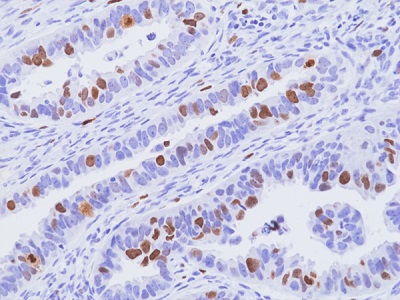
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded human ovarian papillary serous carcinoma tissue sections, using anti-Ki67 rabbit monoclonal antibody (Clone RM521) at 1:100 dilution, for 1hr at room temperature.
anti-Ki-67 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM521)
REV-31-1413-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetMKI67
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-Ki-67 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM521)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- Antibody SpecificityThis antibody reacts to human Ki-67.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM521
- Gene ID4288
- Target nameMKI67
- Target descriptionmarker of proliferation Ki-67
- Target synonymsantigen identified by monoclonal antibody Ki-67; antigen Ki67; KIA; MIB-; MIB-1; Molecular Immunology Borstel antibody 1; PPP1R105; proliferation marker protein Ki-67; proliferation-related Ki-67 antigen; protein phosphatase 1, regulatory subunit 105
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP46013
- Protein NameProliferation marker protein Ki-67
- Scientific DescriptionKi-67 is a nuclear protein that is expressed during various stages in the cell cycle, particularly during the late G1, S, G2, and M phases. The protein has a forkhead-associated domain (FHA) through which it associates with euchromatin at the peri chromosomal layer, the centromeric heterochromatin and the nucleolus. Ki-67 is shown to have a cell cycle-dependent topographical distribution with perinucleolar expression at G1, expression in the nuclear matrix at G2 and expression on the chromosomes during M phase. Ki-67 is commonly used as a proliferation marker because it is not detected in G0 cells, but increases steadily from G1 through mitosis. Ki-67 antibodies are useful in establishing the cell growing fraction in neoplasms. In neoplastic tissues, the prognostic value is comparable to the tritiated thymidine-labelling index. The correlation between low Ki-67 index and histologically low-grade tumors is strong. Ki-67 is routinely used as a neuronal marker of cell cycling and proliferation. In breast cancer, Ki67 identifies a high proliferative subset of patients with ER-positive breast cancer who derive greater benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human Ki-67. Isotype: Rabbit IgG. Immunogen: A peptide corresponding to the internal region of human Ki-67. Applications: IHC, WB. Ki-67 is a nuclear protein that is expressed during various stages in the cell cycle, particularly during the late G1, S, G2, and M phases. The protein has a forkhead-associated domain (FHA) through which it associates with euchromatin at the peri chromosomal layer, the centromeric heterochromatin and the nucleolus. Ki-67 is shown to have a cell cycle-dependent topographical distribution with perinucleolar expression at G1, expression in the nuclear matrix at G2 and expression on the chromosomes during M phase. Ki-67 is commonly used as a proliferation marker because it is not detected in G0 cells, but increases steadily from G1 through mitosis. Ki-67 antibodies are useful in establishing the cell growing fraction in neoplasms. In neoplastic tissues, the prognostic value is comparable to the tritiated thymidine-labelling index. The correlation between low Ki-67 index and histologically low-grade tumors is strong. Ki-67 is routinely used as a neuronal marker of cell cycling and proliferation. In breast cancer, Ki67 identifies a high proliferative subset of patients with ER-positive breast cancer who derive greater benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C
- UNSPSC12352203
