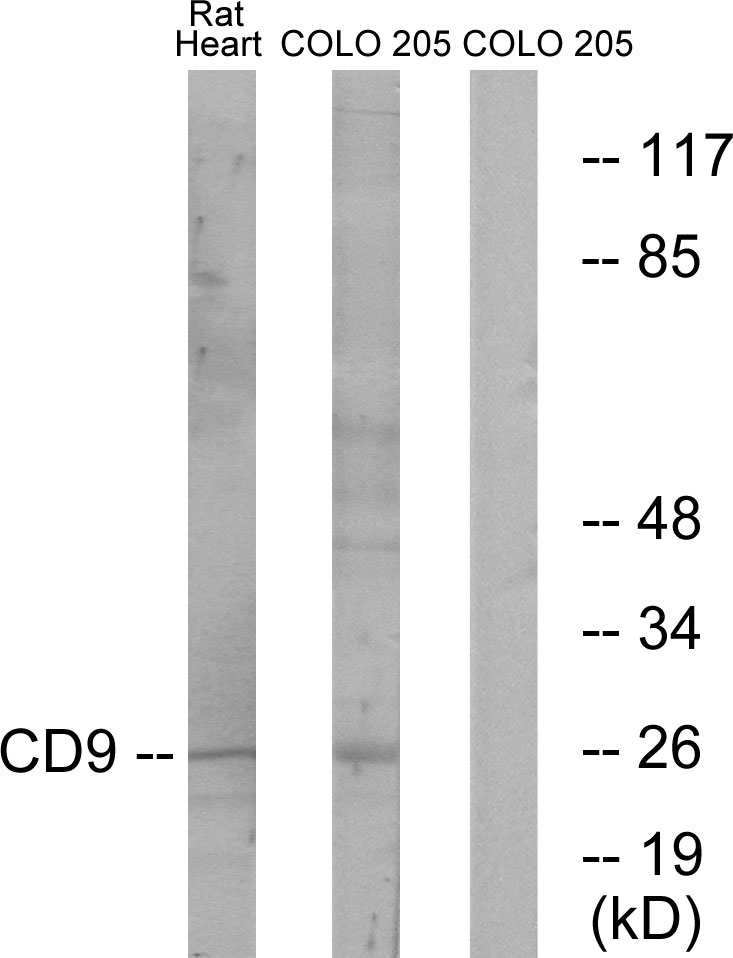
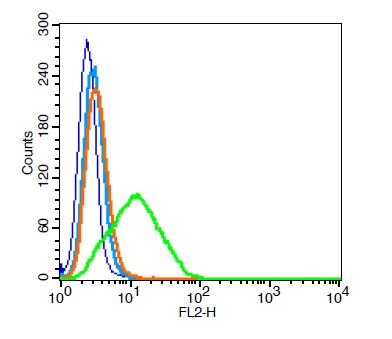
CD9 antibody [MM2/57] (FITC)
GTX76183
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin, Neutralisation/Blocking
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityBovine, Canine, Equine, Feline, Ferret, Human, Mammals, Mink, Mouse, Porcine, Primate, Rabbit, Rat
TargetCD9
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameCD9 antibody [MM2/57] (FITC)
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteFACS: Neat. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin, Neutralisation/Blocking
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDMM2/57
- Concentration0.1 mg/ml
- ConjugateFITC
- Gene ID928
- Target nameCD9
- Target descriptionCD9 molecule
- Target synonymsBTCC-1, DRAP-27, MIC3, MRP-1, TSPAN-29, TSPAN29, CD9 antigen, 5H9 antigen, BA-2/p24 antigen, CD9 antigen (p24), antigen CD9, cell growth-inhibiting gene 2 protein, leukocyte antigen MIC3, motility related protein-1, tetraspanin-29
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG2b
- Protein IDP21926
- Protein NameCD9 antigen
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a member of the transmembrane 4 superfamily, also known as the tetraspanin family. Tetraspanins are cell surface glycoproteins with four transmembrane domains that form multimeric complexes with other cell surface proteins. The encoded protein functions in many cellular processes including differentiation, adhesion, and signal transduction, and expression of this gene plays a critical role in the suppression of cancer cell motility and metastasis. [provided by RefSeq, Jan 2011]
- ReactivityBovine, Canine, Equine, Feline, Ferret, Human, Mammals, Mink, Mouse, Porcine, Primate, Rabbit, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Esmaeili A, Hosseini S, Kamali A, et al. Co-aggregation of MSC/chondrocyte in a dynamic 3D culture elevates the therapeutic effect of secreted extracellular vesicles on osteoarthritis in a rat model. Sci Rep. 2022,12(1):19827. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-22592-4Read this paper
- Hosseinzadeh M, Kamali A, Hosseini S, et al. Higher Chondrogenic Potential of Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Mesenchymal Stem Cells Compared to Chondrocytes-EVs In Vitro. Biomed Res Int. 2021,2021:9011548. doi: 10.1155/2021/9011548Read this paper
- Ogunnaike M, Wang H, Zempleni J. Bovine mammary alveolar MAC-T cells afford a tool for studies of bovine milk exosomes in drug delivery. Int J Pharm. 2021,610:121263. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.121263Read this paper
- Tong L, Hao H, Zhang Z, et al. Milk-derived extracellular vesicles alleviate ulcerative colitis by regulating the gut immunity and reshaping the gut microbiota. Theranostics. 2021,11(17):8570-8586. doi: 10.7150/thno.62046Read this paper
- Park SM, An JH, Lee JH, et al. Extracellular vesicles derived from DFO-preconditioned canine AT-MSCs reprogram macrophages into M2 phase. PLoS One. 2021,16(7):e0254657. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0254657Read this paper
- Liu X, Liu S, Luo D, et al. Involvement of Circulating Exosomal MicroRNAs in Jian-Pi-Yi-Shen Formula Protection Against Adenine-Induced Chronic Kidney Disease. Front Pharmacol. 2020,11:622658. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.622658Read this paper
- Gaballa R, Ali HEA, Mahmoud MO, et al. Exosomes-Mediated Transfer of Itga2 Promotes Migration and Invasion of Prostate Cancer Cells by Inducing Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Cancers (Basel). 2020,12(8). doi: 10.3390/cancers12082300Read this paper
- Tong L, Hao H, Zhang X, et al. Oral Administration of Bovine Milk-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Alters the Gut Microbiota and Enhances Intestinal Immunity in Mice. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2020,64(8):e1901251. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201901251Read this paper
- An JH, Li Q, Ryu MO, et al. TSG-6 in extracellular vesicles from canine mesenchymal stem/stromal is a major factor in relieving DSS-induced colitis. PLoS One. 2020,15(2):e0220756. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0220756Read this paper
- An JH, Li Q, Bhang DH, et al. TNF-α and INF-γ primed canine stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles alleviate experimental murine colitis. Sci Rep. 2020,10(1):2115. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58909-4Read this paper