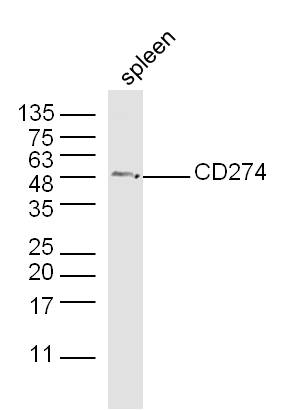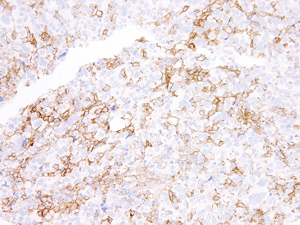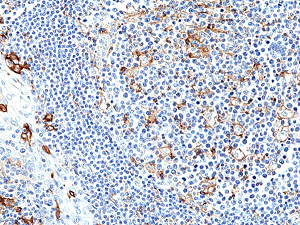
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human tonsil tissue section using anti-PD-L1 rabbit monoclonal antibody (Clone RM320) at a 1:250 dilution.
anti-PD-L1 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM320)
REV-31-1205-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetCd274
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-PD-L1 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM320)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM320
- Gene ID60533
- Target nameCd274
- Target descriptionCD274 antigen
- Target synonymsA530045L16Rik, B7h1, Pdcd1l1, Pdcd1lg1, Pdl1, programmed cell death 1 ligand 1, B7 homolog 1, PDCD1 ligand 1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ9EP73
- Protein NameProgrammed cell death 1 ligand 1
- Scientific DescriptionProgrammed death ligand 1 (PD-L1, B7-H1 or CD274) is a member of the growing B7 family of immune proteins that provide signals for both stimulating and inhibiting T cell activation. PD-L1 is a transmembrane protein involved in suppressing the immune system and rendering tumor cells resistant to CD8+ T cell-mediated lysis through binding of the Programmed Death-1 (PD-1) receptor. PD-L1 is widely expressed in several organs such as heart, skeletal muscle, placenta and lung, and in lower amounts in thymus, spleen, kidney and liver. Overexpression of PD-L1 may allow cancer cells to evade the actions of the host immune system. In renal cell carcinoma, upregulation of PD-L1 has been linked to increased tumor aggressiveness and risk of death, and, in ovarian cancer, higher expression of this protein has lead to significantly poorer prognosis. PD-L1 has also been linked to systemic lupus erythematosus and cutaneous melanoma. When considered in adjunct with CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte density, expression levels of PD-L1 may be a useful predictor of multiple cancer types, including stage III non-small cell lung cancer, hormone receptor negative breast cancer and sentinel lymph node melanoma. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human PD-L1 (CD274) (B7-H1). Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1, B7-H1 or CD274) is a member of the growing B7 family of immune proteins that provide signals for both stimulating and inhibiting T cell activation. PD-L1 is a transmembrane protein involved in suppressing the immune system and rendering tumor cells resistant to CD8+ T cell-mediated lysis through binding of the Programmed Death-1 (PD-1) receptor. PD-L1 is widely expressed in several organs such as heart, skeletal muscle, placenta and lung, and in lower amounts in thymus, spleen, kidney and liver. Overexpression of PD-L1 may allow cancer cells to evade the actions of the host immune system. In renal cell carcinoma, upregulation of PD-L1 has been linked to increased tumor aggressiveness and risk of death, and, in ovarian cancer, higher expression of this protein has lead to significantly poorer prognosis. PD-L1 has also been linked to systemic lupus erythematosus and cutaneous melanoma. When considered in adjunct with CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte density, expression levels of PD-L1 may be a useful predictor of multiple cancer types, including stage III non-small cell lung cancer, hormone receptor negative breast cancer and sentinel lymph node melanoma.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161



![PD-L1 antibody [HL2293] detects PD-L1 protein at cell membrane and nucleus by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse placenta. PD-L1 stained by PD-L1 antibody [HL2293] (GTX638348) diluted at 1:1000. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX638348/GTX638348_T-44984_20230714_IHC-P_M_23080901_176.webp)