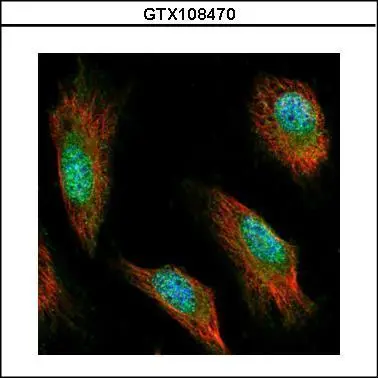
![Syntenin 1 antibody [C2C3], C-term detects Syntenin 1 protein by immunohistochemical analysis. Samples: Frozen Sectioned adult mouse brain. Green: Syntenin 1 protein stained by Syntenin 1 antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX108470) diluted at 1:250. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920).
Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 10 min Syntenin 1 antibody [C2C3], C-term detects Syntenin 1 protein by immunohistochemical analysis. Samples: Frozen Sectioned adult mouse brain. Green: Syntenin 1 protein stained by Syntenin 1 antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX108470) diluted at 1:250. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920).
Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 10 min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX108470/GTX108470_39806_20171127_IHC-Fr_M_w_23060120_143.webp)
Syntenin 1 antibody [C2C3], C-term detects Syntenin 1 protein by immunohistochemical analysis. Samples: Frozen Sectioned adult mouse brain. Green: Syntenin 1 protein stained by Syntenin 1 antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX108470) diluted at 1:250. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920).
Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 10 min
Syntenin 1 antibody [C2C3], C-term
GTX108470
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetSDCBP
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameSyntenin 1 antibody [C2C3], C-term
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. ICC/IF: 1:100-1:1000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. IHC-Fr: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.78 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID6386
- Target nameSDCBP
- Target descriptionsyndecan binding protein
- Target synonymsMDA-9, MDA9, SDCBP1, ST1, SYCL, TACIP18, syntenin-1, melanoma differentiation associated protein-9, pro-TGF-alpha cytoplasmic domain-interacting protein 18, scaffold protein Pbp1, syndecan binding protein (syntenin), syndecan-binding protein 1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDO00560
- Protein NameSyntenin-1
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene was initially identified as a molecule linking syndecan-mediated signaling to the cytoskeleton. The syntenin protein contains tandemly repeated PDZ domains that bind the cytoplasmic, C-terminal domains of a variety of transmembrane proteins. This protein may also affect cytoskeletal-membrane organization, cell adhesion, protein trafficking, and the activation of transcription factors. The protein is primarily localized to membrane-associated adherens junctions and focal adhesions but is also found at the endoplasmic reticulum and nucleus. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Korvenlaita N, Gómez-Budia M, Scoyni F, et al. Dynamic release of neuronal extracellular vesicles containing miR-21a-5p is induced by hypoxia. J Extracell Vesicles. 2023,12(1):e12297. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12297Read this paper
- Haynes BA, Yang LF, Huyck RW, et al. Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Human Adipose Tissue Vasculature Alters the Particulate Secretome and Induces Endothelial Dysfunction. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2019,39(10):2168-2191. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.312826Read this paper
- Kowal J, Arras G, Colombo M, et al. Proteomic comparison defines novel markers to characterize heterogeneous populations of extracellular vesicle subtypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016,113(8):E968-77. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1521230113Read this paper

![Syntenin 1 antibody [C2C3], C-term detects Syntenin 1 protein at cytosol on rat fore brain by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded rat fore brain. Syntenin 1 antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX108470) dilution: 1:500.
Antigen Retrieval: Trilogy? (EDTA based, pH 8.0) buffer, 15min Syntenin 1 antibody [C2C3], C-term detects Syntenin 1 protein at cytosol on rat fore brain by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded rat fore brain. Syntenin 1 antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX108470) dilution: 1:500.
Antigen Retrieval: Trilogy? (EDTA based, pH 8.0) buffer, 15min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX108470/GTX108470_39806_IHC_R_w_23060120_367.webp)
![Syntenin 1 antibody [C2C3], C-term detects Syntenin 1 protein by immunohistochemical analysis. Samples: Frozen Sectioned adult mouse brain. Green: Syntenin 1 protein stained by Syntenin 1 antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX108470) diluted at 1:250. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920).
Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 10 min Syntenin 1 antibody [C2C3], C-term detects Syntenin 1 protein by immunohistochemical analysis. Samples: Frozen Sectioned adult mouse brain. Green: Syntenin 1 protein stained by Syntenin 1 antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX108470) diluted at 1:250. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920).
Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 10 min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX108470/GTX108470_41766_20171127_IHC-Fr_M_w_23060120_930.webp)
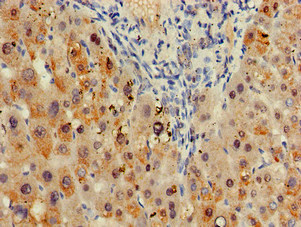
![Syntenin 1 antibody [C2C3], C-term detects Syntenin 1 protein at cytosol on mouse kidney by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse kidney. Syntenin 1 antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX108470) dilution: 1:500.
Antigen Retrieval: Trilogy? (EDTA based, pH 8.0) buffer, 15min Syntenin 1 antibody [C2C3], C-term detects Syntenin 1 protein at cytosol on mouse kidney by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse kidney. Syntenin 1 antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX108470) dilution: 1:500.
Antigen Retrieval: Trilogy? (EDTA based, pH 8.0) buffer, 15min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX108470/GTX108470_39806_IHC_M_w_23060120_247.webp)
![Syntenin 1 antibody [C2C3], C-term detects Syntenin 1 protein at cytosol on mouse kidney by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse kidney. Syntenin 1 antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX108470) dilution: 1:500.
Antigen Retrieval: Trilogy? (EDTA based, pH 8.0) buffer, 15min Syntenin 1 antibody [C2C3], C-term detects Syntenin 1 protein at cytosol on mouse kidney by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse kidney. Syntenin 1 antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX108470) dilution: 1:500.
Antigen Retrieval: Trilogy? (EDTA based, pH 8.0) buffer, 15min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX108470/GTX108470_39806_IHC_M_2_w_23060120_819.webp)
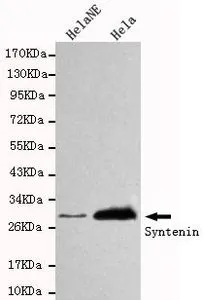
![HeLa whole cell extracts and HeLa exosome extract (3.5 μg) were separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Syntenin 1 antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX108470) diluted at 1:250. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. HeLa whole cell extracts and HeLa exosome extract (3.5 μg) were separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Syntenin 1 antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX108470) diluted at 1:250. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX108470/GTX108470_39806_20190607_WB_Fraction_w_23060120_384.webp)
![Various whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Syntenin 1 antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX108470) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody, and the signal was developed with Trident femto Western HRP Substrate. Corresponding RNA expression data are based on Human Protein Atlas program. Various whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Syntenin 1 antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX108470) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody, and the signal was developed with Trident femto Western HRP Substrate. Corresponding RNA expression data are based on Human Protein Atlas program.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX108470/GTX108470_39806_20250912_WB_TPM_watermark_25091820_180.webp)
![Zebrafish tissue extract (30 μg) was separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Syntenin 1 antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX108470) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Zebrafish tissue extract (30 μg) was separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Syntenin 1 antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX108470) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX108470/GTX108470_39806_20251003_WB_Z_brain_25100823_484.webp)