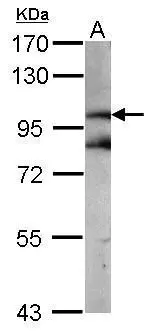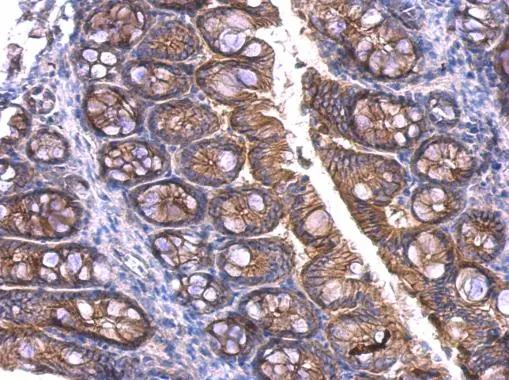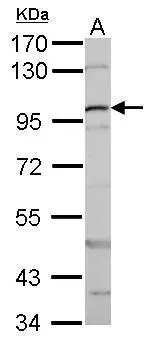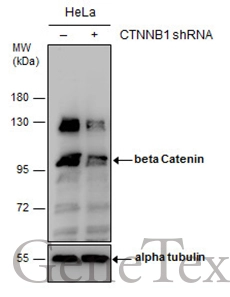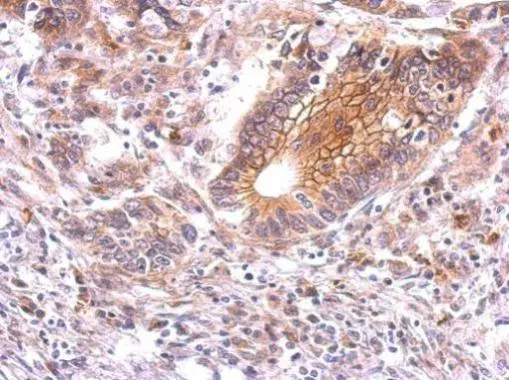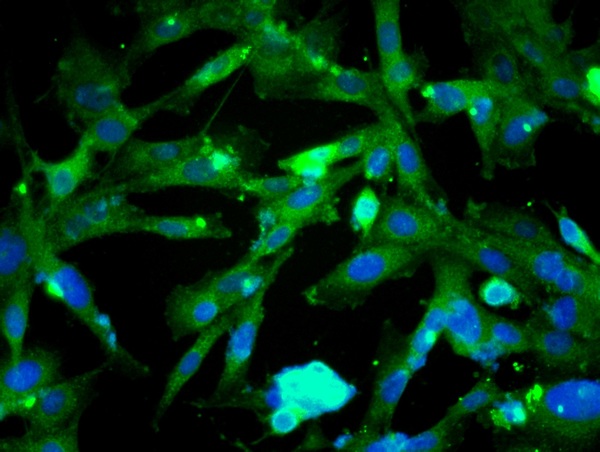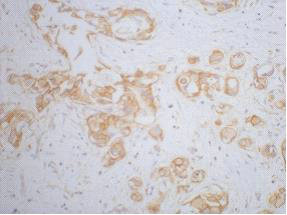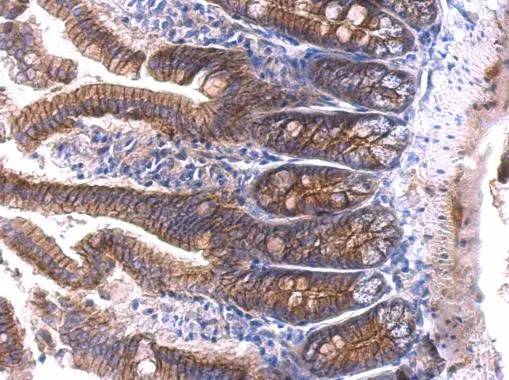
beta Catenin antibody detects beta Catenin protein at membrane on mouse intestine by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse intestine. beta Catenin antibody (GTX101254) dilution: 1:500.
Antigen Retrieval: Trilogy? (EDTA based, pH 8.0) buffer, 15min
beta Catenin antibody
GTX101254
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetCTNNB1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product Namebeta Catenin antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1.01 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID1499
- Target nameCTNNB1
- Target descriptioncatenin beta 1
- Target synonymsCTNNB, EVR7, MRD19, NEDSDV, armadillo, catenin beta-1, catenin (cadherin-associated protein), beta 1, 88kDa
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP35222
- Protein NameCatenin beta-1
- Scientific DescriptionBeta-catenin is an adherens junction protein. Adherens junctions (AJs; also called the zonula adherens) are critical for the establishment and maintenance of epithelial layers, such as those lining organ surfaces. AJs mediate adhesion between cells, communicate a signal that neighboring cells are present, and anchor the actin cytoskeleton. In serving these roles, AJs regulate normal cell growth and behavior. At several stages of embryogenesis, wound healing, and tumor cell metastasis, cells form and leave epithelia. This process, which involves the disruption and reestablishment of epithelial cell-cell contacts, may be regulated by the disassembly and assembly of AJs. AJs may also function in the transmission of the contact inhibition signal, which instructs cells to stop dividing once an epithelial sheet is complete.[supplied by OMIM]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161