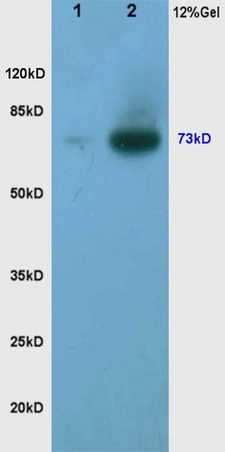
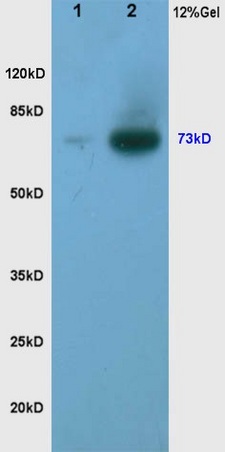
WB analysis of various samples using GTX51565 TORC2 (phospho Ser171) antibody. Dilution : 1:200 Lane 1 : human rectal carcinoma lysates Lane 2 : human gastric carcinoma lysates
TORC2 (phospho Ser171) antibody
GTX51565
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetCRTC2
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameTORC2 (phospho Ser171) antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:300-1000. IHC-P: 1:50-400. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID200186
- Target nameCRTC2
- Target descriptionCREB regulated transcription coactivator 2
- Target synonymsTORC-2, TORC2, CREB-regulated transcription coactivator 2, transducer of regulated cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) 2
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ53ET0
- Protein NameCREB-regulated transcription coactivator 2
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a member of the transducers of regulated cAMP response element-binding protein activity family of transcription coactivators. These proteins promote the transcription of genes targeted by the cAMP response element-binding protein, and therefore play an important role in many cellular processes. Under basal conditions the encoded protein is phosphorylated by AMP-activated protein kinase or the salt-inducible kinases and is sequestered in the cytoplasm. Upon activation by elevated cAMP or calcium, the encoded protein translocates to the nucleus and increases target gene expression. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in this gene may increase the risk of type 2 diabetes. A pseudogene of this gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 5. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
References
- Liraglutide Inhibits Hepatitis C Virus Replication Through an AMP Activated Protein Kinase Dependent Mechanism. Lee MY et al., 2019 Sep 14, Int J Mol SciRead this paper

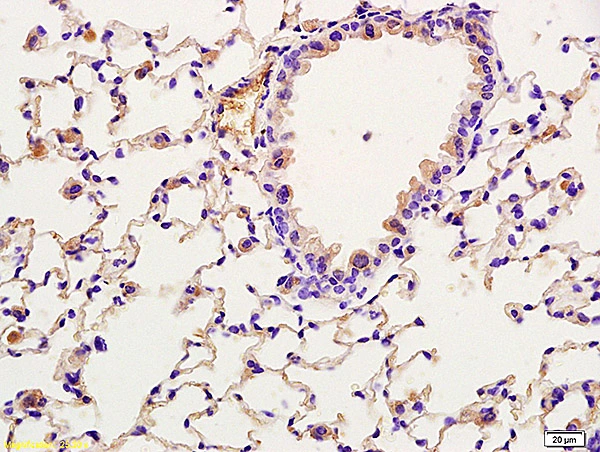

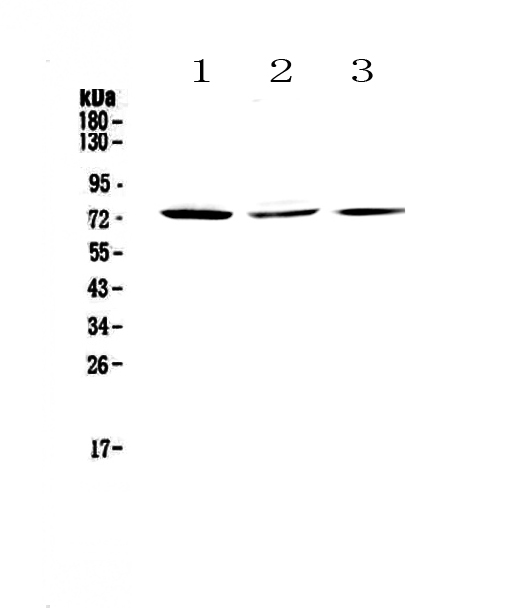



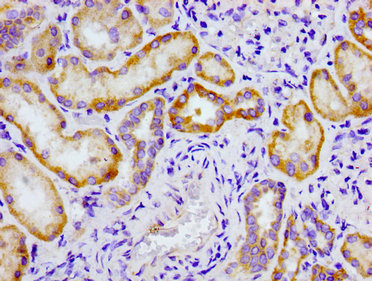
![IHC-P analysis of ovary tumour tissue (left) and lung cancer (right) using GTX82754 TORC2 antibody [5B10].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX82754/GTX82754_20170912_IHC-P_w_23061322_983.webp)

