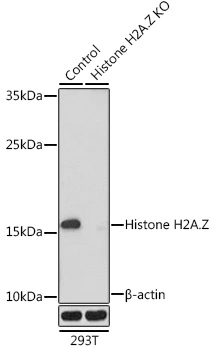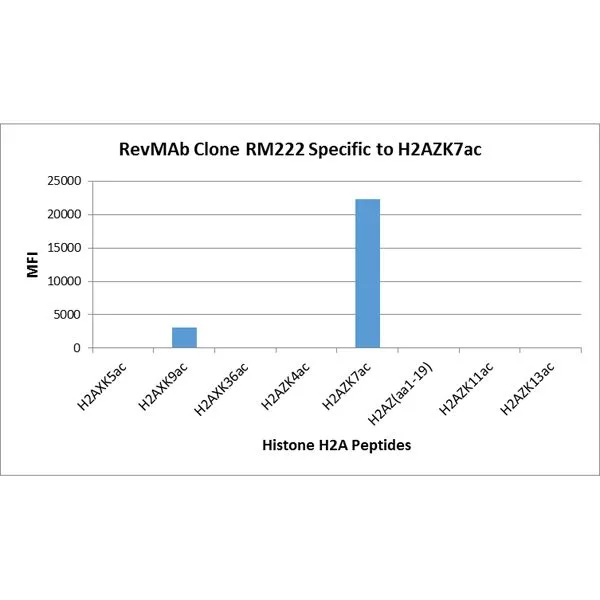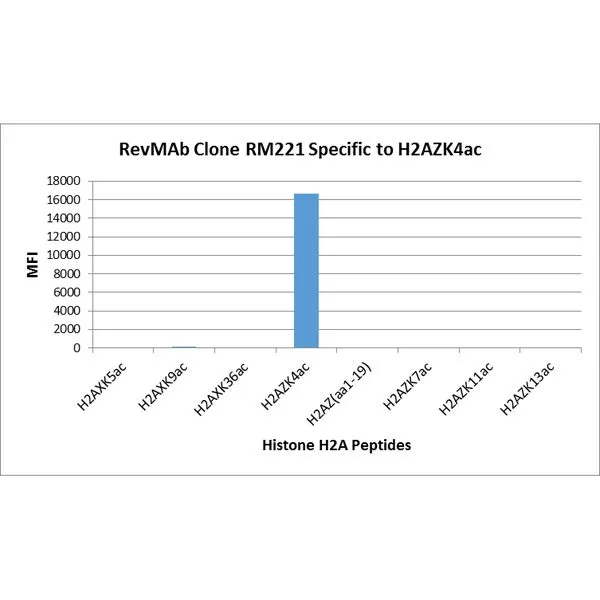
The GTX33591 reacts to Histone H2A.Z acetylatedat Lysine 4 (K4ac). No cross reactivity with non-modifiedLysine 4 or other acetylated Lysines in histone H2A.
Histone H2A.Z (Acetyl Lys4) antibody [RM221]
GTX33591
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetH2AZ1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameHistone H2A.Z (Acetyl Lys4) antibody [RM221]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 0.5 microg/mL - 2 microg/mL. ICC/IF: 1 microg/mL - 2 microg/mL. ELISA: 0.2 microg/mL - 1 microg/mL. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM221
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID3015
- Target nameH2AZ1
- Target descriptionH2A.Z variant histone 1
- Target synonymsH2A.Z-1, H2A.z, H2A/z, H2AFZ, H2AZ, histone H2A.Z, H2A histone family member Z, H2AZ histone
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP0C0S5
- Protein NameHistone H2A.Z
- Scientific DescriptionHistones are basic nuclear proteins that are responsible for the nucleosome structure of the chromosomal fiber in eukaryotes. Nucleosomes consist of approximately 146 bp of DNA wrapped around a histone octamer composed of pairs of each of the four core histones (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4). The chromatin fiber is further compacted through the interaction of a linker histone, H1, with the DNA between the nucleosomes to form higher order chromatin structures. This gene encodes a replication-independent member of the histone H2A family that is distinct from other members of the family. Studies in mice have shown that this particular histone is required for embryonic development and indicate that lack of functional histone H2A leads to embryonic lethality. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203

![ICC/IF analysis of HeLa cells treated with sodium butyrate using GTX33591 Histone H2A.Z (Acetyl Lys4) antibody [RM221]. Red : Primary antibody Green : Actin ICC/IF analysis of HeLa cells treated with sodium butyrate using GTX33591 Histone H2A.Z (Acetyl Lys4) antibody [RM221]. Red : Primary antibody Green : Actin](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX33591/GTX33591_20200909_ICCIF_148_w_23060800_255.webp)
![WB analysis of acid extracts from HeLa cells treated (+) or untreated (-) with sodium butyrate using GTX33591 Histone H2A.Z (Acetyl Lys4) antibody [RM221]. Dilution : 0.5microg/ml WB analysis of acid extracts from HeLa cells treated (+) or untreated (-) with sodium butyrate using GTX33591 Histone H2A.Z (Acetyl Lys4) antibody [RM221]. Dilution : 0.5microg/ml](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX33591/GTX33591_20200909_WB_267_w_23060800_678.webp)
![ICC/IF analysis of HeLa cells using GTX60915 Histone H2A.Z antibody [RM215]. Red : Primary antibody Green : Actin](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX60915/GTX60915_20200909_ICCIF_183_w_23061202_303.webp)