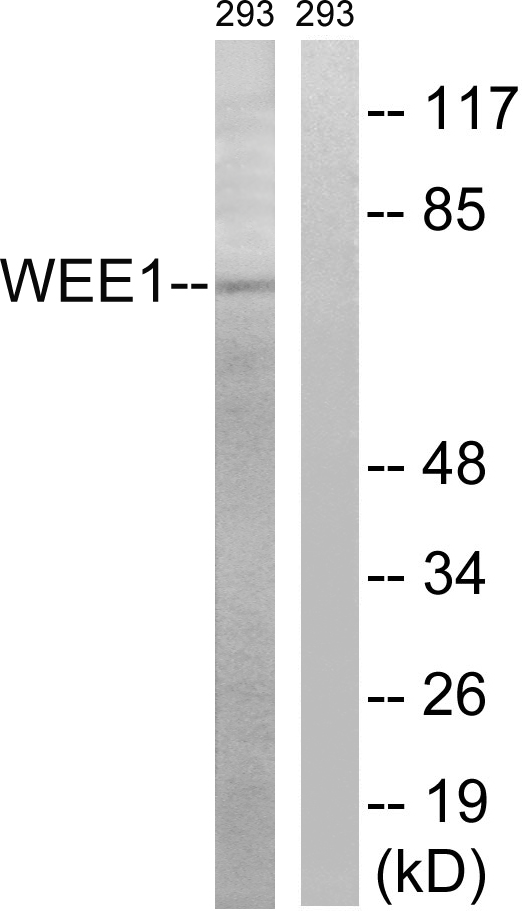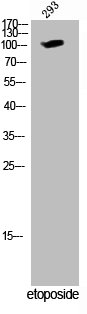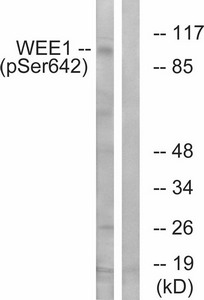
Western blot analysis of extracts from 293 cells treated with etoposide using WEE1 (Phospho-Ser642) Antibody.The lane on the right is treated with the antigen-specific peptide.
Phospho-WEE1 (Ser642) Antibody
CSB-PA062918
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetWEE1
Overview
- SupplierCusabio
- Product NamePhospho-WEE1 (Ser642) Antibody
- Delivery Days Customer20
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID7465
- Target nameWEE1
- Target descriptionWEE1 G2 checkpoint kinase
- Target synonymsWEE1A, WEE1hu, wee1-like protein kinase, WEE1 homolog, WEE1+ homolog, protein kinase, wee1A kinase
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP30291
- Protein NameWee1-like protein kinase
- Scientific DescriptionActs as a negative regulator of entry into mitosis (G2 to M transition) by protecting the nucleus from cytoplasmically activated cyclin B1-complexed CDK1 before the onset of mitosis by mediating phosphorylation of CDK1 on Tyr-15. Specifically phosphorylates and inactivates cyclin B1-complexed CDK1 reaching a maximum during G2 phase and a minimum as cells enter M phase. Phosphorylation of cyclin B1-CDK1 occurs exclusively on Tyr-15 and phosphorylation of monomeric CDK1 does not occur. Its activity increases during S and G2 phases and decreases at M phase when it is hyperphosphorylated. A correlated decrease in protein level occurs at M/G1 phase, probably due to its degradation. Watanabe N., EMBO J. 14:1878-1891(1995). Cichutek A., Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 93:277-283(2001). Igarashi M., Nature 353:80-83(1991)
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C
- UNSPSC41116161