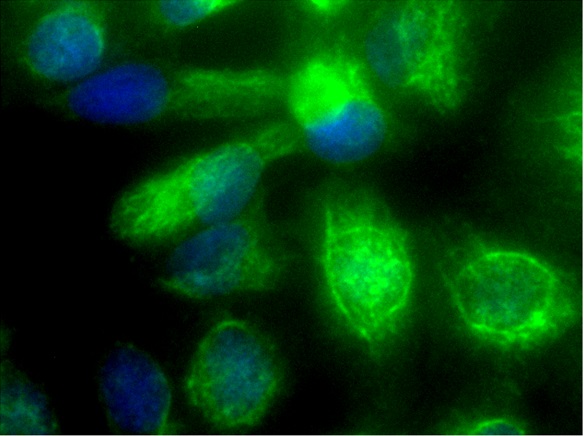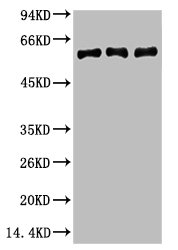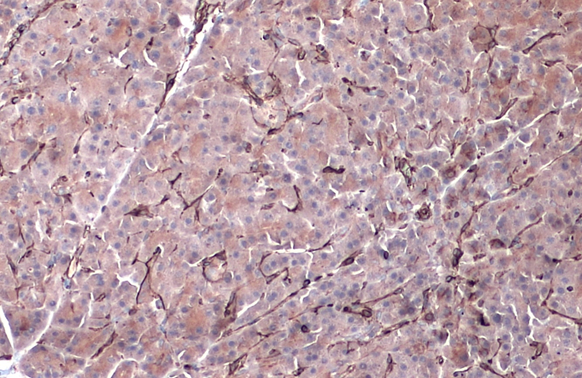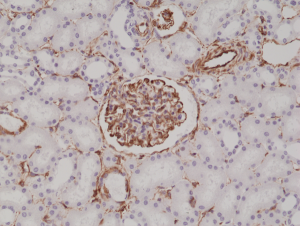
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human kidney tissue sections using anti-Vimentin rabbit monoclonal antibody (clone RM289) at a 1:200 dilution.
anti-Vimentin (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM289)
REV-31-1173-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetVIM
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-Vimentin (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM289)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM289
- Gene ID7431
- Target nameVIM
- Target descriptionvimentin
- Target synonymsvimentin, epididymis secretory sperm binding protein
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP08670
- Protein NameVimentin
- Scientific DescriptionRecombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human Vimentin. It may also react to mouse or rat Vimentin, as predicted by immunogen homology. Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Vimentin is a developmentally regulated intermediate filament protein (IFP) found in mesenchymal cells. It is believed to be involved in the intracellular transport of proteins between the nucleus and plasma membrane. Unlike other IFP proteins, vimentin is expressed, along with desmin, during the early stages of cellular development. During the development process, vimentin is exchanged for new, tissue-specific IFPs. Vimentin has been implicated to be involved in the rate of steroid synthesis via its role as a storage network for steroidogenic cholesterol containing lipid droplets. Vimentin phosphorylation by a protein kinase causes the breakdown of intermediate filaments and activation of an ATP and myosin light chain dependent contractile event. This results in cytoskeletal changes that facilitate the interaction of the lipid droplets within mitochondria and subsequent transport of cholesterol to the organelles lead to an increase in steroid synthesis. Vimentin has been used as a sarcoma tumor marker to identify mesenchyme. - Vimentin is a developmentally regulated intermediate filament protein (IFP) found in mesenchymal cells. It is believed to be involved in the intracellular transport of proteins between the nucleus and plasma membrane. Unlike other IFP proteins, vimentin is expressed, along with desmin, during the early stages of cellular development. During the development process, vimentin is exchanged for new, tissue-specific IFPs. Vimentin has been implicated to be involved in the rate of steroid synthesis via its role as a storage network for steroidogenic cholesterol containing lipid droplets. Vimentin phosphorylation by a protein kinase causes the breakdown of intermediate filaments and activation of an ATP and myosin light chain dependent contractile event. This results in cytoskeletal changes that facilitate the interaction of the lipid droplets within mitochondria and subsequent transport of cholesterol to the organelles lead to an increase in steroid synthesis. Vimentin has been used as a sarcoma tumor marker to identify mesenchyme.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161