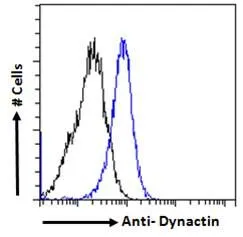
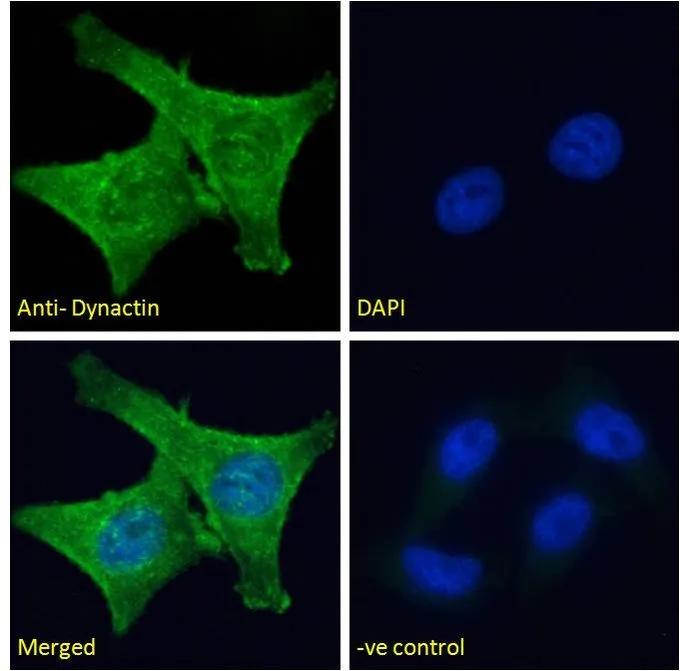
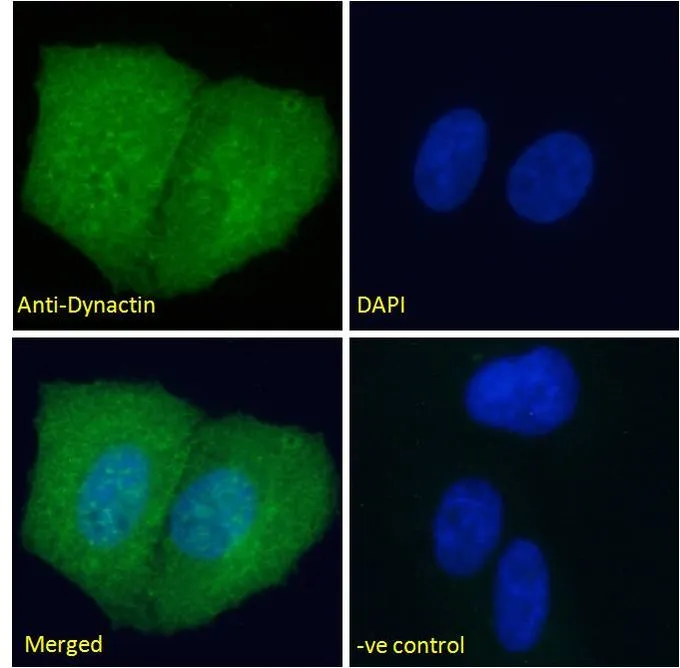
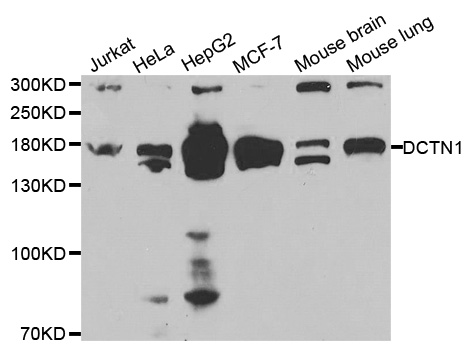
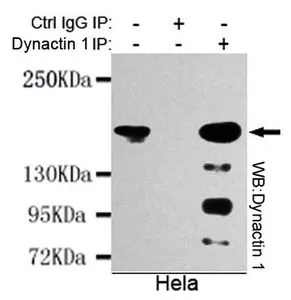
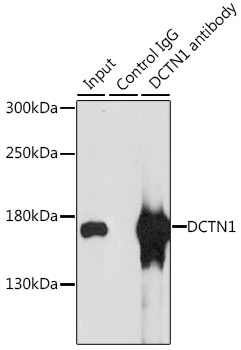
WB analysis of human cerebellum lysate using GTX11806 DCTN1 antibody, C-term. Dilution : 1microg/ml Loading : 35microg protein in RIPA buffer
DCTN1 antibody, C-term
GTX11806
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetDCTN1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameDCTN1 antibody, C-term
- Delivery Days Customer7
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1-2microg/ml. ICC/IF: 10microg/ml. IHC-P: 2-4microg/ml. FACS: 10microg/ml. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.50 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID1639
- Target nameDCTN1
- Target descriptiondynactin subunit 1
- Target synonymsDAP-150, DP-150, HMND14, P135, dynactin subunit 1, 150 kDa dynein-associated polypeptide, dynactin 1 (p150, glued homolog, Drosophila)
- HostGoat
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ14203
- Protein NameDynactin subunit 1
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes the largest subunit of dynactin, a macromolecular complex consisting of 10 subunits ranging in size from 22 to 150 kD. Dynactin binds to both microtubules and cytoplasmic dynein. Dynactin is involved in a diverse array of cellular functions, including ER-to-Golgi transport, the centripetal movement of lysosomes and endosomes, spindle formation, chromosome movement, nuclear positioning, and axonogenesis. This subunit interacts with dynein intermediate chain by its domains directly binding to dynein and binds to microtubules via a highly conserved glycine-rich cytoskeleton-associated protein (CAP-Gly) domain in its N-terminus. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. Mutations in this gene cause distal hereditary motor neuronopathy type VIIB (HMN7B) which is also known as distal spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy (dSBMA). [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2008]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203