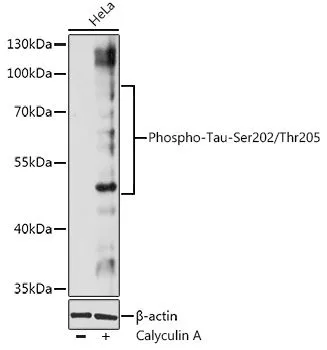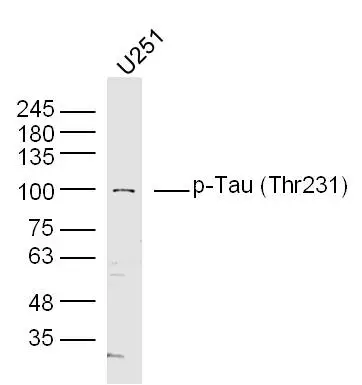
WB analysis of U251 cell lysate using GTX01563 Tau (phospho Thr231) antibody. Dilution : 1:300
Tau (phospho Thr231) antibody
GTX01563
ApplicationsWestern Blot
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetMAPT
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameTau (phospho Thr231) antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:300-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID4137
- Target nameMAPT
- Target descriptionmicrotubule associated protein tau
- Target synonymsDDPAC, FTD1, FTDP-17, MAPTL, MSTD, MTBT1, MTBT2, PPND, PPP1R103, TAU, Tau-PHF6, tau-40, microtubule-associated protein tau, G protein beta1/gamma2 subunit-interacting factor 1, PHF-tau, Tau-derived paired helical filament hexapeptide, neurofibrillary tangle protein, paired helical filament-tau, protein phosphatase 1, regulatory subunit 103
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP10636
- Protein NameMicrotubule-associated protein tau
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes the microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT) whose transcript undergoes complex, regulated alternative splicing, giving rise to several mRNA species. MAPT transcripts are differentially expressed in the nervous system, depending on stage of neuronal maturation and neuron type. MAPT gene mutations have been associated with several neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimers disease, Picks disease, frontotemporal dementia, cortico-basal degeneration and progressive supranuclear palsy. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
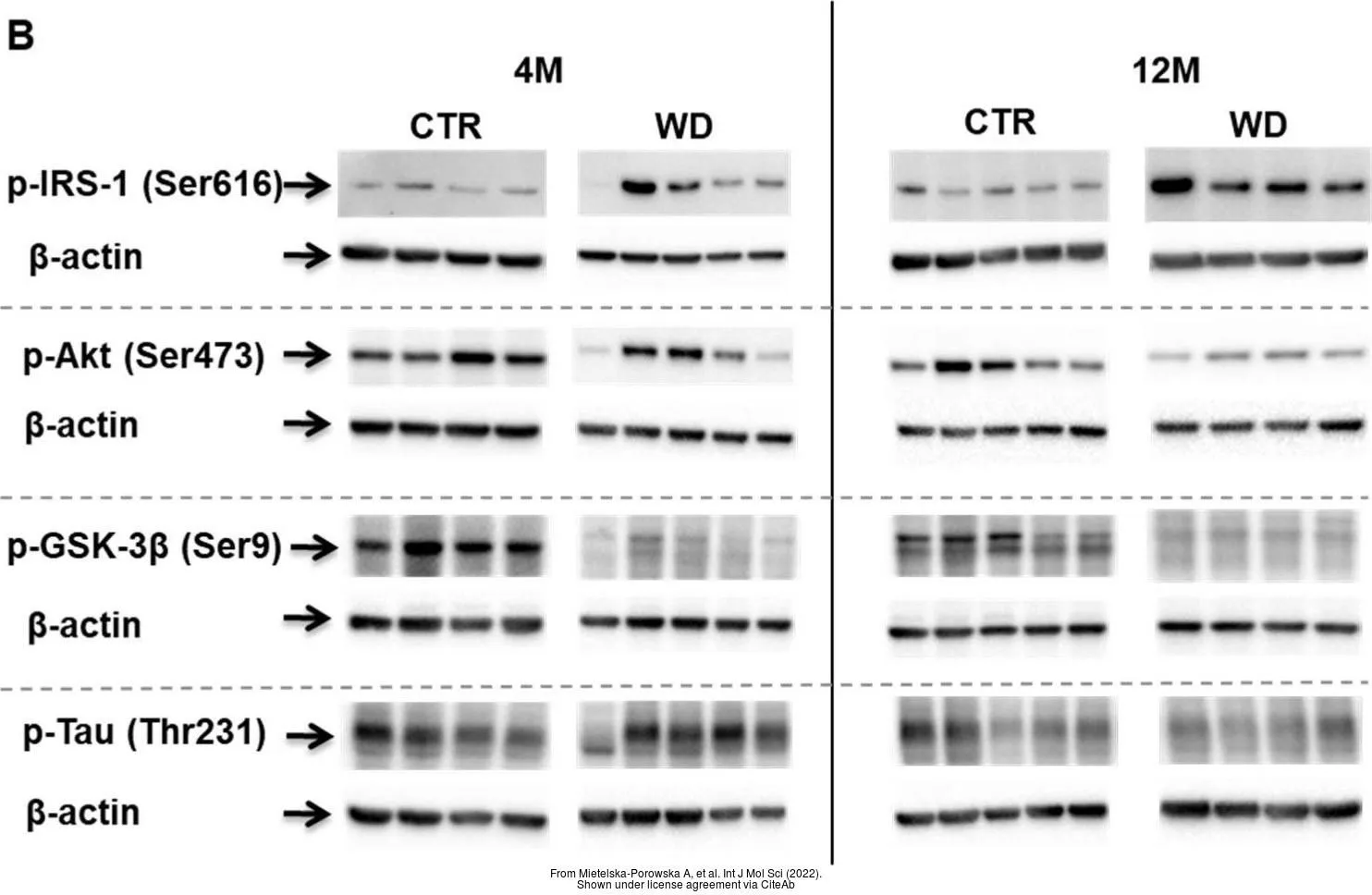
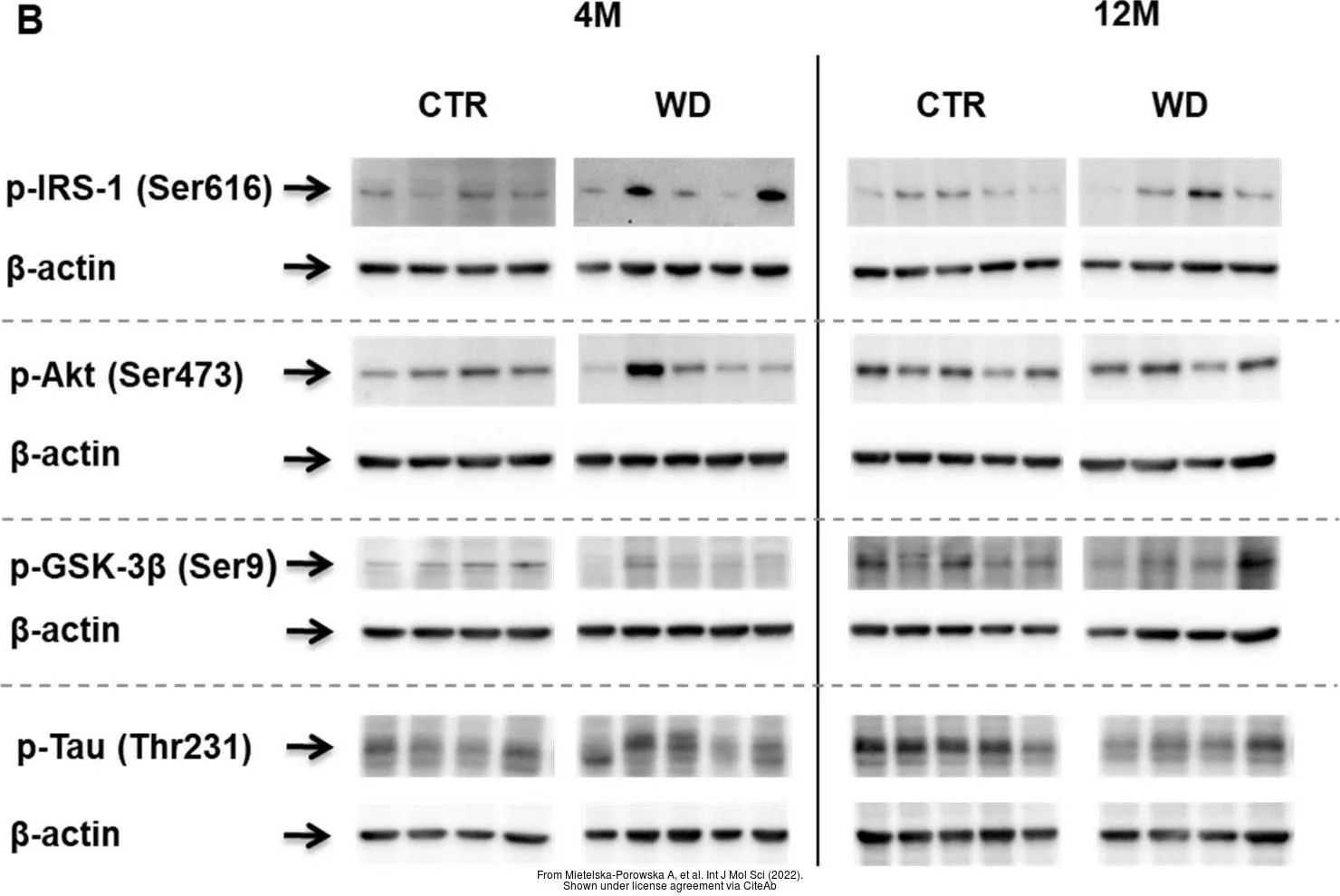
- Mietelska-Porowska A, Domańska J, Want A, et al. Induction of Brain Insulin Resistance and Alzheimer's Molecular Changes by Western Diet. Int J Mol Sci. 2022,23(9). doi: 10.3390/ijms23094744Read this paper
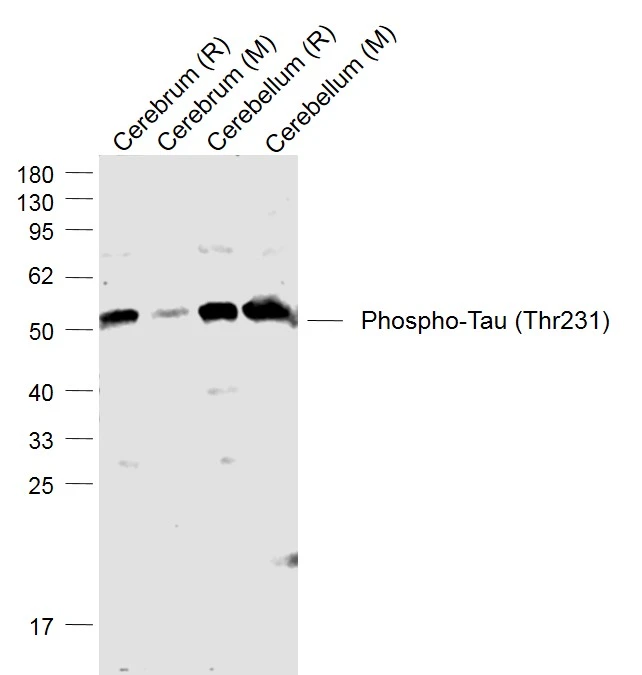
- Shen Y, Hu H, Fan C, et al. Sensorineural hearing loss may lead to dementia-related pathological changes in hippocampal neurons. Neurobiol Dis. 2021,156:105408. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2021.105408Read this paper




![IHC-P analysis of rat brain tissue section using GTX03204 Tau (phospho Ser396) antibody [GT1292]. Dilution : 1:100](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX03204/GTX03204_20210615_IHC-P_89_w_23053123_804.webp)