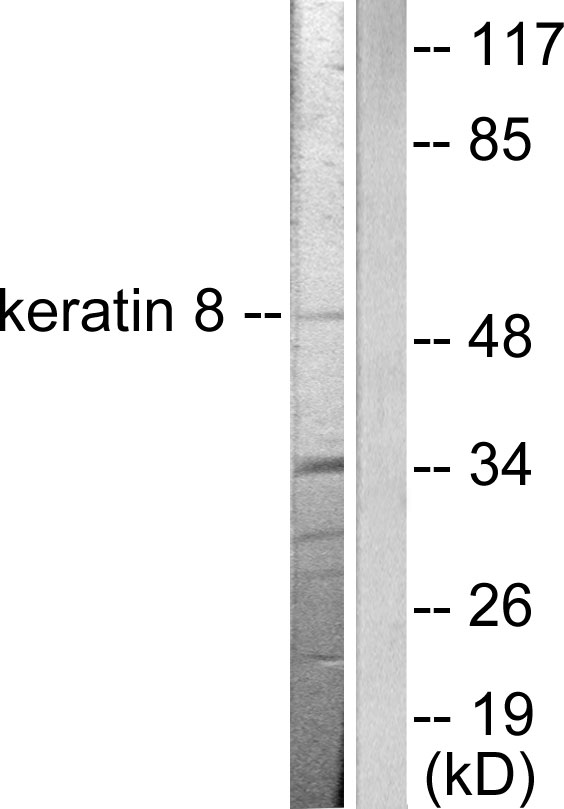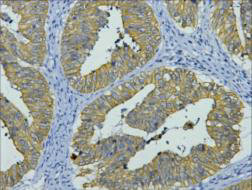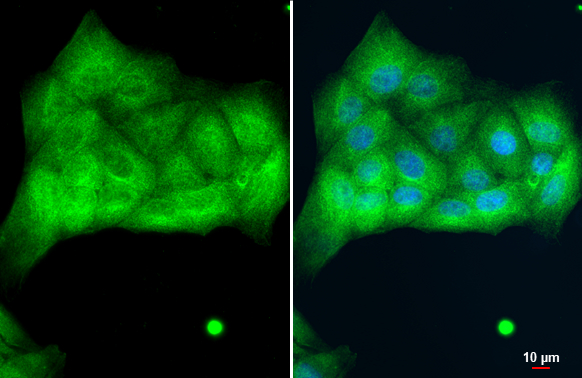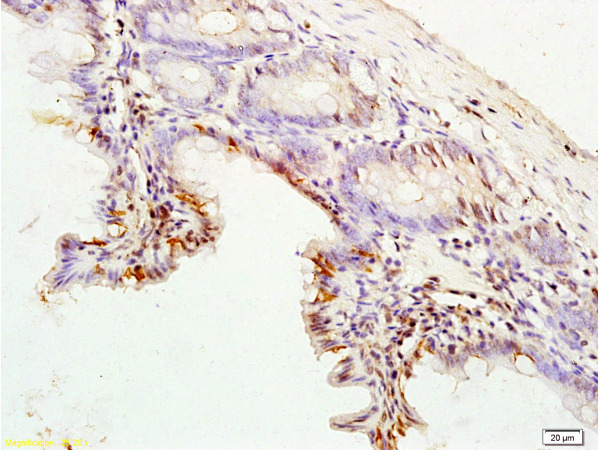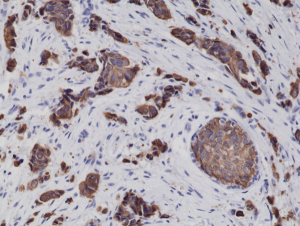
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human breast cancer tissue sections using Anti-CK8 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (Clone RM266) at a 1:2000 dilution.
anti-Cytokeratin-8 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM266)
REV-31-1148-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetKRT8
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-Cytokeratin-8 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM266)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM266
- Gene ID3856
- Target nameKRT8
- Target descriptionkeratin 8
- Target synonymsCARD2, CK-8, CK8, CYK8, K2C8, K8, KO, keratin, type II cytoskeletal 8, cytokeratin-8, keratin 8, type II, type-II keratin Kb8
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP05787
- Protein NameKeratin, type II cytoskeletal 8
- Scientific DescriptionCytokeratins are keratin proteins found in the intracytoplasmic cytoskeleton of epithelial tissue (at least 20 different polypeptides). They are an important component of intermediate filaments, which help cells resist mechanical stress. Expression of these cytokeratins within epithelial cells is largely specific to particular organs or tissues. The subsets of cytokeratins which an epithelial cell expresses depends mainly on the type of epithelium, the moment in the course of terminal differentiation and the stage of development. Thus a specific cytokeratin expression profile allows the identification of epithelial cells. Furthermore, this applies also to the malignant counterparts of the epithelia, (carcinomas). Cytokeratin subtype expression patterns are used to an increasing extent in the distinction of different types of epithelial malignancies. The cytokeratin antibodies are not only of assistance in the differential diagnosis of tumors using immunohistochemistry on tissue sections, but are also a useful tool in cytopathology and flow cytometric assays. Cytokeratin-8 is a member of the type II (basic or neutral) cytokeratin family. Type II keratins, in general, are heteropolymeric structural proteins coexpressed during differentiation of simple and stratified epithelial tissues. Cytokeratin-8 typically dimerizes with cytokeratin-18 to form an intermediate filament in simple single-layered epithelial cells. This protein plays a role in maintaining cellular structural integrity and also functions in signal transduction and cellular differentiation. Mutations in this gene cause cryptogenic cirrhosis. In combination cytokeratin-8 and cytokeratin-18 are used in immunohistochemistry to demonstrate certain forms of cancer. In normal tissue, it reacts mainly with secretory epithelia, but not with squamous epithelium. It is considered useful in identifying microscopic metastases of breast carcinoma in lymph nodes, and in distinguishing Pagets disease from malignant melanoma. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human CK8 (Cytokeratin-8). Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Cytokeratins are keratin proteins found in the intracytoplasmic cytoskeleton of epithelial tissue (at least 20 different polypeptides). They are an important component of intermediate filaments, which help cells resist mechanical stress. Expression of these cytokeratins within epithelial cells is largely specific to particular organs or tissues. The subsets of cytokeratins which an epithelial cell expresses depends mainly on the type of epithelium, the moment in the course of terminal differentiation and the stage of development. Thus a specific cytokeratin expression profile allows the identification of epithelial cells. Furthermore, this applies also to the malignant counterparts of the epithelia, (carcinomas). Cytokeratin subtype expression patterns are used to an increasing extent in the distinction of different types of epithelial malignancies. The cytokeratin antibodies are not only of assistance in the differential diagnosis of tumors using immunohistochemistry on tissue sections, but are also a useful tool in cytopathology and flow cytometric assays. Cytokeratin-8 is a member of the type II (basic or neutral) cytokeratin family. Type II keratins, in general, are heteropolymeric structural proteins coexpressed during differentiation of simple and stratified epithelial tissues. Cytokeratin-8 typically dimerizes with cytokeratin-18 to form an intermediate filament in simple single-layered epithelial cells. This protein plays a role in maintaining cellular structural integrity and also functions in signal transduction and cellular differentiation. Mutations in this gene cause cryptogenic cirrhosis. In combination cytokeratin-8 and cytokeratin-18 are used in immunohistochemistry to demonstrate certain forms of cancer. In normal tissue, it reacts mainly with secretory epithelia, but not with squamous epithelium. It is considered useful in identifying microscopic metastases of breast carcinoma in lymph nodes, and in distinguishing Pagets disease from malignant melanoma.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161