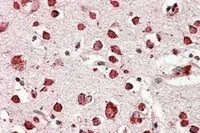
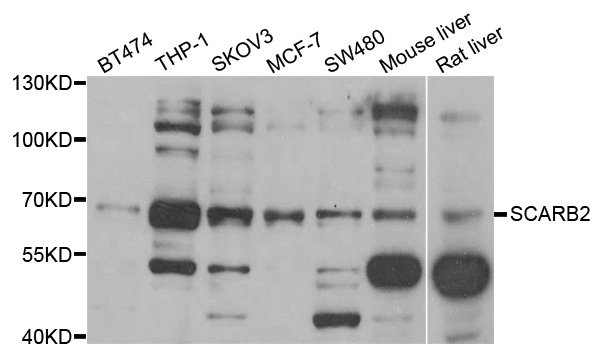
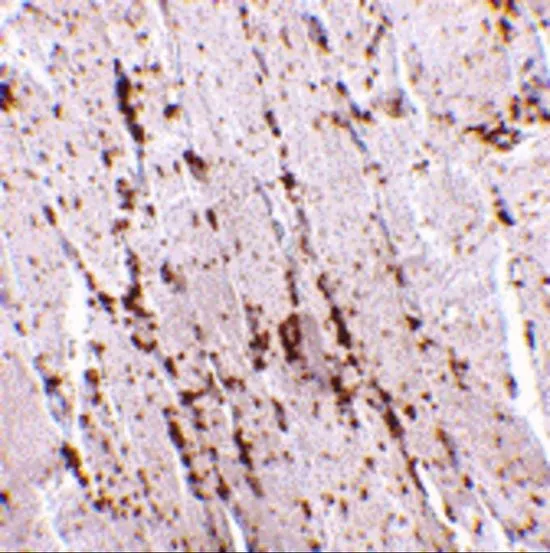
WB analysis of human cerebral cortex lysate using GTX88440 LIMP II antibody, Internal. Dilution : 0.1microg/ml Loading : 35microg protein in RIPA buffer
LIMP II antibody, Internal
GTX88440
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetSCARB2
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameLIMP II antibody, Internal
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 0.1-0.3microg/ml. IHC-P: 3-5microg/ml. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.50 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID950
- Target nameSCARB2
- Target descriptionscavenger receptor class B member 2
- Target synonymsAMRF, CD36L2, EPM4, HLGP85, LGP85, LIMP-2, LIMPII, SR-BII, lysosome membrane protein 2, 85 kDa lysosomal membrane sialoglycoprotein, 85 kDa lysosomal sialoglycoprotein scavenger receptor class B, member 2, CD36 antigen (collagen type I receptor, thrombospondin receptor)-like 2 (lysosomal integral membrane protein II), CD36 antigen-like 2, LIMP II, lysosome membrane protein II
- HostGoat
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ14108
- Protein NameLysosome membrane protein 2
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene is a type III glycoprotein that is located primarily in limiting membranes of lysosomes and endosomes. Earlier studies in mice and rat suggested that this protein may participate in membrane transportation and the reorganization of endosomal/lysosomal compartment. The protein deficiency in mice was reported to impair cell membrane transport processes and cause pelvic junction obstruction, deafness, and peripheral neuropathy. Further studies in human showed that this protein is a ubiquitously expressed protein and that it is involved in the pathogenesis of HFMD (hand, foot, and mouth disease) caused by enterovirus-71 and possibly by coxsackievirus A16. Mutations in this gene caused an autosomal recessive progressive myoclonic epilepsy-4 (EPM4), also known as action myoclonus-renal failure syndrome (AMRF). Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene.[provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203