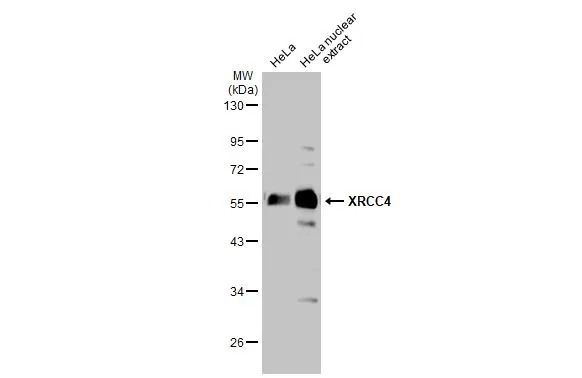
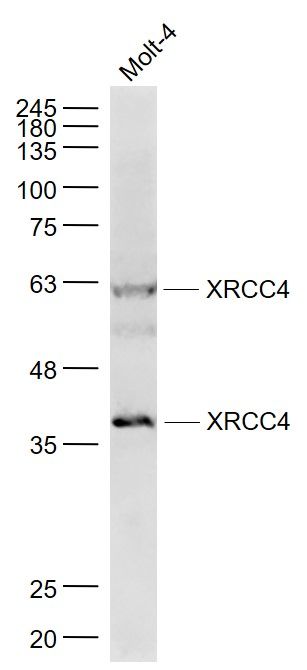
HeLa whole cell and nuclear extracts (30 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with XRCC4 antibody (GTX109632) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.
XRCC4 antibody
GTX109632
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetXRCC4
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameXRCC4 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. ICC/IF: 1:100-1:1000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.09 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID7518
- Target nameXRCC4
- Target descriptionX-ray repair cross complementing 4
- Target synonymsSSMED, hXRCC4, DNA repair protein XRCC4, X-ray repair complementing defective repair in Chinese hamster cells 4
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ13426
- Protein NameDNA repair protein XRCC4
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene functions together with DNA ligase IV and the DNA-dependent protein kinase in the repair of DNA double-strand break by non-homologous end joining and the completion of V(D)J recombination events. The non-homologous end-joining pathway is required both for normal development and for suppression of tumors. This gene functionally complements XR-1 Chinese hamster ovary cell mutant, which is impaired in DNA double-strand breaks produced by ionizing radiation and restriction enzymes. Alternative transcription initiation and alternative splicing generates several transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161

![XRCC4 antibody detects XRCC4 protein at nucleus by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: HeLa cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: XRCC4 stained by XRCC4 antibody (GTX109632) diluted at 1:200. Red: alpha Tubulin, a cytoskeleton marker, stained by alpha Tubulin antibody [GT114] (GTX628802) diluted at 1:1000. XRCC4 antibody detects XRCC4 protein at nucleus by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: HeLa cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: XRCC4 stained by XRCC4 antibody (GTX109632) diluted at 1:200. Red: alpha Tubulin, a cytoskeleton marker, stained by alpha Tubulin antibody [GT114] (GTX628802) diluted at 1:1000.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX109632/GTX109632_44286_20220415_ICC_IF_w_23060500_590.webp)
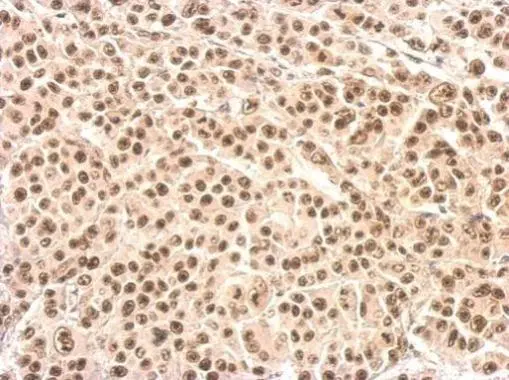





![IHC-P analysis of endometrium adenocarcinoma tissue using GTX83406 XRCC4 antibody [4H9]. Antigen retrieval : Heat-induced epitope retrieval by 10mM citrate buffer, pH6.0, 100oC for 10min. Dilution : 1:50](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX83406/GTX83406_1331_IHC-P_w_23061322_570.webp)