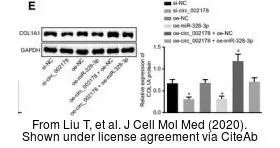
![COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term detects COL1A1 protein at vesicle by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: SK-N-SH cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: COL1A1 stained by COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX112731) diluted at 1:500. Red: alpha Tubulin, a cytoskeleton marker, stained by alpha Tubulin antibody [GT114] (GTX628802) diluted at 1:1000. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920). COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term detects COL1A1 protein at vesicle by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: SK-N-SH cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: COL1A1 stained by COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX112731) diluted at 1:500. Red: alpha Tubulin, a cytoskeleton marker, stained by alpha Tubulin antibody [GT114] (GTX628802) diluted at 1:1000. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920).](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX112731/GTX112731_44629_20221007_ICC_IF_22112723_376.webp)
COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term detects COL1A1 protein at vesicle by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: SK-N-SH cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: COL1A1 stained by COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX112731) diluted at 1:500. Red: alpha Tubulin, a cytoskeleton marker, stained by alpha Tubulin antibody [GT114] (GTX628802) diluted at 1:1000. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920).
COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term
GTX112731
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityFish, Human, Mouse, Rat
TargetCOL1A1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameCOL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. ICC/IF: 1:100-1:1000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. IP: 1:100-1:500. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.09 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID1277
- Target nameCOL1A1
- Target descriptioncollagen type I alpha 1 chain
- Target synonymsCAFYD, EDSARTH1, EDSC, OI1, OI2, OI3, OI4, collagen alpha-1(I) chain, alpha-1 type I collagen, alpha1(I) procollagen, collagen Col1-ColIII-1, collagen Col1-ColIII-2, collagen alpha 1 chain type I, collagen alpha-1(I) chain preproprotein, collagen of skin, tendon and bone, alpha-1 chain, collagen, type I, alpha 1, pro-alpha-1 collagen type 1, type I proalpha 1, type I procollagen alpha 1 chain
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP02452
- Protein NameCollagen alpha-1(I) chain
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes the pro-alpha1 chains of type I collagen whose triple helix comprises two alpha1 chains and one alpha2 chain. Type I is a fibril-forming collagen found in most connective tissues and is abundant in bone, cornea, dermis and tendon. Mutations in this gene are associated with osteogenesis imperfecta types I-IV, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VIIA, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome Classical type, Caffey Disease and idiopathic osteoporosis. Reciprocal translocations between chromosomes 17 and 22, where this gene and the gene for platelet-derived growth factor beta are located, are associated with a particular type of skin tumor called dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans, resulting from unregulated expression of the growth factor. Two transcripts, resulting from the use of alternate polyadenylation signals, have been identified for this gene. [provided by R. Dalgleish]
- ReactivityFish, Human, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161

![COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term detects COL1A1 protein at vesicle by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: NIH-3T3 cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: COL1A1 stained by COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX112731) diluted at 1:500. Red: alpha Tubulin, a cytoskeleton marker, stained by alpha Tubulin antibody [GT114] (GTX628802) diluted at 1:1000. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920). COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term detects COL1A1 protein at vesicle by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: NIH-3T3 cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: COL1A1 stained by COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX112731) diluted at 1:500. Red: alpha Tubulin, a cytoskeleton marker, stained by alpha Tubulin antibody [GT114] (GTX628802) diluted at 1:1000. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920).](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX112731/GTX112731_44713_20220916_ICC_IF_23041719_504.webp)
![Immunoprecipitation of COL1A1 protein from SK-N-AS whole cell extracts using 5 μg of COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX112731). Western blot analysis was performed using COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX112731) diluted at 1:500. EasyBlot anti-Rabbit IgG (GTX221666-01) was used as a secondary reagent. Immunoprecipitation of COL1A1 protein from SK-N-AS whole cell extracts using 5 μg of COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX112731). Western blot analysis was performed using COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX112731) diluted at 1:500. EasyBlot anti-Rabbit IgG (GTX221666-01) was used as a secondary reagent.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX112731/GTX112731_41794_20151120_IP_w_23060500_607.webp)
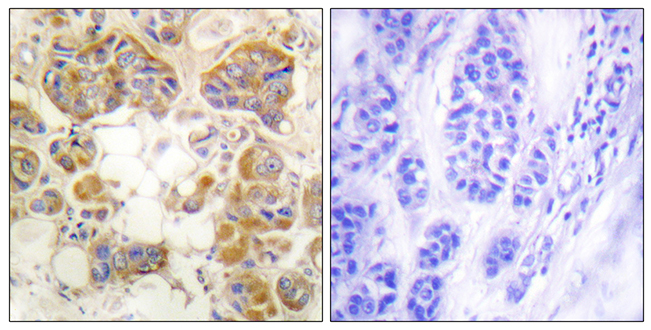
![COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term detects COL1A1 protein at secreted on human endometrial carcinoma by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded human endometrial carcinoma. COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX112731) diluted at 1:500.
Antigen Retrieval: Trilogy? (EDTA based, pH 8.0) buffer, 15min COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term detects COL1A1 protein at secreted on human endometrial carcinoma by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded human endometrial carcinoma. COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX112731) diluted at 1:500.
Antigen Retrieval: Trilogy? (EDTA based, pH 8.0) buffer, 15min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX112731/GTX112731_41794_20141212_IHC_3_w_23060500_574.webp)
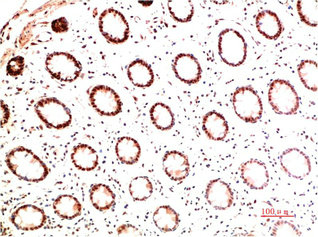
![COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term detects secreted COL1A1 protein in human colon cancer by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded human colon cancer. COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX112731) diluted at 1:500.
Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term detects secreted COL1A1 protein in human colon cancer by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded human colon cancer. COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX112731) diluted at 1:500.
Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX112731/GTX112731_42669_20161205_IHC-P_H_2_w_23060500_336.webp)
![COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term detects COL1A1 protein at secreted on human cervical carcinoma by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded human cervical carcinoma. COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX112731) dilution: 1:500.
Antigen Retrieval: Trilogy? (EDTA based, pH 8.0) buffer, 15min COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term detects COL1A1 protein at secreted on human cervical carcinoma by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded human cervical carcinoma. COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX112731) dilution: 1:500.
Antigen Retrieval: Trilogy? (EDTA based, pH 8.0) buffer, 15min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX112731/GTX112731_40380_IHC_w_23060500_596.webp)
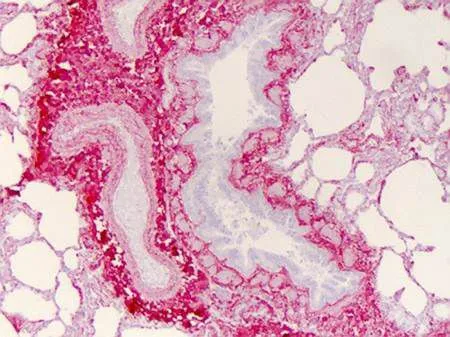
![COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term detects COL1A1 protein at secreted on human lung carcinoma by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded human lung carcinoma. COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX112731) diluted at 1:500.
Antigen Retrieval: Trilogy? (EDTA based, pH 8.0) buffer, 15min COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term detects COL1A1 protein at secreted on human lung carcinoma by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded human lung carcinoma. COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX112731) diluted at 1:500.
Antigen Retrieval: Trilogy? (EDTA based, pH 8.0) buffer, 15min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX112731/GTX112731_41794_20141212_IHC_2_w_23060500_759.webp)
![COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term detects secreted COL1A1 protein in human breast carcinoma by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded human breast carcinoma. COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX112731) diluted at 1:500.
Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term detects secreted COL1A1 protein in human breast carcinoma by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded human breast carcinoma. COL1A1 antibody [N1N2], N-term (GTX112731) diluted at 1:500.
Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX112731/GTX112731_42669_20161205_IHC-P_H_w_23060500_576.webp)