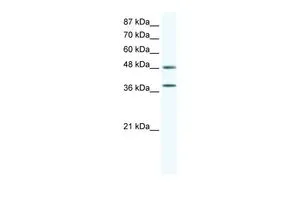
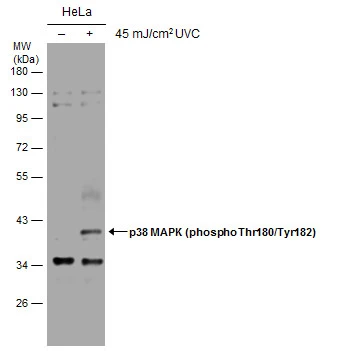
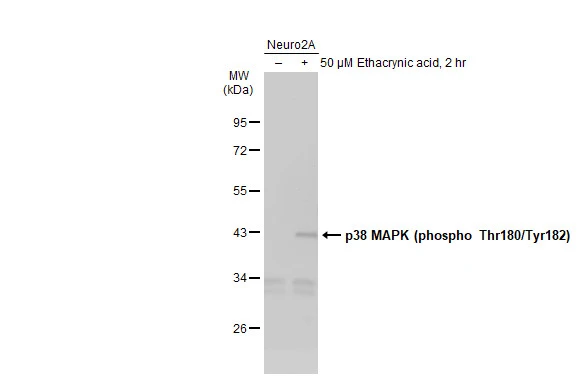
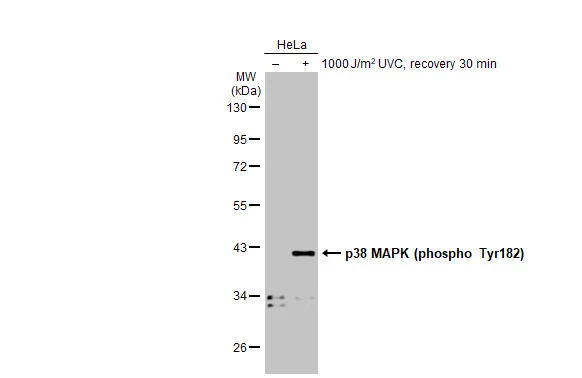
p38 MAPK (phospho Thr180/Tyr182) antibody
GTX24822
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetMAPK14
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product Namep38 MAPK (phospho Thr180/Tyr182) antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:2000. ICC/IF: 1 microg/ml. IHC-P: 1:10-1:100. FACS: 3-5 microg/106 cells. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID1432
- Target nameMAPK14
- Target descriptionmitogen-activated protein kinase 14
- Target synonymsCSBP, CSBP1, CSBP2, CSPB1, EXIP, Mxi2, PRKM14, PRKM15, RK, SAPK2A, p38, p38ALPHA, mitogen-activated protein kinase 14, CSAID-binding protein, MAP kinase 14, MAP kinase Mxi2, MAP kinase p38 alpha, MAX-interacting protein 2, cytokine suppressive anti-inflammatory drug binding protein, mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 alpha, p38 MAP kinase, p38 mitogen activated protein kinase, p38alpha Exip, stress-activated protein kinase 2A
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ16539
- Protein NameMitogen-activated protein kinase 14
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene is a member of the MAP kinase family. MAP kinases act as an integration point for multiple biochemical signals, and are involved in a wide variety of cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, transcription regulation and development. This kinase is activated by various environmental stresses and proinflammatory cytokines. The activation requires its phosphorylation by MAP kinase kinases (MKKs), or its autophosphorylation triggered by the interaction of MAP3K7IP1/TAB1 protein with this kinase. The substrates of this kinase include transcription regulator ATF2, MEF2C, and MAX, cell cycle regulator CDC25B, and tumor suppressor p53, which suggest the roles of this kinase in stress related transcription and cell cycle regulation, as well as in genotoxic stress response. Four alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene encoding distinct isoforms have been reported. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Sun Y, Chen X, Xie Y, et al. TRPM7 promotes lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory dysfunction in renal tubular epithelial cells. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2022,10(7):e641. doi: 10.1002/iid3.641Read this paper
- Ho KH, Lee YT, Chen PH, et al. Guanabenz Sensitizes Glioblastoma Cells to Sunitinib by Inhibiting GADD34-Mediated Autophagic Signaling. Neurotherapeutics. 2021,18(2):1371-1392. doi: 10.1007/s13311-020-00961-zRead this paper
- Huang C, Lu HF, Chen YH, et al. Curcumin, demethoxycurcumin, and bisdemethoxycurcumin induced caspase-dependent and -independent apoptosis via Smad or Akt signaling pathways in HOS cells. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2020,20(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s12906-020-2857-1Read this paper
- Yang CH, Yip HK, Chen HF, et al. Long-term Therapeutic Effects of Extracorporeal Shock Wave-Assisted Melatonin Therapy on Mononeuropathic Pain in Rats. Neurochem Res. 2019,44(4):796-810. doi: 10.1007/s11064-018-02713-0Read this paper
- Ghasemi A, Hashemy SI, Aghaei M, et al. Leptin induces matrix metalloproteinase 7 expression to promote ovarian cancer cell invasion by activating ERK and JNK pathways. J Cell Biochem. 2018,119(2):2333-2344. doi: 10.1002/jcb.26396Read this paper
- Chen CC, Lin MW, Liang CJ, et al. The Anti-Inflammatory Effects and Mechanisms of Eupafolin in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammatory Responses in RAW264.7 Macrophages. PLoS One. 2016,11(7):e0158662. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0158662Read this paper
- Lee YR, Wu WC, Ji WT, et al. Reversine suppresses oral squamous cell carcinoma via cell cycle arrest and concomitantly apoptosis and autophagy. J Biomed Sci. 2012,19(1):9. doi: 10.1186/1423-0127-19-9Read this paper


![ELISA analysis of antigen using GTX60771 p38 MAPK antibody [8G4D11].
Black : Control antigen 100ng
Purple : Antigen 10ng
Blue : Antigen 50ng
Red : Antigen 100ng](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX60771/GTX60771_20170912_ELISA_w_23061123_607.webp)
![Various whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with p38 MAPK antibody [HL1006] (GTX635797) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX635797/GTX635797_44116_20210910_WB_M_w_23061202_588.webp)