![ELISA analysis of antigen using GTX60660 KEAP1 antibody [1F10B6]. Black : Control antigen 100ng Purple : Antigen 10ng Blue : Antigen 50ng Red : Antigen 100ng ELISA analysis of antigen using GTX60660 KEAP1 antibody [1F10B6]. Black : Control antigen 100ng Purple : Antigen 10ng Blue : Antigen 50ng Red : Antigen 100ng](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX60660/GTX60660_20170912_ELISA_w_23061123_339.webp)
ELISA analysis of antigen using GTX60660 KEAP1 antibody [1F10B6]. Black : Control antigen 100ng Purple : Antigen 10ng Blue : Antigen 50ng Red : Antigen 100ng
KEAP1 antibody [1F10B6]
GTX60660
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetKEAP1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameKEAP1 antibody [1F10B6]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1/500 - 1/2000. ICC/IF: 1/50. FACS: 1/200 - 1/400. ELISA: 1/10000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone ID1F10B6
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID9817
- Target nameKEAP1
- Target descriptionkelch like ECH associated protein 1
- Target synonymsINrf2, KLHL19, kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1, KEAP1 delta C, cytosolic inhibitor of Nrf2, kelch-like family member 19, kelch-like protein 19
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG1
- Protein IDQ14145
- Protein NameKelch-like ECH-associated protein 1
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a protein containing KELCH-1 like domains, as well as a BTB/POZ domain. Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 interacts with NF-E2-related factor 2 in a redox-sensitive manner and the dissociation of the proteins in the cytoplasm is followed by transportation of NF-E2-related factor 2 to the nucleus. This interaction results in the expression of the catalytic subunit of gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same isoform have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Arellano Buendia AS, Juárez Rojas JG, García-Arroyo F, et al. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of allicin in the kidney of an experimental model of metabolic syndrome. PeerJ. 2023,11:e16132. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16132Read this paper
- Sánchez-Gloria JL, Martínez-Olivares CE, Del Valle-Mondragón L, et al. Allicin, an Emerging Treatment for Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: An Experimental Study. Int J Mol Sci. 2023,24(16). doi: 10.3390/ijms241612959Read this paper
- Li L, Xuan Y, Zhu B, et al. Protective Effects of Cannabidiol on Chemotherapy-Induced Oral Mucositis via the Nrf2/Keap1/ARE Signaling Pathways. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022,2022:4619760. doi: 10.1155/2022/4619760Read this paper
- Xia L, Gong M, Zou Y, et al. Apatinib Induces Ferroptosis of Glioma Cells through Modulation of the VEGFR2/Nrf2 Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022,2022:9925919. doi: 10.1155/2022/9925919Read this paper
- Arellano-Buendía AS, Castañeda-Lara LG, Loredo-Mendoza ML, et al. Effects of Allicin on Pathophysiological Mechanisms during the Progression of Nephropathy Associated to Diabetes. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020,9(11). doi: 10.3390/antiox9111134Read this paper
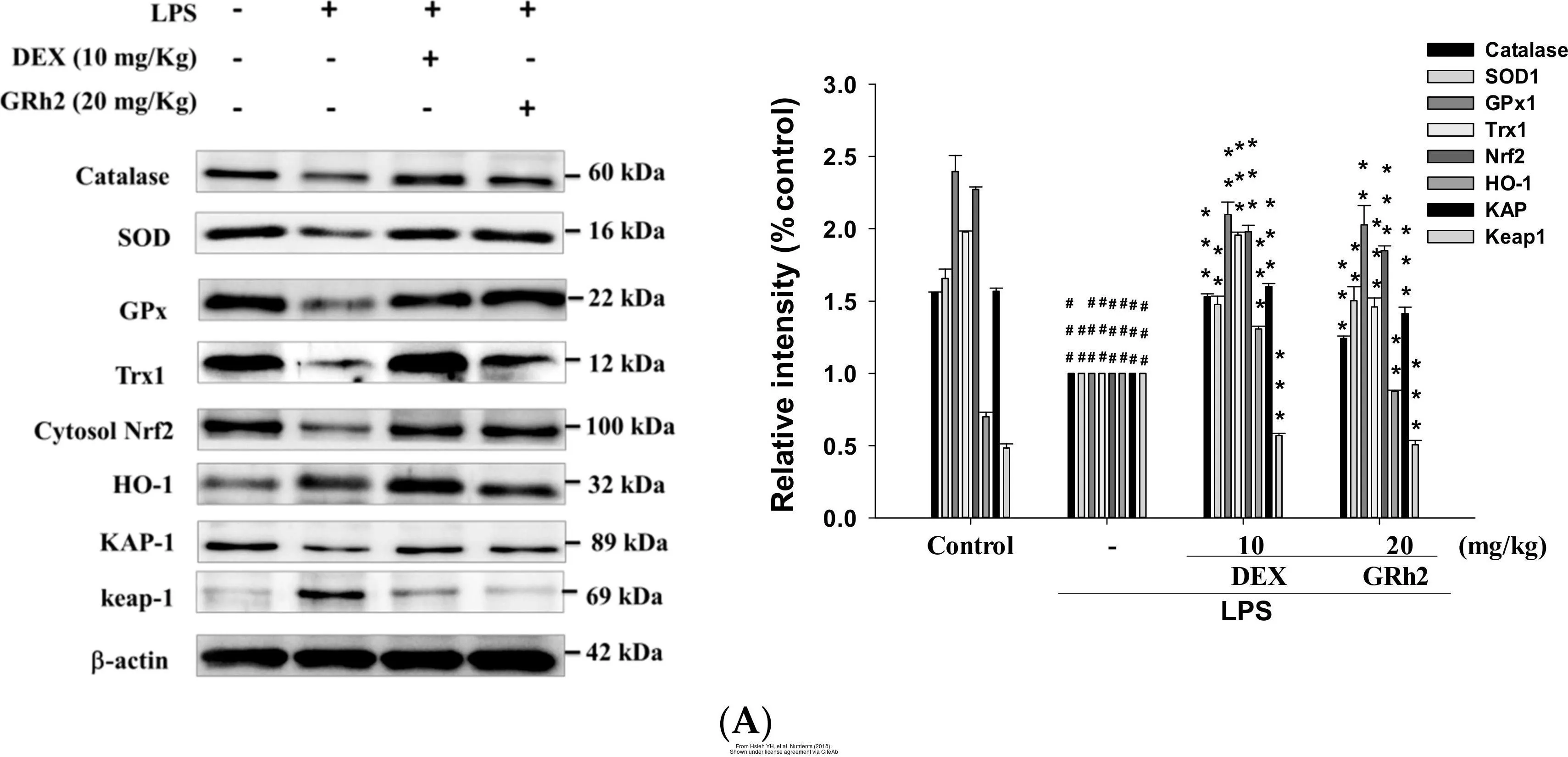
- Hsieh YH, Deng JS, Chang YS, et al. Ginsenoside Rh2 Ameliorates Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury by Regulating the TLR4/PI3K/Akt/mTOR, Raf-1/MEK/ERK, and Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathways in Mice. Nutrients. 2018,10(9). doi: 10.3390/nu10091208Read this paper
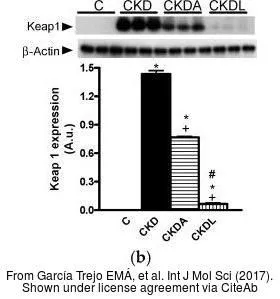
- García Trejo EMÁ, Arellano Buendía AS, Sánchez Reyes O, et al. The Beneficial Effects of Allicin in Chronic Kidney Disease Are Comparable to Losartan. Int J Mol Sci. 2017,18(9). doi: 10.3390/ijms18091980Read this paper

![FACS analysis of HepG2 cells using GTX60660 KEAP1 antibody [1F10B6]. Green : KEAP1 Purple : negative control FACS analysis of HepG2 cells using GTX60660 KEAP1 antibody [1F10B6]. Green : KEAP1 Purple : negative control](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX60660/GTX60660_20170912_FACS_w_23061123_478.webp)
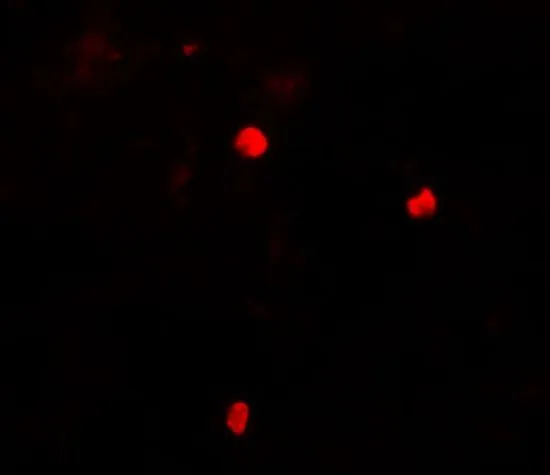
![ICC/IF analysis of HeLa cells using GTX60660 KEAP1 antibody [1F10B6]. Green : KEAP1 Blue: DRAQ5 fluorescent DNA dye Red: Actin filaments ICC/IF analysis of HeLa cells using GTX60660 KEAP1 antibody [1F10B6]. Green : KEAP1 Blue: DRAQ5 fluorescent DNA dye Red: Actin filaments](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX60660/GTX60660_20170912_ICCIF_w_23061123_894.webp)
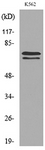
![WB analysis of NIH3T3 (1), and A549 (2) cell lysate using GTX60660 KEAP1 antibody [1F10B6]. WB analysis of NIH3T3 (1), and A549 (2) cell lysate using GTX60660 KEAP1 antibody [1F10B6].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX60660/GTX60660_20170912_WB_w_23061123_961.webp)

![ELISA analysis of antigen using GTX60664 KEAP1 antibody [7G4B10]. Black : Control antigen 100ng Purple : Antigen 10ng Blue : Antigen 50ng Red : Antigen 100ng](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX60664/GTX60664_20170912_ELISA_w_23061123_416.webp)