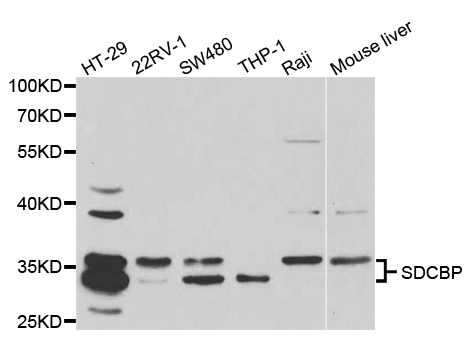
Syntenin 1 antibody [N1], N-term
GTX108391
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Zebra Fish
TargetSDCBP
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameSyntenin 1 antibody [N1], N-term
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. ICC/IF: 1:100-1:1000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. IP: 1:100-1:500. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID6386
- Target nameSDCBP
- Target descriptionsyndecan binding protein
- Target synonymsMDA-9, MDA9, SDCBP1, ST1, SYCL, TACIP18, syntenin-1, melanoma differentiation associated protein-9, pro-TGF-alpha cytoplasmic domain-interacting protein 18, scaffold protein Pbp1, syndecan binding protein (syntenin), syndecan-binding protein 1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDO00560
- Protein NameSyntenin-1
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene was initially identified as a molecule linking syndecan-mediated signaling to the cytoskeleton. The syntenin protein contains tandemly repeated PDZ domains that bind the cytoplasmic, C-terminal domains of a variety of transmembrane proteins. This protein may also affect cytoskeletal-membrane organization, cell adhesion, protein trafficking, and the activation of transcription factors. The protein is primarily localized to membrane-associated adherens junctions and focal adhesions but is also found at the endoplasmic reticulum and nucleus. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Zebra Fish
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Chen JY, Chou HC, Chen YH, et al. High glucose-induced proteome alterations in hepatocytes and its possible relevance to diabetic liver disease. J Nutr Biochem. 2013,24(11):1889-910. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2013.05.006Read this paper
- Yu Y, Schachner M. Syntenin-a promotes spinal cord regeneration following injury in adult zebrafish. Eur J Neurosci. 2013,38(2):2280-9. doi: 10.1111/ejn.12222Read this paper