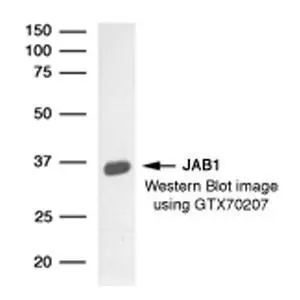
Sample (50 ug of whole cell lysate) A: mouse brain 10% SDS PAGE GTX70203 diluted at 1:10000
Jab1 antibody [2A10.8]
GTX70203
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityDrosophila, Human, Mouse, Rat
TargetCOPS5
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameJab1 antibody [2A10.8]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. IP: 0.5 - 1 microg/ml. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone ID2A10.8
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID10987
- Target nameCOPS5
- Target descriptionCOP9 signalosome subunit 5
- Target synonymsCSN5, JAB1, MOV-34, SGN5, COP9 signalosome complex subunit 5, 38 kDa Mov34 homolog, COP9 constitutive photomorphogenic homolog subunit 5, jun activation domain-binding protein 1, signalosome subunit 5, testis secretory sperm-binding protein Li 231m
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG2b
- Protein IDQ92905
- Protein NameCOP9 signalosome complex subunit 5
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene is one of the eight subunits of COP9 signalosome, a highly conserved protein complex that functions as an important regulator in multiple signaling pathways. The structure and function of COP9 signalosome is similar to that of the 19S regulatory particle of 26S proteasome. COP9 signalosome has been shown to interact with SCF-type E3 ubiquitin ligases and act as a positive regulator of E3 ubiquitin ligases. This protein is reported to be involved in the degradation of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor CDKN1B/p27Kip1. It is also known to be an coactivator that increases the specificity of JUN/AP1 transcription factors. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- ReactivityDrosophila, Human, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161

![Jab1 antibody [2A10.8] Jab1 antibody [2A10.8]](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX70203/Jab1-antibody-2A10.8-GTX70203-IHC-1_w_23061221_129.webp)

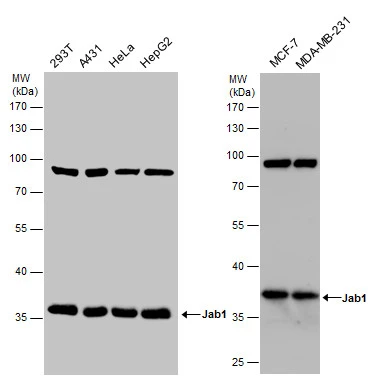
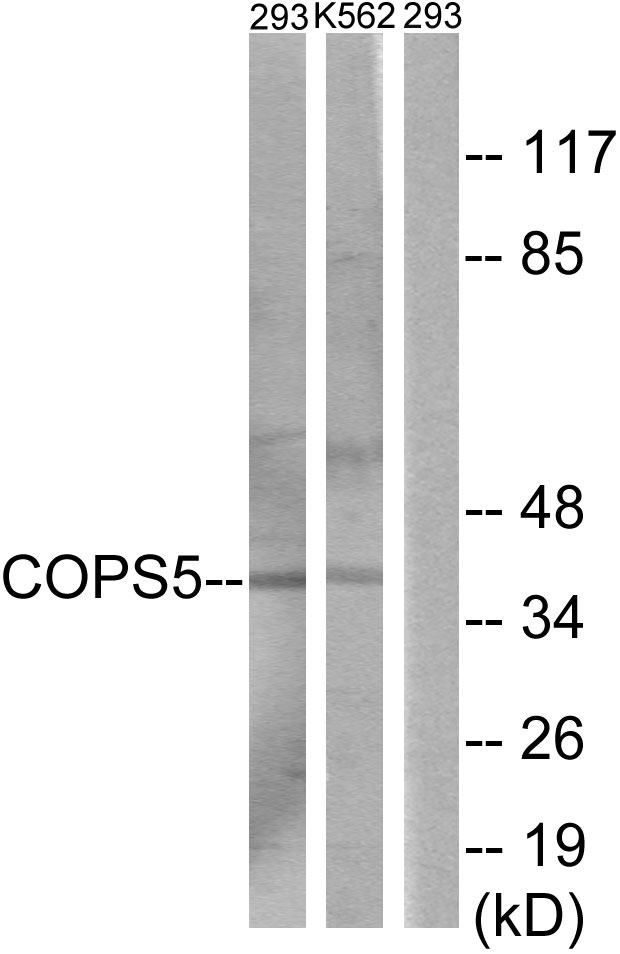

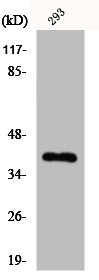


![Jab1 antibody [N1C1] detects Jab1 protein on zebrafish by whole mount immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: 2 days-post-fertilization zebrafish embryo. Jab1 antibody [N1C1] (GTX113927) dilution: 1:100.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX113927/GTX113927_40150_20150427_IHC-Wm_Z_22111423_536.webp)
![Jab1 antibody [6C3.38]](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX70205/Jab1-antibody-6C3.38-GTX70205-IHC-1_w_23061221_598.webp)