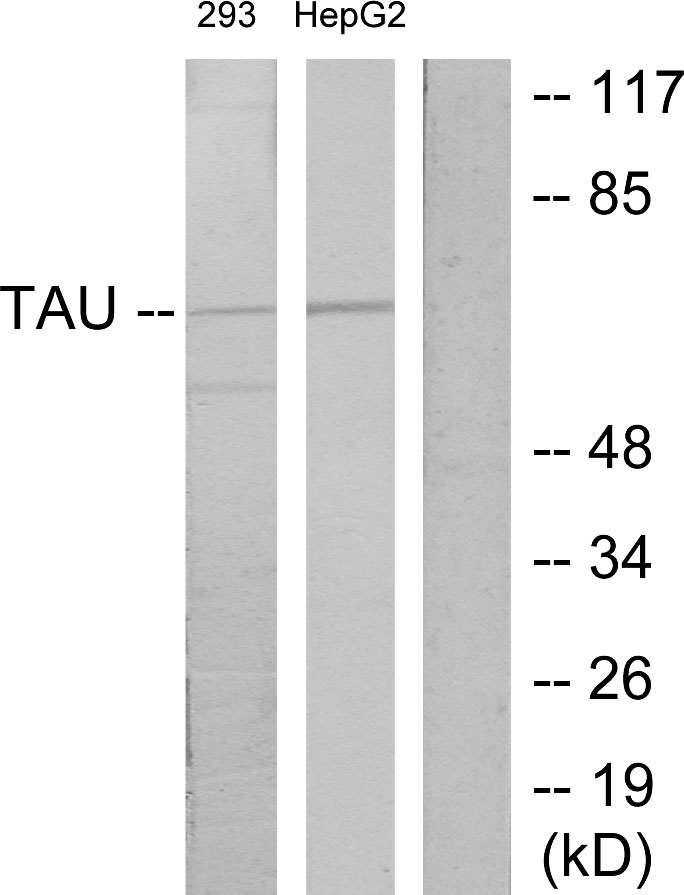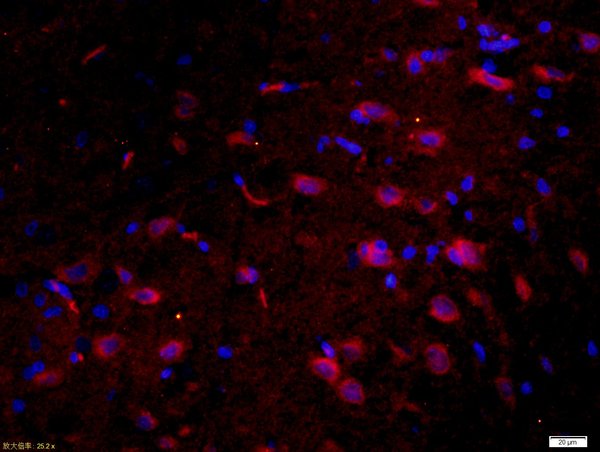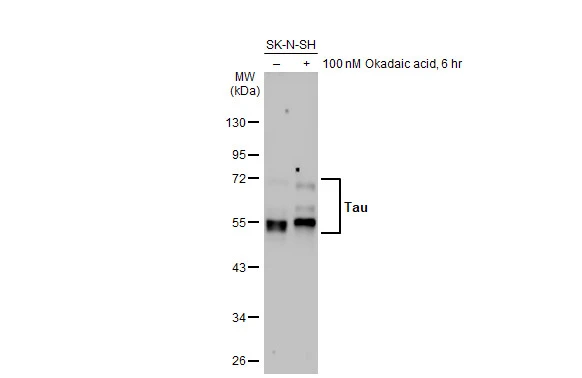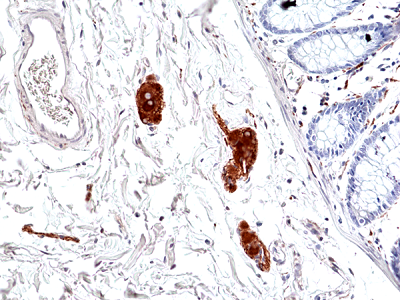
anti-Phospho-Tau (Ser396), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM461)
REV-31-1353-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetMAPT
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-Phospho-Tau (Ser396), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM461)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM461
- Gene ID4137
- Target nameMAPT
- Target descriptionmicrotubule associated protein tau
- Target synonymsDDPAC, FTD1, FTDP-17, MAPTL, MSTD, MTBT1, MTBT2, PPND, PPP1R103, TAU, Tau-PHF6, tau-40, microtubule-associated protein tau, G protein beta1/gamma2 subunit-interacting factor 1, PHF-tau, Tau-derived paired helical filament hexapeptide, neurofibrillary tangle protein, paired helical filament-tau, protein phosphatase 1, regulatory subunit 103
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP10636
- Protein NameMicrotubule-associated protein tau
- Scientific DescriptionRecombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to Tau only when phosphorylated at Ser396. There is no cross-reactivity to Tau that is not phosphorylated. This antibody reacts to human, mouse or rat Phospho-Tau (Ser396). Applications: IHC, WB. Clone: RM461. Isotype: Rabbit IgG. Formulation: Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Tau is a neuronal microtubule-associated protein found predominantly on axons. The function of Tau is to promote tubulin polymerization and stabilize microtubules. The C-terminus binds axonal microtubules while the N- terminus binds neural plasma membrane components, suggesting that tau functions as a linker protein between both. Axonal polarity is predetermined by TAU/MAPT localization (in the neuronal cell) in the domain of the cell body defined by the centrosome. The short isoforms allow plasticity of the cytoskeleton while the longer isoforms may preferentially play a role in its stabilization. In its hyper-phosphorylated form, Tau is the major component of paired helical filaments (PHF), the building block of neurofibrillary lesions in Alzheimers diseases (AD) brain. Hyper-phosphorylation impairs the microtubule binding function of Tau, resulting in the destabilization of microtubules in AD brains, ultimately leading to the degeneration of the affected neurons. Numerous serine/threonine kinases phosphorylate Tau, including GSK-3beta, protein kinase A (PKA), cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (cdk5) and casein kinase II. Hyper-phosphorylated Tau is found in neurofibrillary lesions in a range and other central nervous system disorders such as Picks disease, frontotemporal dementia, cortico-basal degeneration and progressive supranuclear palsy. - Tau is a neuronal microtubule-associated protein found predominantly on axons. The function of Tau is to promote tubulin polymerization and stabilize microtubules. The C-terminus binds axonal microtubules while the N- terminus binds neural plasma membrane components, suggesting that tau functions as a linker protein between both. Axonal polarity is predetermined by TAU/MAPT localization (in the neuronal cell) in the domain of the cell body defined by the centrosome. The short isoforms allow plasticity of the cytoskeleton while the longer isoforms may preferentially play a role in its stabilization. In its hyper-phosphorylated form, Tau is the major component of paired helical filaments (PHF), the building block of neurofibrillary lesions in Alzheimers diseases (AD) brain. Hyper-phosphorylation impairs the microtubule binding function of Tau, resulting in the destabilization of microtubules in AD brains, ultimately leading to the degeneration of the affected neurons. Numerous serine/threonine kinases phosphorylate Tau, including GSK-3beta, protein kinase A (PKA), cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (cdk5) and casein kinase II. Hyper-phosphorylated Tau is found in neurofibrillary lesions in a range and other central nervous system disorders such as Picks disease, frontotemporal dementia, cortico-basal degeneration and progressive supranuclear palsy.
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161