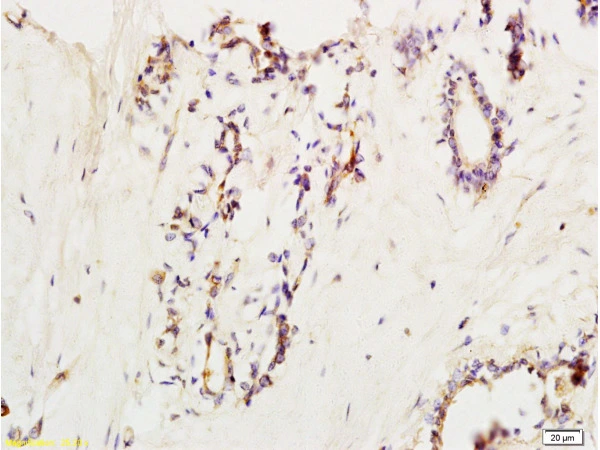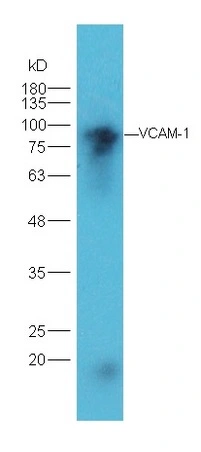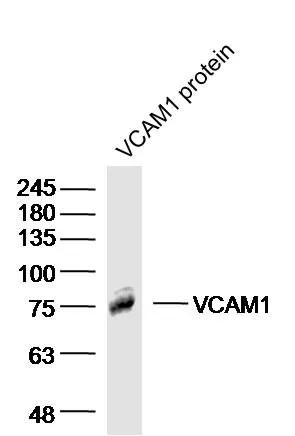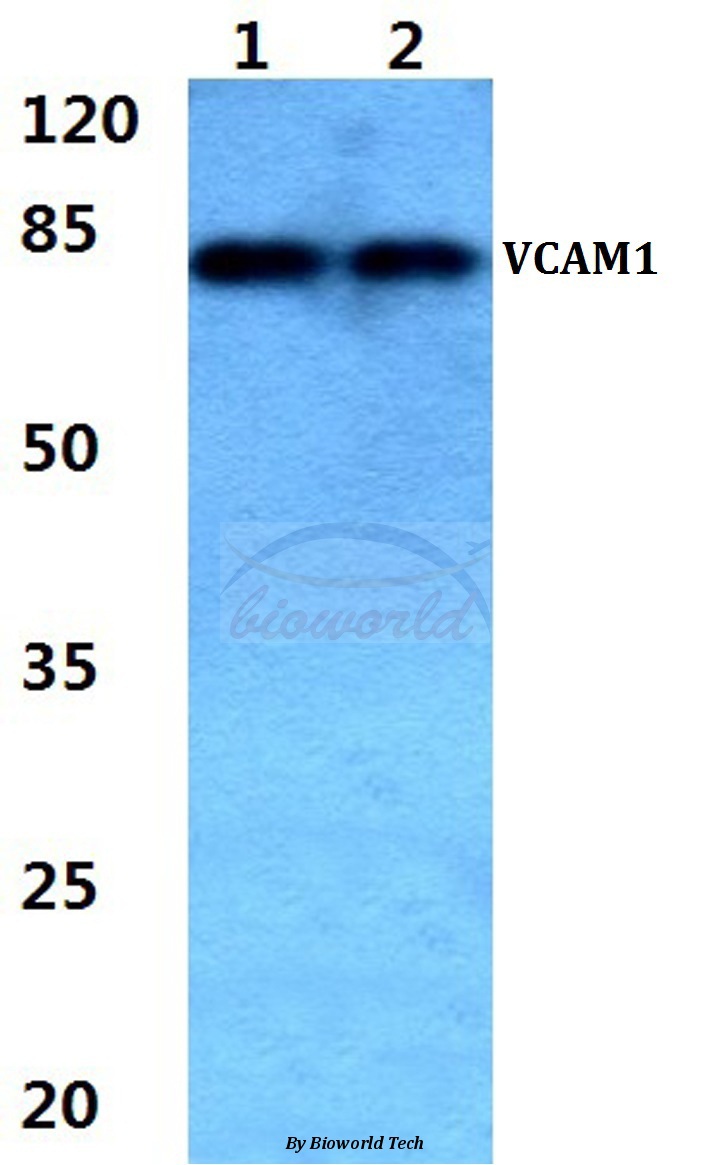
IHC-P analysis of rabbit brain carcinoma tissue using GTX17547 VCAM1 / CD106 antibody. Dilution : 1:300
VCAM1 / CD106 antibody
GTX17547
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rabbit, Rat
TargetVCAM1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameVCAM1 / CD106 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:300-1000. IHC-P: 1:50-400. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID7412
- Target nameVCAM1
- Target descriptionvascular cell adhesion molecule 1
- Target synonymsCD106, INCAM-100, vascular cell adhesion protein 1, CD106 antigen
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP19320
- Protein NameVascular cell adhesion protein 1
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene is a member of the Ig superfamily and encodes a cell surface sialoglycoprotein expressed by cytokine-activated endothelium. This type I membrane protein mediates leukocyte-endothelial cell adhesion and signal transduction, and may play a role in the development of artherosclerosis and rheumatoid arthritis. Three alternatively spliced transcripts encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rabbit, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Chiang HY, Chu PH, Lee TH. MFG-E8 mediates arterial aging by promoting the proinflammatory phenotype of vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biomed Sci. 2019,26(1):61. doi: 10.1186/s12929-019-0559-0Read this paper