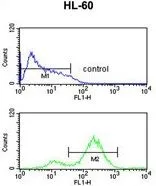
FACS analysis of HL-60 cells using GTX82525 eIF4E antibody. Top histogram : negative control Bottom histogram : HL-60 cells
eIF4E antibody
GTX82525
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, Western Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mammals
TargetEIF4E
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameeIF4E antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:1000. IHC-P: 1:50-1:100. FACS: 1:10-1:50. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, Western Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID1977
- Target nameEIF4E
- Target descriptioneukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E
- Target synonymsAUTS19, CBP, EIF4E1, EIF4EL1, EIF4F, eIF-4E, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E, eIF-4F 25 kDa subunit, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E-like 1, mRNA cap-binding protein
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP06730
- Protein NameEukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene is a component of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4F complex, which recognizes the 7-methylguanosine cap structure at the 5 end of messenger RNAs. The encoded protein aids in translation initiation by recruiting ribosomes to the 5-cap structure. Association of this protein with the 4F complex is the rate-limiting step in translation initiation. This gene acts as a proto-oncogene, and its expression and activation is associated with transformation and tumorigenesis. Several pseudogenes of this gene are found on other chromosomes. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants. [provided by RefSeq, Sep 2015]
- ReactivityHuman, Mammals
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Logan SM, Wu CW, Storey KB. The squirrel with the lagging eIF2: Global suppression of protein synthesis during torpor. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol. 2019,227:161-171. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2018.10.014Read this paper




![WB analysis of HeLa (1), HEK293 (2) and K562 (3) cell lysate using GTX60420 eIF4E antibody [5D11].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX60420/GTX60420_20170912_WB_w_23061123_620.webp)
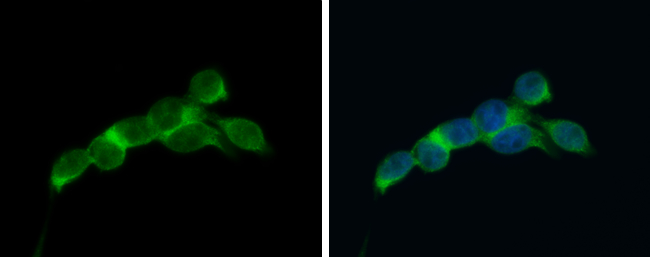
![eIF4E antibody [HL1553] detects eIF4E protein at cytoplasm by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: HeLa cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: eIF4E stained by eIF4E antibody [HL1553] (GTX637028) diluted at 1:500. Red: alpha Tubulin, a cytoskeleton marker, stained by alpha Tubulin antibody [GT114] (GTX628802) diluted at 1:1000. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920).](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX637028/GTX637028_T-44697_20220624_ICC_IF_22071401_367.webp)
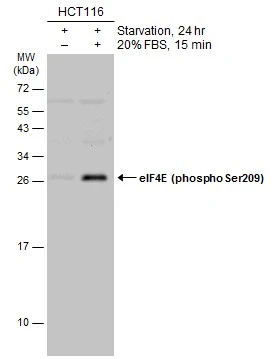
![Various whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with eIF4E antibody [HL1554] (GTX637029) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX637029/GTX637029_T-44697_20220617_WB_M_R_22062121_206.webp)
![Various whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with eIF4E antibody [HL1555] (GTX637030) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX637030/GTX637030_T-44697_20220617_WB_M_R_22062121_522.webp)