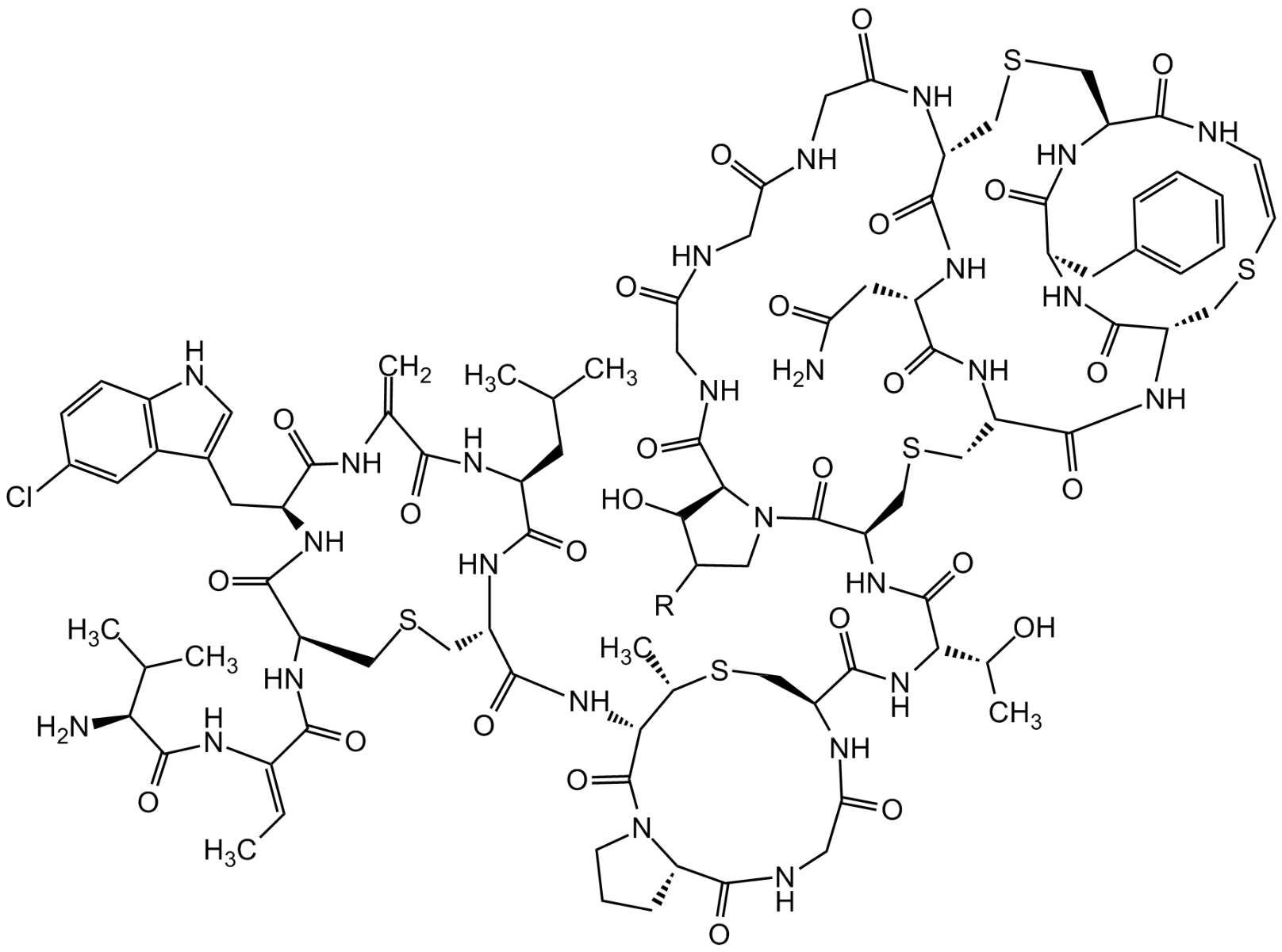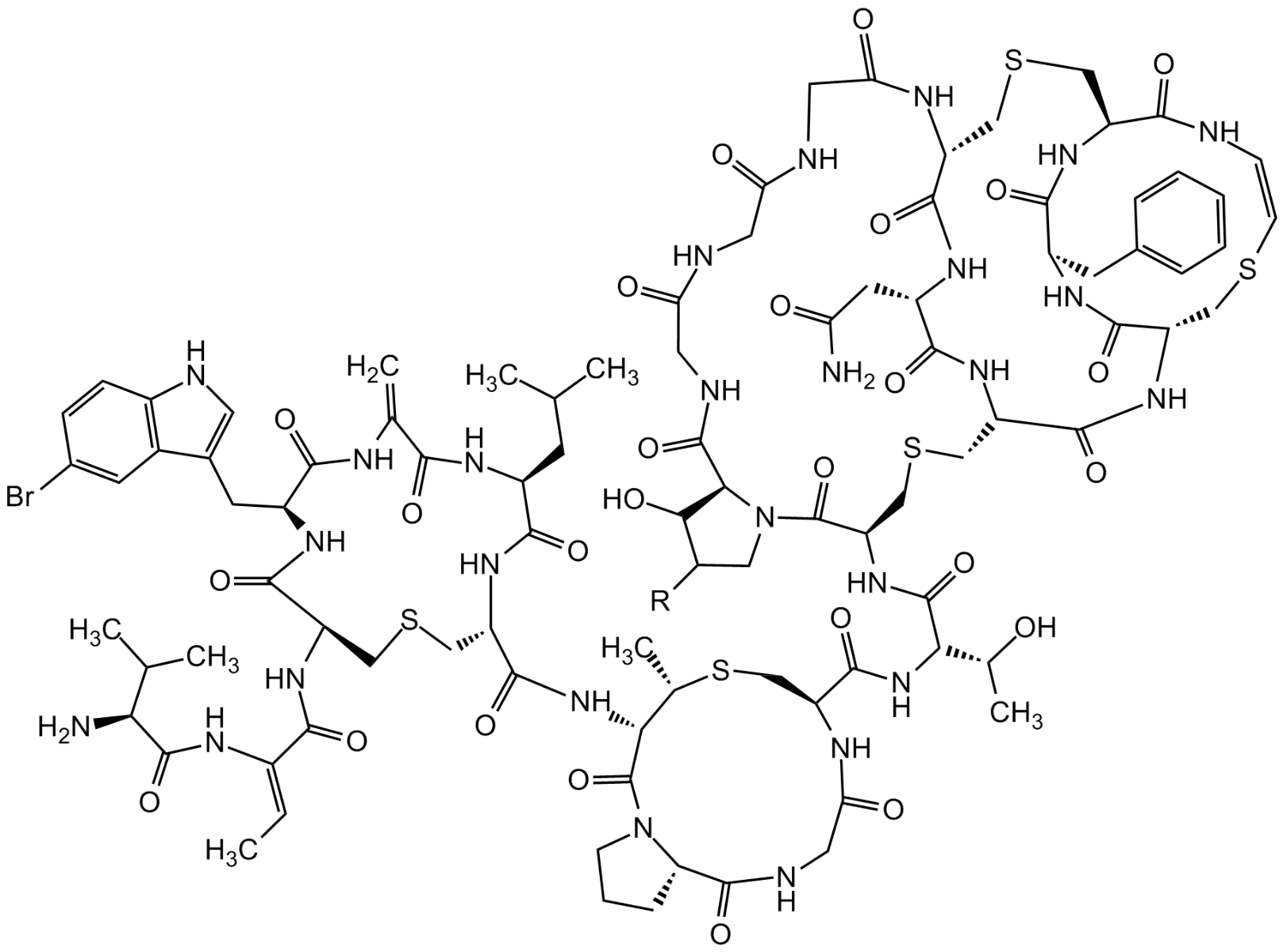
Chemical Structure
NAI-857 [1648733-25-5] [1648733-25-5]
AG-CN2-0311
CAS Number1648733-25-5
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>85%
Molecular Weight2170.4
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameNAI-857 [1648733-25-5] [1648733-25-5]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number1648733-25-5
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>85%
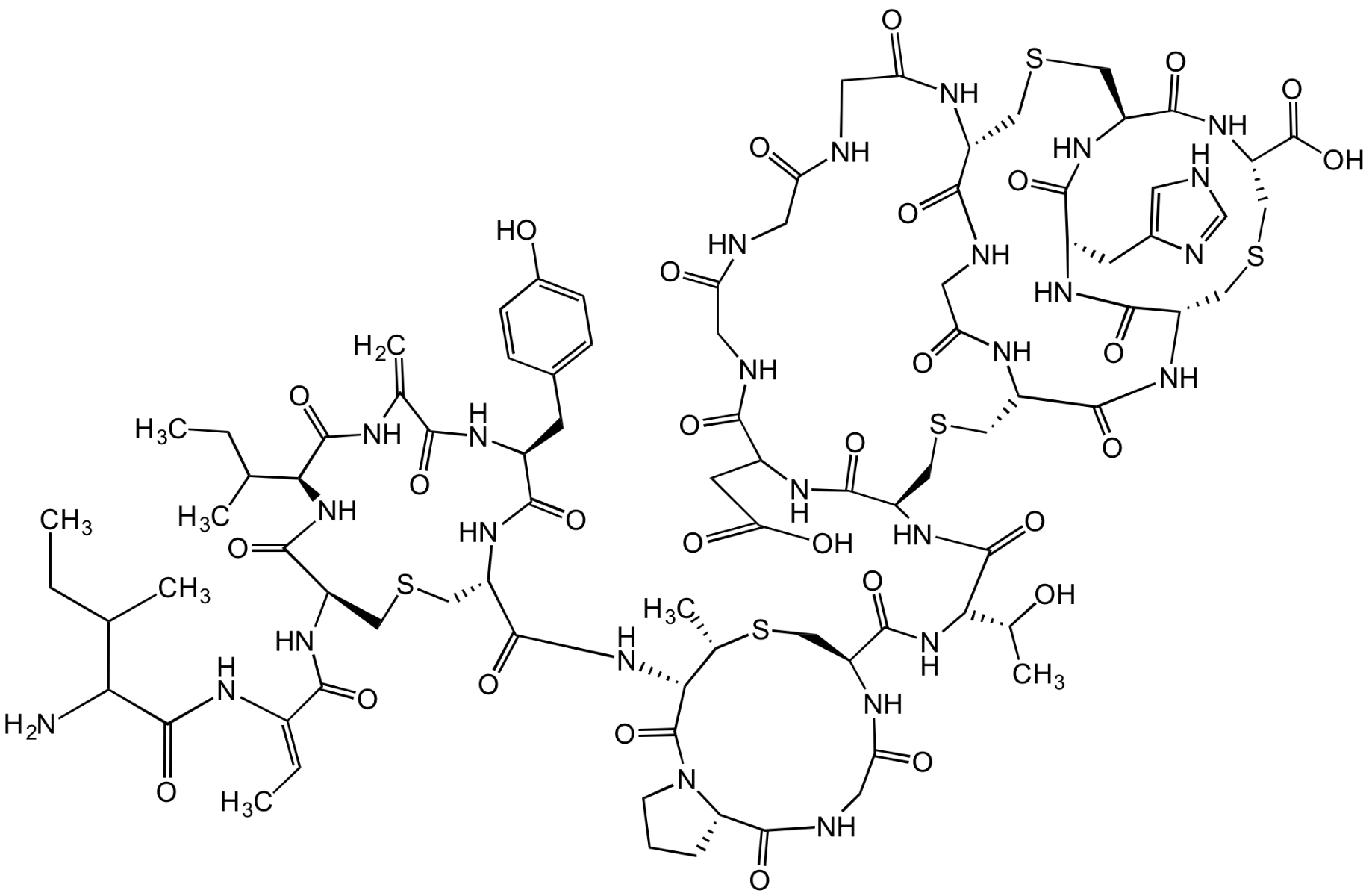
- Molecular FormulaC88H124N26O29S5
- Molecular Weight2170.4
- Scientific DescriptionAntibacterial class I lantibiotic. Inhibits cell wall synthesis and consequently bacterial growth by forming a complex with lipid intermediate II (Lipid II), a key intermediate in peptidoglycan biosynthesis. Interferes with late stages of cell wall biosynthesis leading to accumulation of the soluble peptidoglycan precursor UDP-N-acetylmuramic acid-pentapeptide (UDP-MurNAc-pentapeptide) in the cytoplasm less efficient than NAI-107 (AG-CN2-0307 https://adipogen.com/ag-cn2-0307-nai-107-microbisporicin.html ). Active against Streptococcus pyogenes and weak antibacterial activity against other tested Gram-positive pathogens. - Chemical. CAS: 1648732-25-5. Formula: C88H124N26O29S5. MW: 2170.4. Isolated from Strepomyces sp. Antibacterial class I lantibiotic. Inhibits cell wall synthesis and consequently bacterial growth by forming a complex with lipid intermediate II (Lipid II), a key intermediate in peptidoglycan biosynthesis. Interfers with late stages of cell wall biosynthesis leading to accumulation of the soluble peptidoglycan precursor UDP-N-acetylmuramic acid-pentapeptide (UDP-MurNAc-pentapeptide) in the cytoplasm less efficient than NAI-107. Active against Streptococcus pyogenes and weak antibacterial activity against other tested Gram-positive pathogens.
- SMILESO=C(NCC(NCC(NCC(N1)=O)=O)=O)C(CC(O)=O)NC([C@@H](CSC[C@@H](C(N[C@@H](CSC2)C(NC3CC4=CNC=N4)=O)=O)NC(CNC([C@H]1CSC[C@@H](C(N[C@@H]2C(O)=O)=O)NC3=O)=O)=O)NC([C@H](NC([C@@H]5CS[C@@H](C)[C@H](C(N6[C@H](C(NCC(N5)=O)=O)CCC6)=O)NC([C@H]7NC([C@H](CC8=CC=C(O)C=C8)NC(C(NC([C@H](C(CC)C)NC([C@H](NC(/C(NC(C(N)C(C)CC)=O)=C/C)=O)CSC7)=O)=O)=C)=O)=O)=O)=O)[C@H](O)C)=O)=O
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200