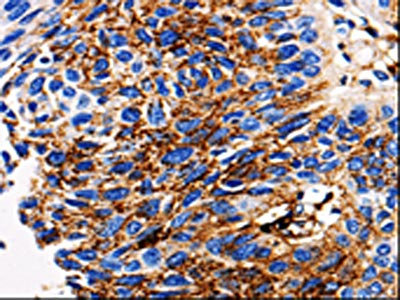
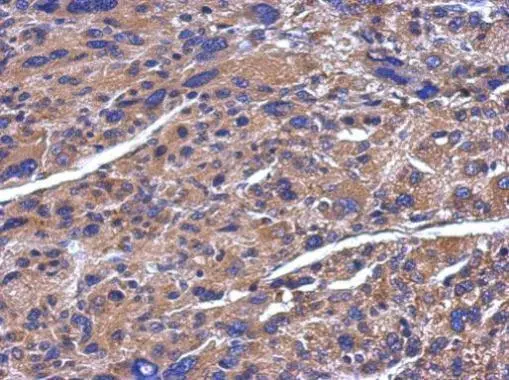
![ADAMTS5 antibody [N3C2], Internal detects ADAMTS5 protein at cytosol on human hepatoma by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded human hepatoma. ADAMTS5 antibody [N3C2], Internal (GTX123657) dilution: 1:250. Scale bar = 100 μm.
Antigen Retrieval: Trilogy? (EDTA based, pH 8.0) buffer, 15min ADAMTS5 antibody [N3C2], Internal detects ADAMTS5 protein at cytosol on human hepatoma by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded human hepatoma. ADAMTS5 antibody [N3C2], Internal (GTX123657) dilution: 1:250. Scale bar = 100 μm.
Antigen Retrieval: Trilogy? (EDTA based, pH 8.0) buffer, 15min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX123657/GTX123657_40737_CT_IHC_w_23060522_161.webp)
ADAMTS5 antibody [N3C2], Internal detects ADAMTS5 protein at cytosol on human hepatoma by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded human hepatoma. ADAMTS5 antibody [N3C2], Internal (GTX123657) dilution: 1:250. Scale bar = 100 μm.
Antigen Retrieval: Trilogy? (EDTA based, pH 8.0) buffer, 15min
ADAMTS5 antibody [N3C2], Internal
GTX123657
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetADAMTS5
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameADAMTS5 antibody [N3C2], Internal
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:10000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1.58 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID11096
- Target nameADAMTS5
- Target descriptionADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif 5
- Target synonymsADAM-TS 11, ADAM-TS 5, ADAM-TS5, ADAMTS-11, ADAMTS-5, ADAMTS11, ADMP-2, A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 5, a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 11, a disintegrin-like and metalloprotease (reprolysin type) with thrombospondin type 1 motif, 5 (aggrecanase-2), aggrecanase-2
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ9UNA0
- Protein NameA disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 5
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a member of the ADAMTS (a disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs) protein family. Members of the family share several distinct protein modules, including a propeptide region, a metalloproteinase domain, a disintegrin-like domain, and a thrombospondin type 1 (TS) motif. Individual members of this family differ in the number of C-terminal TS motifs, and some have unique C-terminal domains. The enzyme encoded by this gene contains two C-terminal TS motifs and functions as aggrecanase to cleave aggrecan, a major proteoglycan of cartilage. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161

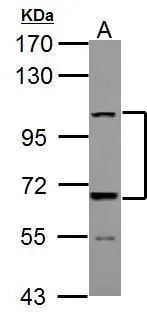
![Untreated (–) and treated (+) RMS 13 whole cell extract (30 μg) were separated by 7.5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with ADAMTS5 antibody [N3C2], Internal (GTX123657) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Untreated (–) and treated (+) RMS 13 whole cell extract (30 μg) were separated by 7.5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with ADAMTS5 antibody [N3C2], Internal (GTX123657) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX123657/GTX123657_45350_20240419_WB_treatment_BFA_24112622_624.webp)
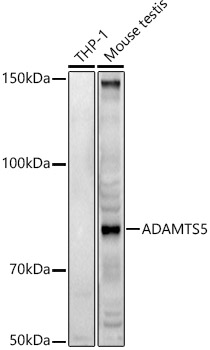
![Mouse tissue extracts (50 μg) was separated by 7.5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with ADAMTS5 antibody [N3C2], Internal (GTX123657) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Mouse tissue extracts (50 μg) was separated by 7.5% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with ADAMTS5 antibody [N3C2], Internal (GTX123657) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX123657/GTX123657_45350_20240517_WB_M_brownadipose_24112622_884.webp)