![C9orf72 antibody [GT1553] detects C9orf72 protein at cytoplasmic granule by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: DIV9 rat E18 primary hippocampal neuron cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: C9orf72 stained by C9orf72 antibody [GT1553] (GTX634482) diluted at 1:250. Red: Tau, an Axon marker, stained by Tau antibody (GTX130462) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920). C9orf72 antibody [GT1553] detects C9orf72 protein at cytoplasmic granule by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: DIV9 rat E18 primary hippocampal neuron cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: C9orf72 stained by C9orf72 antibody [GT1553] (GTX634482) diluted at 1:250. Red: Tau, an Axon marker, stained by Tau antibody (GTX130462) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920).](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX634482/GTX634482_44825_20230119_ICC_IF_R_23021401_412.webp)
C9orf72 antibody [GT1553] detects C9orf72 protein at cytoplasmic granule by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: DIV9 rat E18 primary hippocampal neuron cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: C9orf72 stained by C9orf72 antibody [GT1553] (GTX634482) diluted at 1:250. Red: Tau, an Axon marker, stained by Tau antibody (GTX130462) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920).
C9orf72 antibody [GT1553]
GTX634482
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetC9orf72
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameC9orf72 antibody [GT1553]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:100-1:1000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDGT1553
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID203228
- Target nameC9orf72
- Target descriptionC9orf72-SMCR8 complex subunit
- Target synonymsALSFTD, DENND9, DENNL72, FTDALS, FTDALS1, guanine nucleotide exchange factor C9orf72, guanine nucleotide exchange C9orf72, protein C9orf72
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG2a
- Protein IDQ96LT7
- Protein NameGuanine nucleotide exchange factor C9orf72
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene plays an important role in the regulation of endosomal trafficking, and has been shown to interact with Rab proteins that are involved in autophagy and endocytic transport. Expansion of a GGGGCC repeat from 2-22 copies to 700-1600 copies in the intronic sequence between alternate 5 exons in transcripts from this gene is associated with 9p-linked ALS (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis) and FTD (frontotemporal dementia) (PMID: 21944778, 21944779). Studies suggest that hexanucleotide expansions could result in the selective stabilization of repeat-containing pre-mRNA, and the accumulation of insoluble dipeptide repeat protein aggregates that could be pathogenic in FTD-ALS patients (PMID: 23393093). Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2016]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161

![C9orf72 antibody [GT1553] detects C9orf72 protein at cytoplasm by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse hippocampus. C9orf72 stained by C9orf72 antibody [GT1553] (GTX634482) diluted at 1:100. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min C9orf72 antibody [GT1553] detects C9orf72 protein at cytoplasm by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse hippocampus. C9orf72 stained by C9orf72 antibody [GT1553] (GTX634482) diluted at 1:100. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX634482/GTX634482_43143_20190315_IHC-P_M_2_w_23061202_411.webp)
![Non-transfected (–) and transfected (+) 293T whole cell extracts (60 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with C9orf72 antibody [GT1553] (GTX634482) diluted at 1:500. The HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibody (GTX213111-01) was used to detect the primary antibody, and the signal was developed with Trident ECL plus-Enhanced. Non-transfected (–) and transfected (+) 293T whole cell extracts (60 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with C9orf72 antibody [GT1553] (GTX634482) diluted at 1:500. The HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibody (GTX213111-01) was used to detect the primary antibody, and the signal was developed with Trident ECL plus-Enhanced.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX634482/GTX634482_43143_20181221_WB_shRNA_watermark_w_23061202_893.webp)
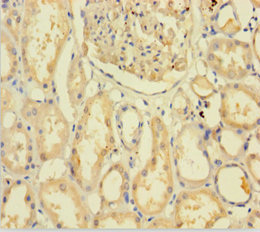
![C9orf72 antibody [GT1553] detects C9orf72 protein at cytoplasm by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse hippocampus. C9orf72 stained by C9orf72 antibody [GT1553] (GTX634482) diluted at 1:100. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min C9orf72 antibody [GT1553] detects C9orf72 protein at cytoplasm by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse hippocampus. C9orf72 stained by C9orf72 antibody [GT1553] (GTX634482) diluted at 1:100. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX634482/GTX634482_43143_20190315_IHC-P_M_w_23061202_180.webp)
![C9orf72 antibody [GT1553] detects C9orf72 protein at cytoplasm by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse hippocampus. C9orf72 stained by C9orf72 antibody [GT1553] (GTX634482) diluted at 1:100. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min C9orf72 antibody [GT1553] detects C9orf72 protein at cytoplasm by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse hippocampus. C9orf72 stained by C9orf72 antibody [GT1553] (GTX634482) diluted at 1:100. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX634482/GTX634482_43143_20190315_IHC-P_M_1_w_23061202_770.webp)
![Non-transfected (–) and transfected (+) 293T whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with C9orf72 antibody [GT1553] (GTX634482) diluted at 1:5000. The HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibody (GTX213111-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Non-transfected (–) and transfected (+) 293T whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with C9orf72 antibody [GT1553] (GTX634482) diluted at 1:5000. The HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibody (GTX213111-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX634482/GTX634482_43143_20180316_WB_B_w_23061202_946.webp)
![Various whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with C9orf72 antibody [GT1553] (GTX634482) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibody (GTX213111-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Various whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with C9orf72 antibody [GT1553] (GTX634482) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibody (GTX213111-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX634482/GTX634482_43143_20180316_WB_M_w_23061202_446.webp)
![Various whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with C9orf72 antibody [GT1553] (GTX634482) diluted at 1:500. The HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibody (GTX213111-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Various whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with C9orf72 antibody [GT1553] (GTX634482) diluted at 1:500. The HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibody (GTX213111-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX634482/GTX634482_43143_20180413_WB_w_23061202_861.webp)
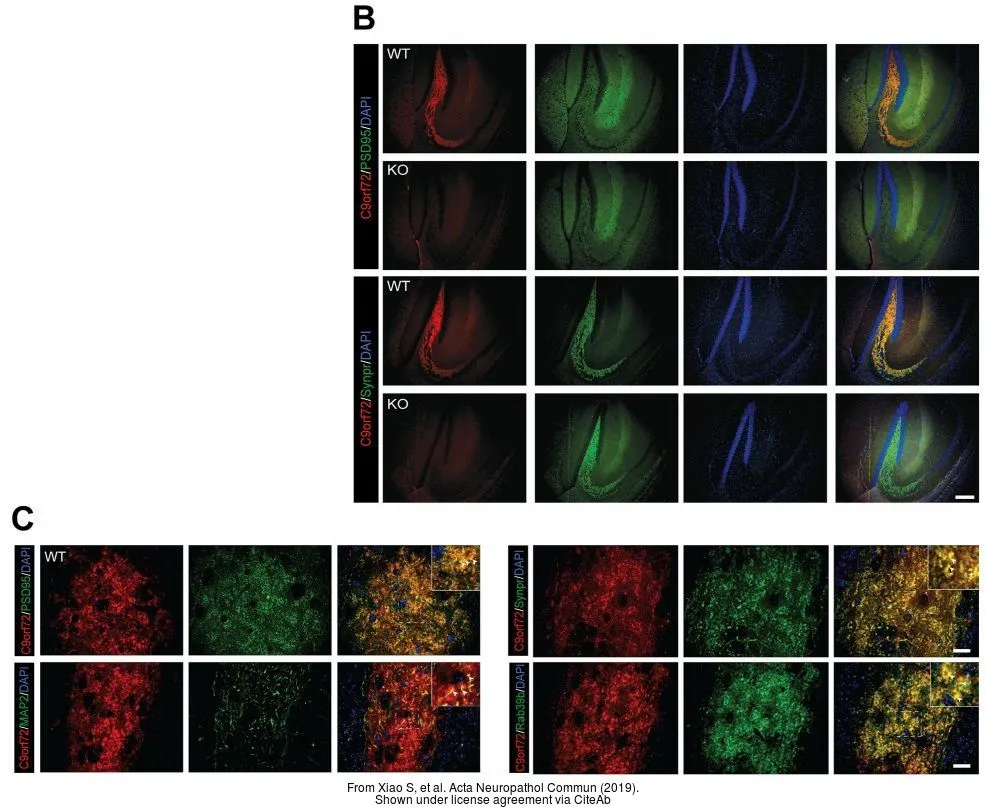
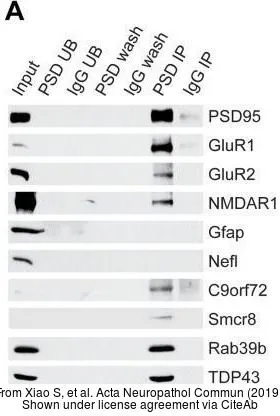

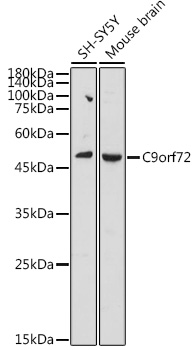

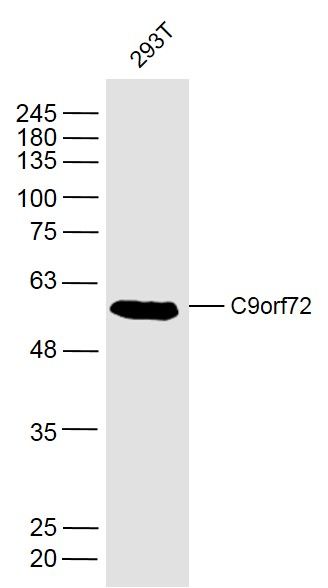


![Immunoprecipitation of C9orf72 protein from SK-N-SH whole cell extracts using 5 μg of C9orf72 antibody [GT779] (GTX632041). Western blot analysis was performed using C9orf72 antibody [GT779] (GTX632041). EasyBlot anti-Mouse IgG (GTX221667-01) was used as a secondary reagent.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX632041/GTX632041_41939_20150612_IP_w_23061202_986.webp)
![C9orf72 antibody [GT779-RB] detects C9orf72 protein at cytoplasm by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: DIV10 rat E18 primary hippocampal neuron cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: C9orf72 stained by C9orf72 antibody [GT779-RB] (GTX635397) diluted at 1:250. Red: Tau, a cytoskeleton marker, stained by Tau antibody [GT287] (GTX634809) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920).](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX635397/GTX635397_43882_20200715_ICC_IF_22072519_115.webp)
![C9orf72 antibody [GT1553-RB] detects C9orf72 protein at cytoplasm by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: DIV10 rat E18 primary hippocampal neuron cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: C9orf72 stained by C9orf72 antibody [GT1553-RB] (GTX635398) diluted at 1:250. Red: Tau, a cytoskeleton marker, stained by Tau antibody [GT287] (GTX634809) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920).](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX635398/GTX635398_44027_20200715_ICC_IF_22072519_728.webp)