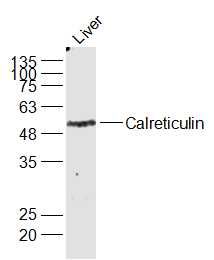
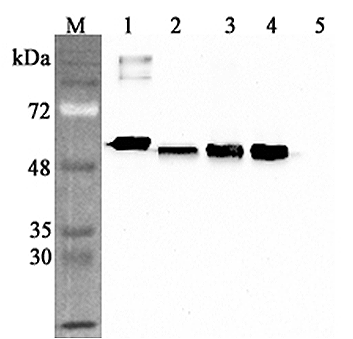
CALR Polyclonal Antibody
RD80468A
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetCALR
Overview
- SupplierReddot Biotech
- Product NameCALR Polyclonal Antibody
- Delivery Days Customer5
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID811
- Target nameCALR
- Target descriptioncalreticulin
- Target synonymsCALR1, CRT, HEL-S-99n, RO, SSA, cC1qR, calreticulin, CRP55, ERp60, HACBP, Sicca syndrome antigen A (autoantigen Ro; calreticulin), calregulin, endoplasmic reticulum resident protein 60, epididymis secretory sperm binding protein Li 99n, grp60
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Scientific DescriptionCalreticulin is a multifunctional protein that acts as a major Ca(2+)-binding (storage) protein in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum. It is also found in the nucleus, suggesting that it may have a role in transcription regulation. Calreticulin binds to the synthetic peptide KLGFFKR, which is almost identical to an amino acid sequence in the DNA-binding domain of the superfamily of nuclear receptors. Calreticulin binds to antibodies in certain sera of systemic lupus and Sjogren patients which contain anti-Ro/SSA antibodies, it is highly conserved among species, and it is located in the endoplasmic and sarcoplasmic reticulum where it may bind calcium. The amino terminus of calreticulin interacts with the DNA-binding domain of the glucocorticoid receptor and prevents the receptor from binding to its specific glucocorticoid response element. Calreticulin can inhibit the binding of androgen receptor to its hormone-responsive DNA element and can inhibit androgen receptor and retinoic acid receptor transcriptional activities in vivo, as well as retinoic acid-induced neuronal differentiation. Thus, calreticulin can act as an important modulator of the regulation of gene transcription by nuclear hormone receptors. Systemic lupus erythematosus is associated with increased autoantibody titers against calreticulin but calreticulin is not a Ro/SS-A antigen. Earlier papers referred to calreticulin as an Ro/SS-A antigen but this was later disproven. Increased autoantibody titer against human calreticulin is found in infants with complete congenital heart block of both the IgG and IgM classes.
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C
- UNSPSC12352203