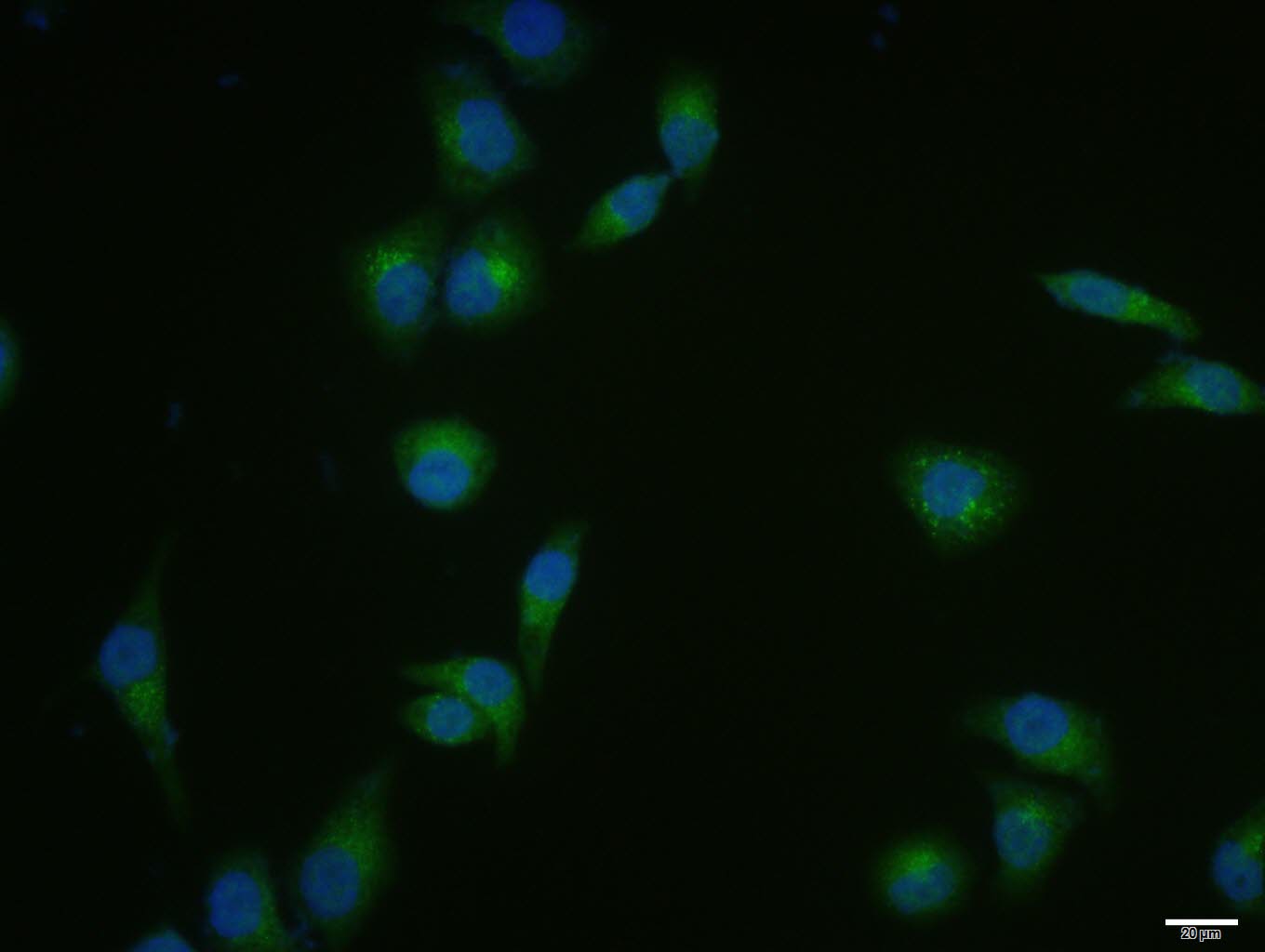
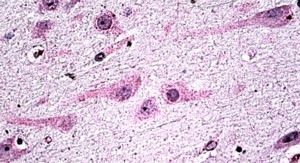
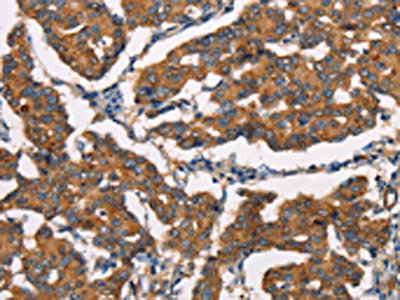
Rabbit anti Human DICER1
X2756P
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetDICER1
Overview
- SupplierNordic-MUbio
- Product NameRabbit anti Human DICER1
- Delivery Days Customer7
- Application Supplier NoteAntibody can be used for immunohistochemical staining (1-5 microg/ml). Optimal concentration should be evaluated by serial dilutions.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- Applications SupplierEnzyme Immunoassay;Western Blotting;Immunohistochemistry;Enzyme Immunoassay;Western Blotting
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Gene ID23405
- Target nameDICER1
- Target descriptiondicer 1, ribonuclease III
- Target synonymsDCR1, Dicer, Dicer1e, GLOW, HERNA, K12H4.8-LIKE, MNG1, RMSE2, aviD, endoribonuclease Dicer, Dicer1, Dcr-1 homolog, dicer 1, double-stranded RNA-specific endoribonuclease, dicer 1, ribonuclease type III, helicase MOI, helicase with RNAse motif
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ9UPY3
- Protein NameEndoribonuclease Dicer
- Scientific DescriptionEndoribonuclease Dicer; DICER; HERNA
- Shelf life instructionSee expiration date on vial
- ReactivityHuman
- Reactivity SupplierHuman
- Reactivity Supplier NoteSynthetic peptide derived from human DICER1 protein.
- UNSPSC12352203