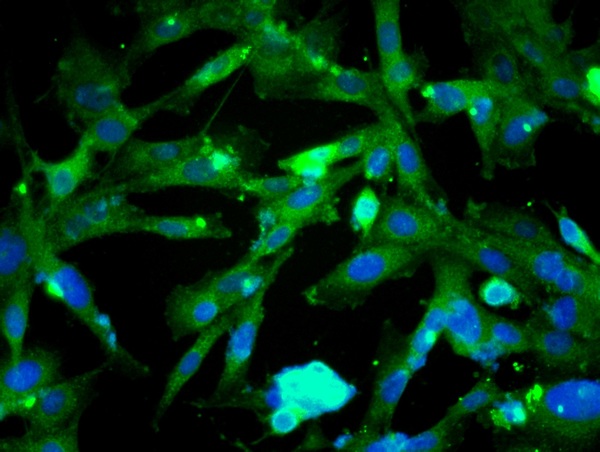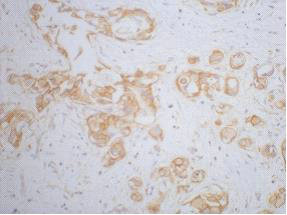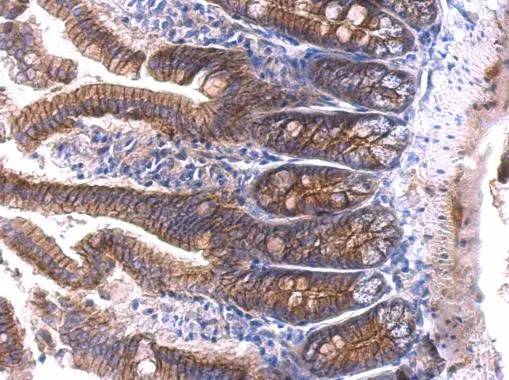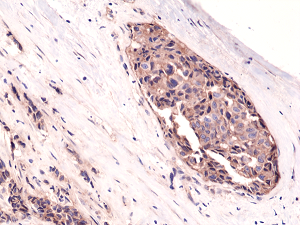
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human breast cancer tissue sections using Anti-beta-Catenin Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (Clone RM276) at a 1:1000 dilution.
anti-Beta-Catenin 1 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM276)
REV-31-1157-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetCTNNB1
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-Beta-Catenin 1 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM276)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM276
- Gene ID1499
- Target nameCTNNB1
- Target descriptioncatenin beta 1
- Target synonymsCTNNB, EVR7, MRD19, NEDSDV, armadillo, catenin beta-1, catenin (cadherin-associated protein), beta 1, 88kDa
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP35222
- Protein NameCatenin beta-1
- Scientific Descriptionbeta-catenin, an adherens junction (AJ) protein, is a dual function protein, involved in regulation and coordination of cell-cell adhesion and gene transcription. AJs are necessary for the creation and maintenance of epithelial cell layers by regulating cell growth and adhesion between cells. Beta-catenin interacts with the cytoplasmic domain of E-cadherin and links E-cadherin to alpha-catenin, which in turn mediates anchorage of the E-cadherin complex to the cortical actin cytoskeleton. Beta-catenin also interacts with several signaling pathways that include tyrosine kinases, phosphatases and Wnt/Wingless. The interplay between beta-catenin, cytoskeletal complexes and signaling pathways may regulate morphogenesis. A pathological role of beta-catenin has been identified in pilomatrixoma (PTR), medulloblastoma (MDB), colorectal cancer (CRC), ovarian cancer and tumor development. In the nucleus, beta-catenin serves to co activate a family of Lef/Tcf transcription factors that stimulate transcription of target genes including those encoding cyclin D and c-myc that promote cell proliferation. The influence on cell proliferation is the molecular basis for the role of beta-catenin in tumorgenesis, specifically, solid tumors of the breast, colon, liver, lung, gastric, prostate and skin. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human Beta-Catenin (Catenin beta-1). This antibody may also react to mouse or rat Beta-Catenin, as predicted by immunogen homology. Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. beta-catenin, an adherens junction (AJ) protein, is a dual function protein, involved in regulation and coordination of cell-cell adhesion and gene transcription. AJs are necessary for the creation and maintenance of epithelial cell layers by regulating cell growth and adhesion between cells. Beta-catenin interacts with the cytoplasmic domain of E-cadherin and links E-cadherin to alpha-catenin, which in turn mediates anchorage of the E-cadherin complex to the cortical actin cytoskeleton. Beta-catenin also interacts with several signaling pathways that include tyrosine kinases, phosphatases and Wnt/Wingless. The interplay between beta-catenin, cytoskeletal complexes and signaling pathways may regulate morphogenesis. A pathological role of beta-catenin has been identified in pilomatrixoma (PTR), medulloblastoma (MDB), colorectal cancer (CRC), ovarian cancer and tumor development. In the nucleus, beta-catenin serves to co activate a family of Lef/Tcf transcription factors that stimulate transcription of target genes including those encoding cyclin D and c-myc that promote cell proliferation. The influence on cell proliferation is the molecular basis for the role of beta-catenin in tumorgenesis, specifically, solid tumors of the breast, colon, liver, lung, gastric, prostate and skin.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161