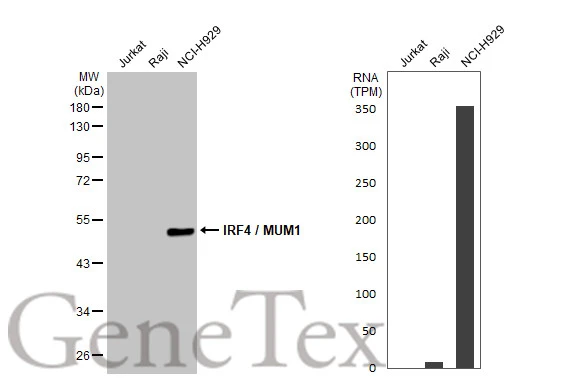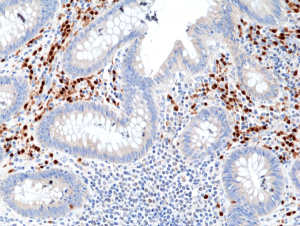
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human Appendix tissue section using anti-MUM1/IRF4 rabbit monoclonal antibody (Clone RM352) at a 1:800 dilution.
anti-IRF4 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM352)
REV-31-1238-00
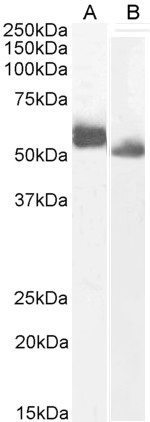
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetIRF4
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-IRF4 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM352)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM352
- Gene ID3662
- Target nameIRF4
- Target descriptioninterferon regulatory factor 4
- Target synonymsIMD131, LSIRF, MUM1, NF-EM5, SHEP8, interferon regulatory factor 4, lymphocyte-specific interferon regulatory factor, multiple myeloma oncogene 1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ15306
- Protein NameInterferon regulatory factor 4
- Scientific DescriptionRecombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human MUM1/IRF4 (Interferon regulatory factor 4). Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. The IRF (interferon regulatory factor) family of transcription factors are characterized by an unique tryptophan pentad repeat DNA-binding domain. The IRFs are important in the regulation of interferons in response to infection by virus, and in the regulation of interferon-inducible genes. MUM1 (IRF4) is lymphocyte specific and negatively regulates toll-like-receptor (TLR) signaling that is central to the activation of innate and adaptive immune systems. A chromosomal translocation involving this gene and the IgH locus, t(6;14)(p25;q32), may be a cause of multiple myeloma. - The IRF (interferon regulatory factor) family of transcription factors are characterized by an unique tryptophan pentad repeat DNA-binding domain. The IRFs are important in the regulation of interferons in response to infection by virus, and in the regulation of interferon-inducible genes. MUM1 (IRF4) is lymphocyte specific and negatively regulates toll-like-receptor (TLR) signaling that is central to the activation of innate and adaptive immune systems. A chromosomal translocation involving this gene and the IgH locus, t(6;14)(p25;q32), may be a cause of multiple myeloma.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161