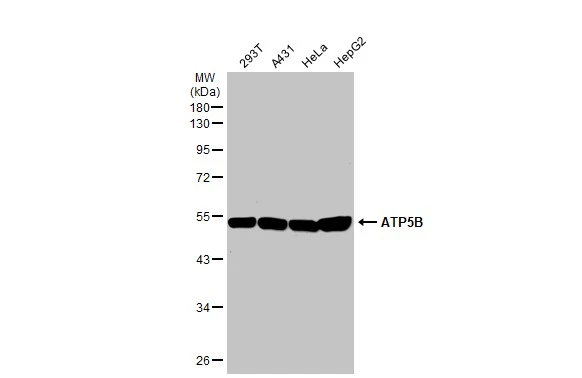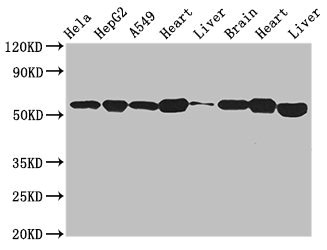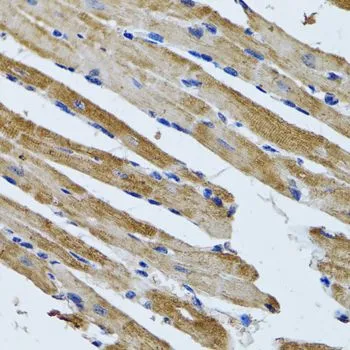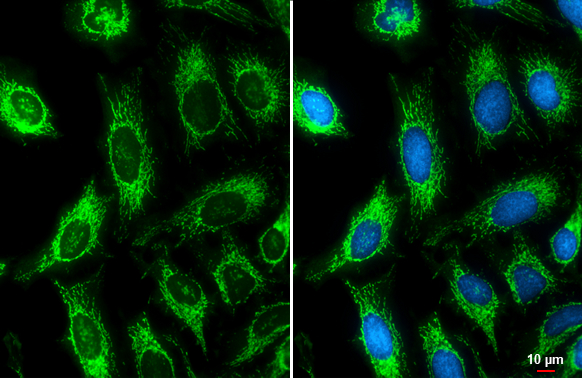
ATP5B antibody detects ATP5B protein at mitochondria by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: HeLa cells were fixed in ice-cold MeOH for 5 min. Green: ATP5B stained by ATP5B antibody (GTX132925) diluted at 1:100. Blue: Hoechst 33342 staining. Scale bar= 10 μm.
ATP5B antibody
GTX132925
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetATP5F1B
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameATP5B antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. ICC/IF: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.52 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID506
- Target nameATP5F1B
- Target descriptionATP synthase F1 subunit beta
- Target synonymsATP5B, ATPMB, ATPSB, HEL-S-271, HUMOP2, ATP synthase F(1) complex subunit beta, mitochondrial, ATP synthase subunit beta, mitochondrial, ATP synthase, H+ transporting, mitochondrial F1 complex, beta polypeptide, epididymis secretory protein Li 271, mitochondrial ATP synthase beta subunit, mitochondrial ATP synthetase, beta subunit
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP06576
- Protein NameATP synthase F(1) complex subunit beta, mitochondrial
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a subunit of mitochondrial ATP synthase. Mitochondrial ATP synthase catalyzes ATP synthesis, utilizing an electrochemical gradient of protons across the inner membrane during oxidative phosphorylation. ATP synthase is composed of two linked multi-subunit complexes: the soluble catalytic core, F1, and the membrane-spanning component, Fo, comprising the proton channel. The catalytic portion of mitochondrial ATP synthase consists of 5 different subunits (alpha, beta, gamma, delta, and epsilon) assembled with a stoichiometry of 3 alpha, 3 beta, and a single representative of the other 3. The proton channel consists of three main subunits (a, b, c). This gene encodes the beta subunit of the catalytic core. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161