen receptor (AR), GLUT1/4, Drosophila Ttk69, Dorsal, CaMK, yeast Septins, and viral CMV-IE1/2, EBV-BZLF1, HPV/BPV-E1. These bindings implicate SUMO in the stabilization of the target proteins and/or their localization to subcellular complexes. SUMO has an apparent molecular weight of ~12kDa and human SUMO-1 (a 101 amino acid polypeptide) shares 50% sequence identity with SUMO-2 and SUMO-3 and with yeast SMT3. SUMO and ubiquitin only show about 18% homology, but both possess a common three-dimensional structure characterized by a tightly packed globular fold with b-sheets wrapped around an a-helix.
- ReactivityYeast
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161