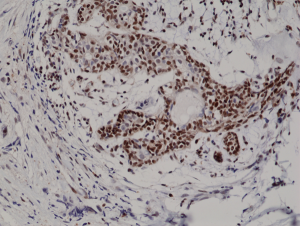
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human breast cancer tissue section using anti-p27Kip1 rabbit monoclonal antibody (clone RM302) at a 1:200 dilution.
anti-p27Kip1 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM302)
REV-31-1187-00
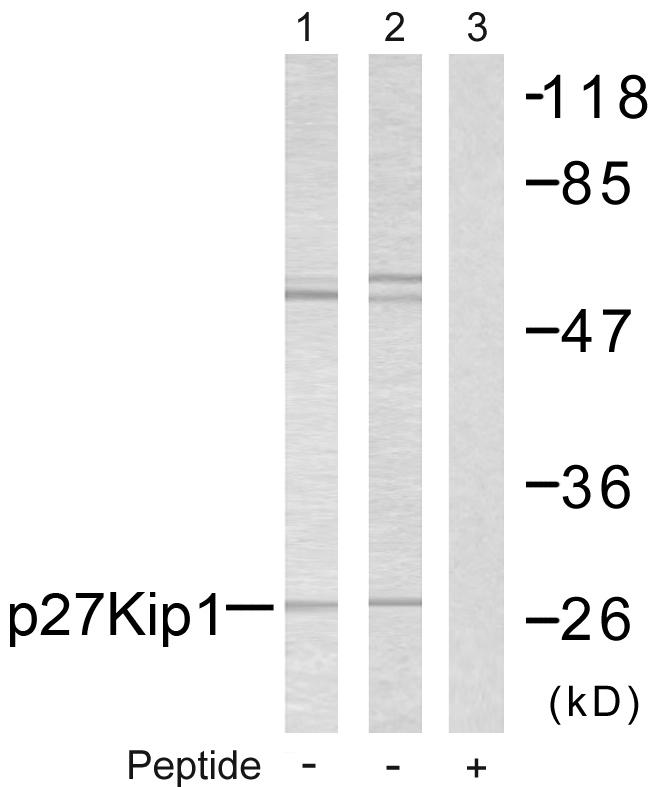
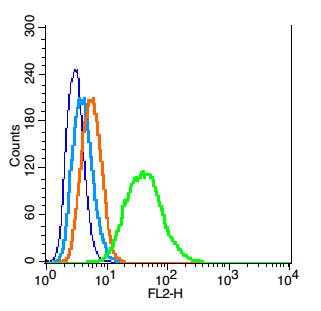
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetCDKN1B
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-p27Kip1 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM302)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM302
- Gene ID1027
- Target nameCDKN1B
- Target descriptioncyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 1B
- Target synonymsCDKN4, KIP1, MEN1B, MEN4, P27KIP1, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B (p27, Kip1)
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP46527
- Protein NameCyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B
- Scientific Descriptionp27Kip1 (p27) is a member of the universal cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor (CDKI) family. p27Kip1 binds to and prevents the activation of cyclin E-CDK2 or cyclin D-CDK4 complexes, and thus controls the cell cycle progression at G1. Degradation of p27Kip1 is triggered by CDK dependent phosphorylation and subsequent ubiquitination by SCF complexes that are required for the cellular transition from quiescence to the proliferative state. p27Kip1 expression is regulated by cell contact inhibition and by specific growth factors, such as transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta. In addition to its role as a CDKI, p27Kip1 is a putative tumor suppressor gene, regulator of drug resistance in solid tumors, and promoter of apoptosis; acts as a safeguard against inflammatory injury; and has a role in cell differentiation. The level of p27Kip1 protein expression decreases during tumor development and progression in some epithelial, lymphoid, and endocrine tissues. This decrease occurs mainly at the post-translational level with protein degradation by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. A large number of studies have characterized p27Kip1 as an independent prognostic factor in various human cancers, including breast, colon and prostate adenocarcinomas. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human p27Kip1 (Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B). It may also react to mouse p27Kip1, as predicted by immunogen homology. Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. p27Kip1 (p27) is a member of the universal cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor (CDKI) family. p27Kip1 binds to and prevents the activation of cyclin E-CDK2 or cyclin D-CDK4 complexes, and thus controls the cell cycle progression at G1. Degradation of p27Kip1 is triggered by CDK dependent phosphorylation and subsequent ubiquitination by SCF complexes that are required for the cellular transition from quiescence to the proliferative state. p27Kip1 expression is regulated by cell contact inhibition and by specific growth factors, such as transforming growth factor (TGF)-beta. In addition to its role as a CDKI, p27Kip1 is a putative tumor suppressor gene, regulator of drug resistance in solid tumors, and promoter of apoptosis; acts as a safeguard against inflammatory injury; and has a role in cell differentiation. The level of p27Kip1 protein expression decreases during tumor development and progression in some epithelial, lymphoid, and endocrine tissues. This decrease occurs mainly at the post-translational level with protein degradation by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. A large number of studies have characterized p27Kip1 as an independent prognostic factor in various human cancers, including breast, colon and prostate adenocarcinomas.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161