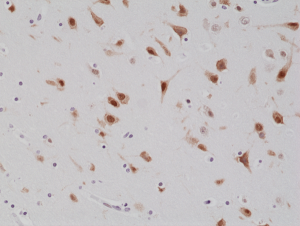
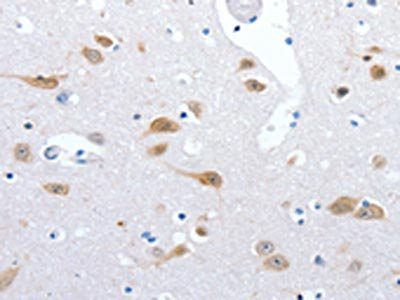
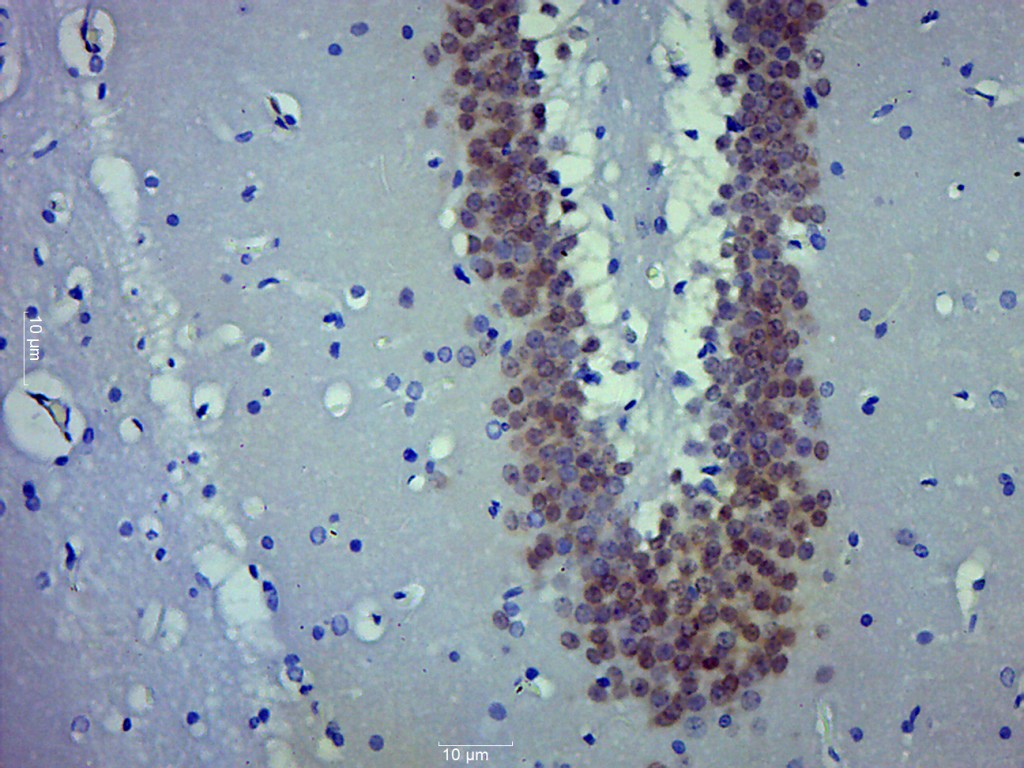
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human brain tissue section using anti-NeuN rabbit monoclonal antibody (Clone RM312) at a 1:1000 dilution.
anti-NeuN (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM312)
REV-31-1198-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetRBFOX3
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-NeuN (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM312)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM312
- Gene ID146713
- Target nameRBFOX3
- Target descriptionRNA binding fox-1 homolog 3
- Target synonymsFOX-3, FOX3, HRNBP3, NEUN, RNA binding protein fox-1 homolog 3, RNA binding protein, fox-1 homolog 3, fox-1 homolog C, hexaribonucleotide binding protein 3, neuN antigen, neuronal nuclei antigen
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDA6NFN3
- Protein NameRNA binding protein fox-1 homolog 3
- Scientific DescriptionNeuN (Fox-3) is a 350 amino acid protein that contains one RRM (RNA recognition motif) domain. Localized to both the nucleus and cytoplasm, NeuN is suggested to regulate alternative splicing events. NeuN is encoded by a gene located on human chromosome 17. Two key tumor suppressor genes are associated with chromosome 17, namely, p53 and BRCA1. Tumor suppressor p53 is necessary for maintenance of cellular genetic integrity by moderating cell fate through DNA repair versus cell death. Like p53, BRCA1 is directly involved in DNA repair, though specifically it is recognized as a genetic determinant of early onset breast cancer and predisposition to cancers of the ovary, colon, prostate gland and fallopian tubes. NeuN antibodies are widely used to label neurons. A few neuronal cell types are not recognized by NeuN antibodies, such as cerebellar Purkinje cells and Golgi cells, olfactory Mitral cells, retinal photoreceptors and gamma motor neurons. However the vast majority of neurons are strongly NeuN positive, and NeuN immunoreactivity has been widely used to identify neurons in tissue culture and in sections and to measure the neuron/glia ratio in brain regions. NeuN immunoreactivity becomes obvious as neurons mature, typically after they have downregulated expression of Doublecortin, a marker seen in the earliest stages of neuronal development. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human NeuN (Fox3, RBFOX3). The clone may also react to mouse or rat NeuN, as predicted by immunogen homology. Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. NeuN (Fox-3) is a 350 amino acid protein that contains one RRM (RNA recognition motif) domain. Localized to both the nucleus and cytoplasm, NeuN is suggested to regulate alternative splicing events. NeuN is encoded by a gene located on human chromosome 17. Two key tumor suppressor genes are associated with chromosome 17, namely, p53 and BRCA1. Tumor suppressor p53 is necessary for maintenance of cellular genetic integrity by moderating cell fate through DNA repair versus cell death. Like p53, BRCA1 is directly involved in DNA repair, though specifically it is recognized as a genetic determinant of early onset breast cancer and predisposition to cancers of the ovary, colon, prostate gland and fallopian tubes. NeuN antibodies are widely used to label neurons. A few neuronal cell types are not recognized by NeuN antibodies, such as cerebellar Purkinje cells and Golgi cells, olfactory Mitral cells, retinal photoreceptors and gamma motor neurons. However the vast majority of neurons are strongly NeuN positive, and NeuN immunoreactivity has been widely used to identify neurons in tissue culture and in sections and to measure the neuron/glia ratio in brain regions. NeuN immunoreactivity becomes obvious as neurons mature, typically after they have downregulated expression of Doublecortin, a marker seen in the earliest stages of neuronal development.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161


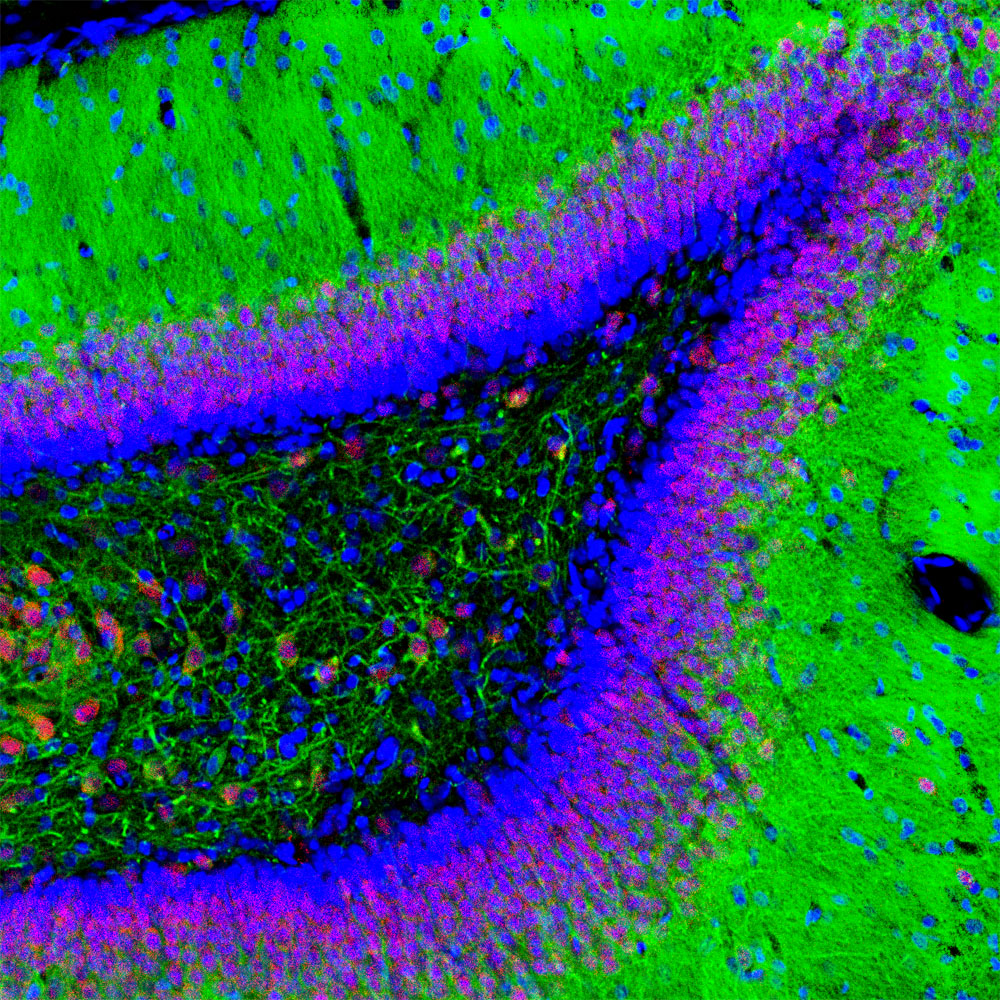



![NeuN antibody detects NeuN protein at nucleus by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: DIV9 rat E18 primary hippocampal neuron cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: NeuN stained by NeuN antibody (GTX132974) diluted at 1:250. Red: Tau, an axon marker, stained by Tau antibody [GT287] (GTX634809) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920).](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX132974/GTX132974_44986_20230519_ICC_IF_R_23053001_624.webp)