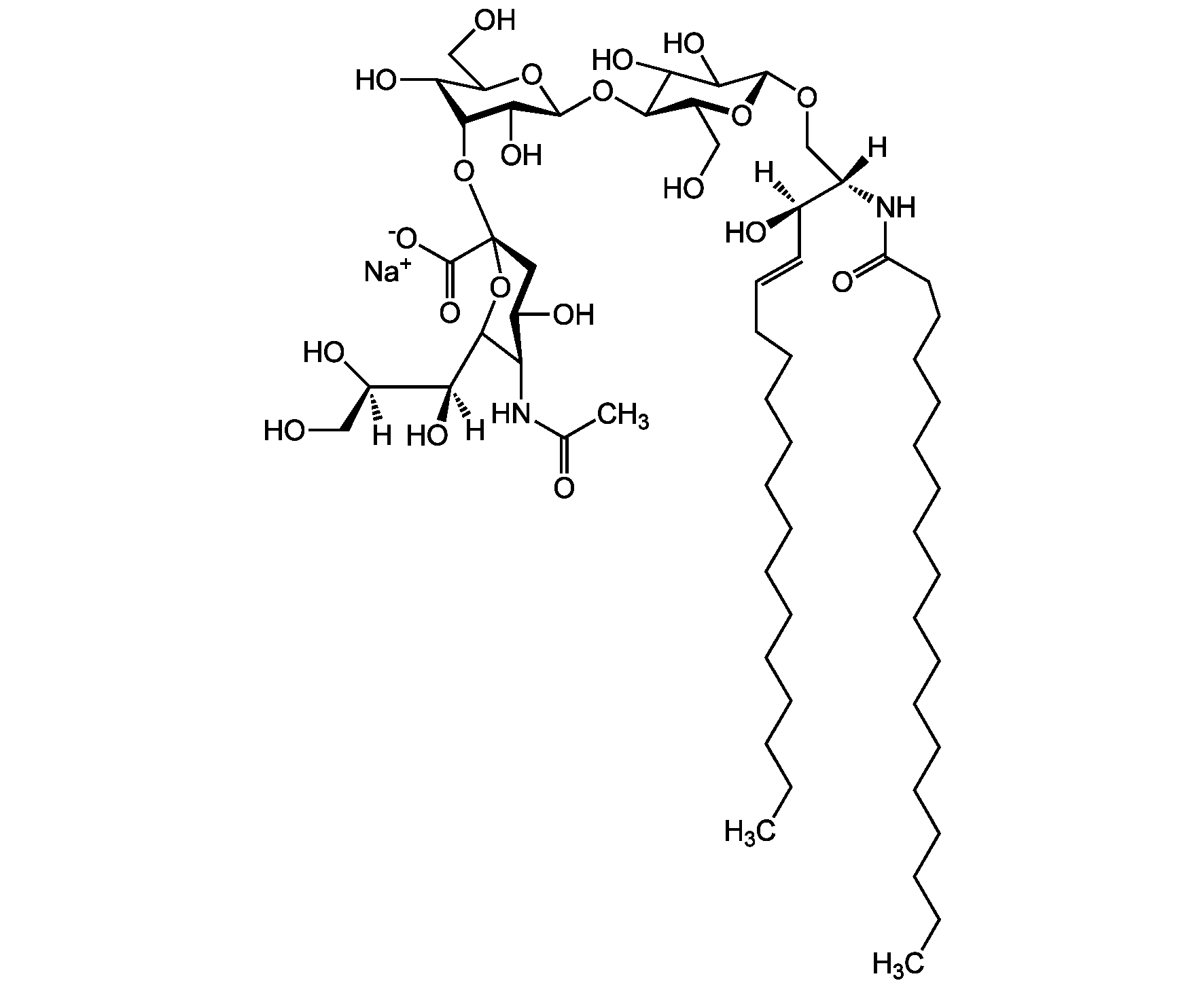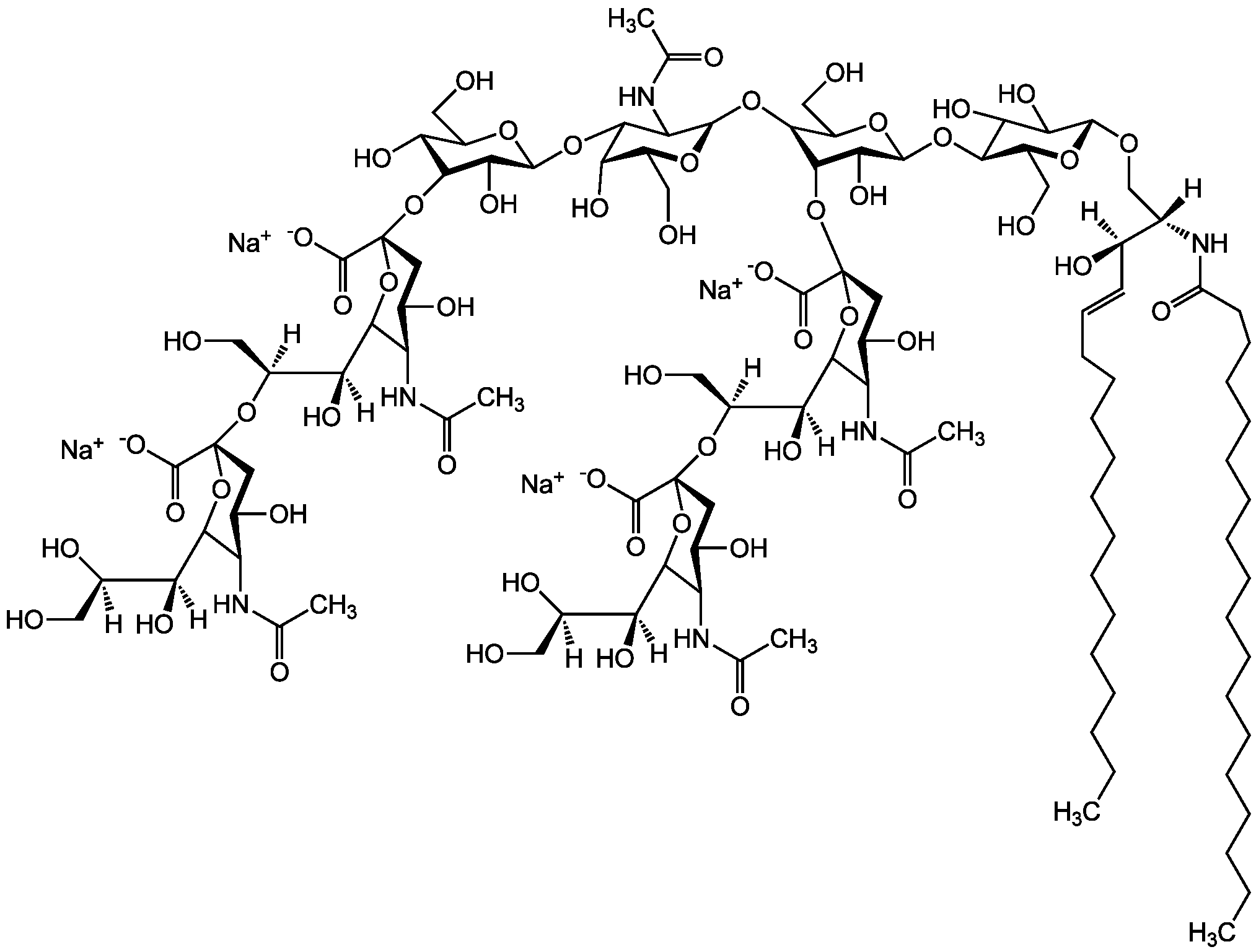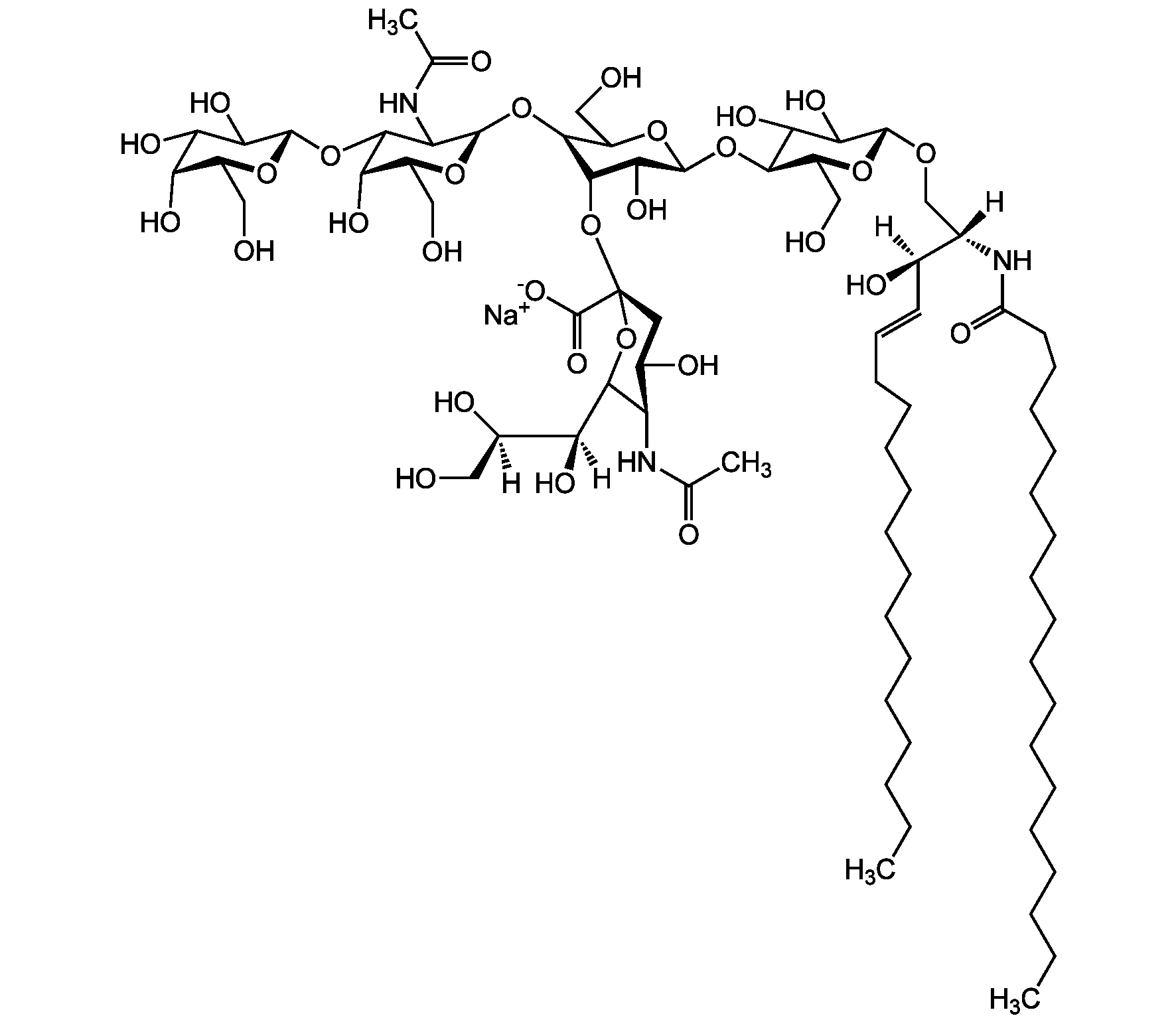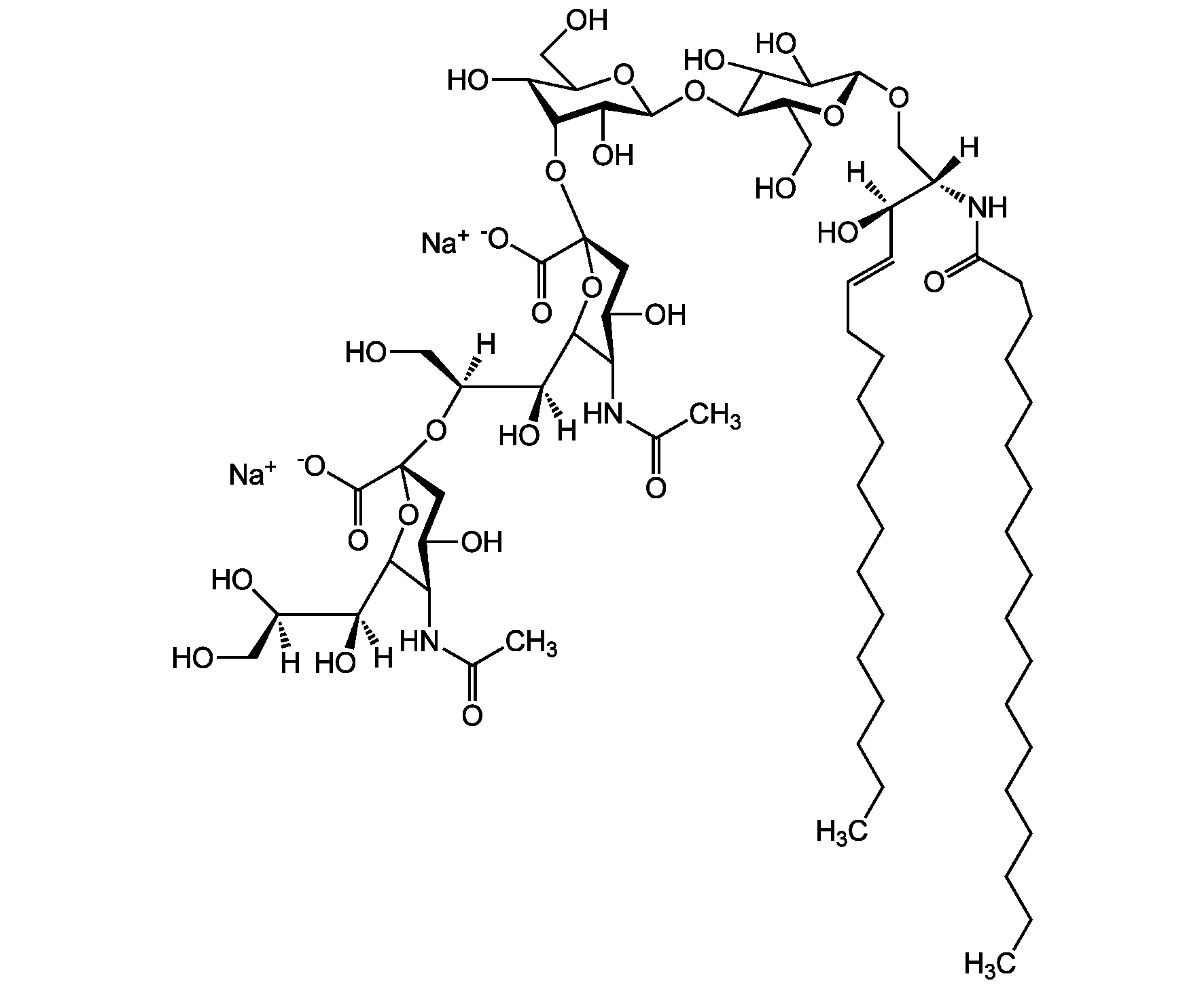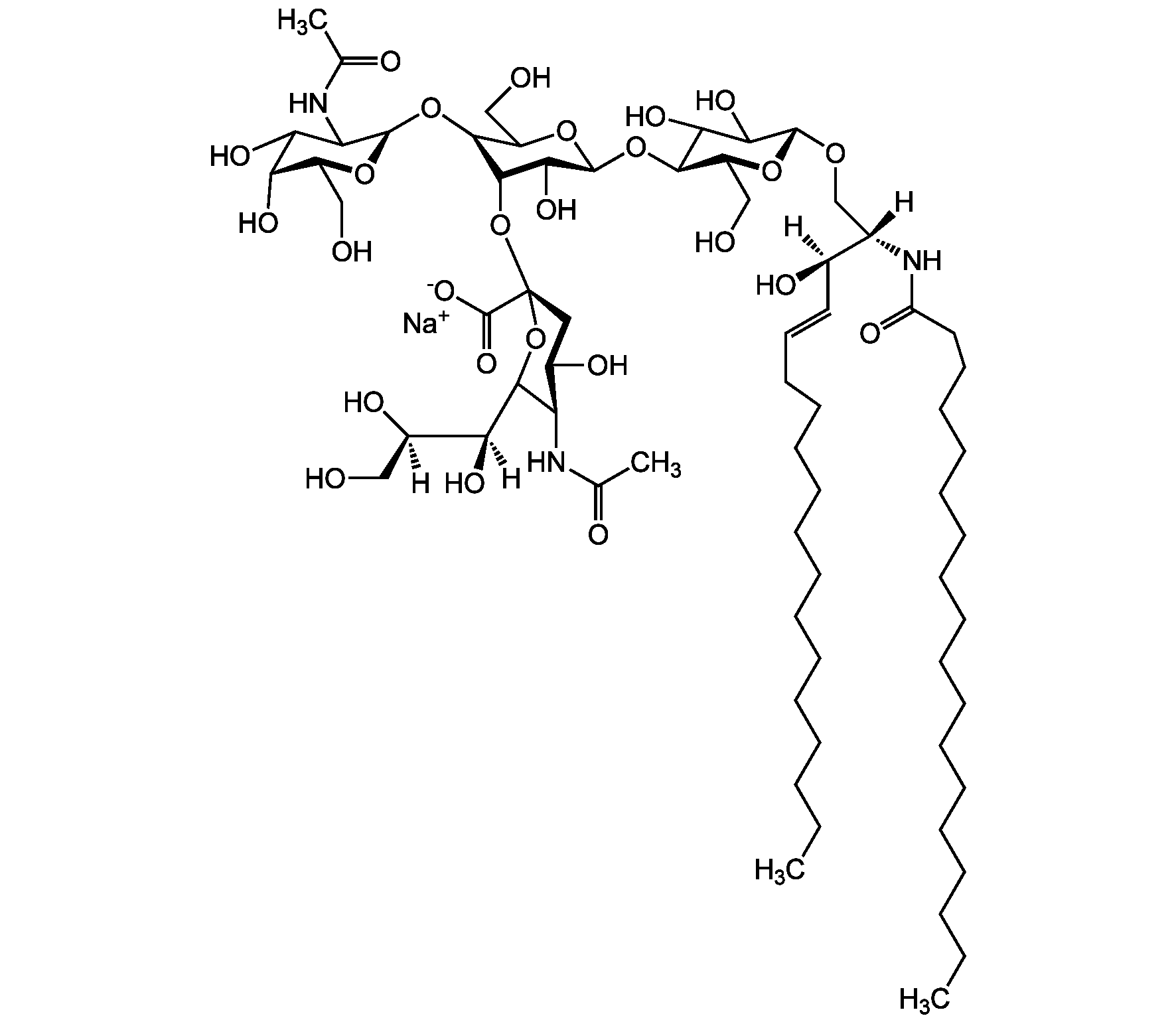
Chemical Structure
Ganglioside GM2 . sodium salt (bovine brain) [19600-01-2] [19600-01-2]
AG-CN2-9001
CAS Number19600-01-2
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight1383.7 . 23.0 (calculated on sphingosine C18:1 and stearic acid)
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameGanglioside GM2 . sodium salt (bovine brain) [19600-01-2] [19600-01-2]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number19600-01-2
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC67H120N3O26 . Na
- Molecular Weight1383.7 . 23.0 (calculated on sphingosine C18:1 and stearic acid)
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 19600-01-2. Formula: C67H120N3O26 . Na. MW: 1383.7 . 23.0 (calculated on sphingosine C18:1 and stearic acid). Isolated from bovine brain. Gangliosides are acidic glycosphingolipids that form lipid rafts in the outer leaflet of the cell plasma membrane, especially in neuronal cells in the central nervous system. They participate in cellular proliferation, differentiation, adhesion, signal transduction, cell-to-cell interactions, tumorigenesis and metastasis. The accumulation of gangliosides has been linked to several diseases. Ganglioside GM2 is a very minor component of the nervous system, but it is accumulated in brains from Tay-Sachs and Sandhoff disease patients, due to genetic defect of lysosomal beta-hexosaminidase. - Gangliosides are acidic glycosphingolipids that form lipid rafts in the outer leaflet of the cell plasma membrane, especially in neuronal cells in the central nervous system. They participate in cellular proliferation, differentiation, adhesion, signal transduction, cell-to-cell interactions, tumorigenesis and metastasis. The accumulation of gangliosides has been linked to several diseases. Ganglioside GM2 is a very minor component of the nervous system, but it is accumulated in brains from Tay-Sachs and Sandhoff disease patients, due to genetic defect of lysosomal beta-hexosaminidase.
- SMILES[Na+].[H][C@@](O)(CO)[C@]([H])(O)C1O[C@@](CC(O)[C@H]1NC(C)=O)(O[C@@H]1C(O)[C@H](O[C@H]2C(O)C(O)[C@H](OC[C@]([H])(NC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCC)[C@]([H])(O)\C=C\CCCCCCCCCCCCC)O[C@H]2CO)OC(CO)[C@@H]1O[C@H]1O[C@@H](CO)[C@H](O)C(O)C1NC(C)=O)C([O-])=O
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200