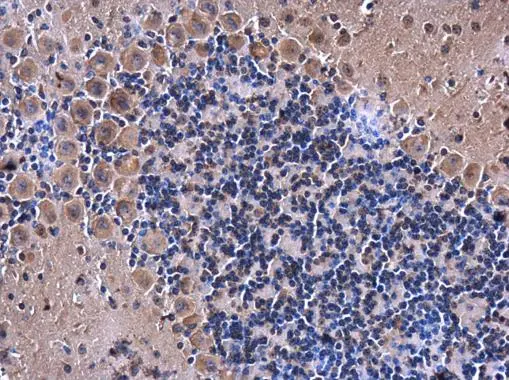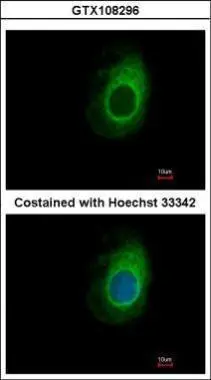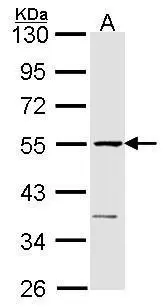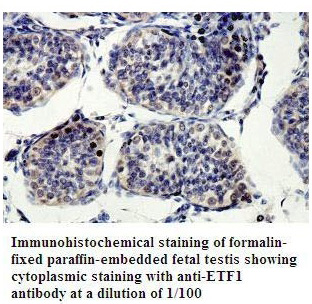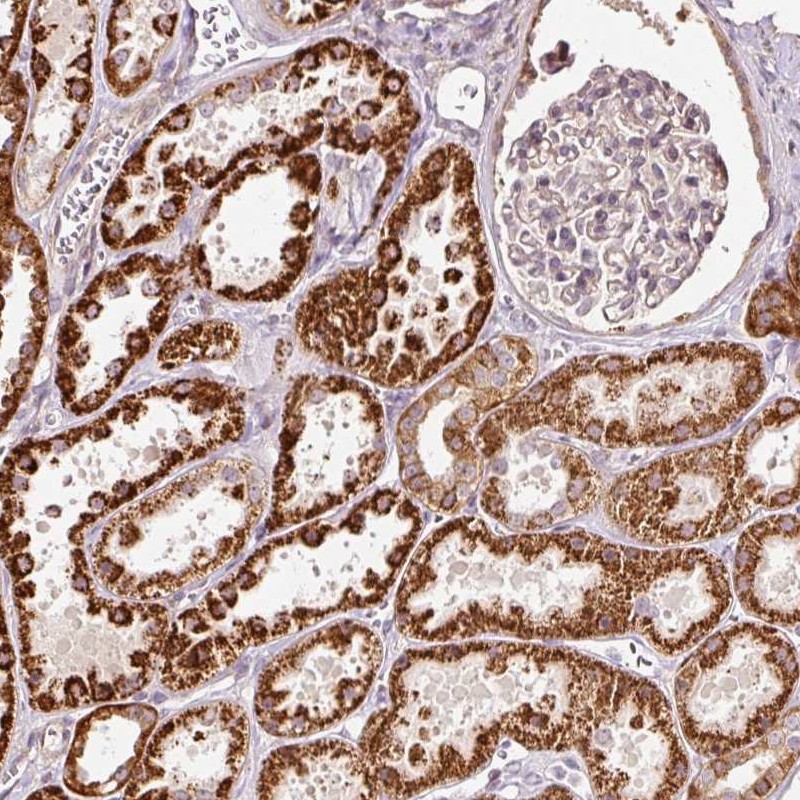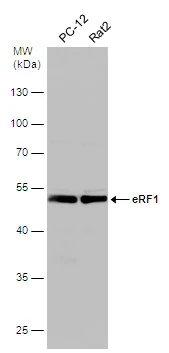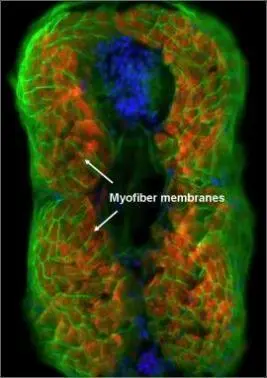
eRF1 antibody detects eRF1 protein on myofiber membranes by immunohistochemical analysis Sample: Agarose-embedded zebrafish embryo eRF1 antibody (GTX108296) dilution: 1:200. Image provided with permission courtesy of Dr. T. Schilling at UC, Irvine.
eRF1 antibody
GTX108296
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Zebra Fish
TargetETF1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameeRF1 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. ICC/IF: 1:100-1:1000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.8 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID2107
- Target nameETF1
- Target descriptioneukaryotic translation termination factor 1
- Target synonymsD5S1995, ERF, ERF1, RF1, SUP45L1, TB3-1, eukaryotic peptide chain release factor subunit 1, polypeptide chain release factor 1, protein Cl1, sup45 (yeast omnipotent suppressor 45) homolog-like 1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP62495
- Protein NameEukaryotic peptide chain release factor subunit 1
- Scientific DescriptionTermination of protein biosynthesis and release of the nascent polypeptide chain are signaled by the presence of an in-frame stop codon at the aminoacyl site of the ribosome. The process of translation termination is universal and is mediated by protein release factors (RFs) and GTP. A class 1 RF recognizes the stop codon and promotes the hydrolysis of the ester bond linking the polypeptide chain with the peptidyl site tRNA, a reaction catalyzed at the peptidyl transferase center of the ribosome. Class 2 RFs, which are not codon specific and do not recognize codons, stimulate class 1 RF activity and confer GTP dependency upon the process. In prokaryotes, both class 1 RFs, RF1 and RF2, recognize UAA; however, UAG and UGA are decoded specifically by RF1 and RF2, respectively. In eukaryotes, eRF1, or ETF1, the functional counterpart of RF1 and RF2, functions as an omnipotent RF, decoding all 3 stop codons (Frolova et al., 1994 [PubMed 7990965]).[supplied by OMIM]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Zebra Fish
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161