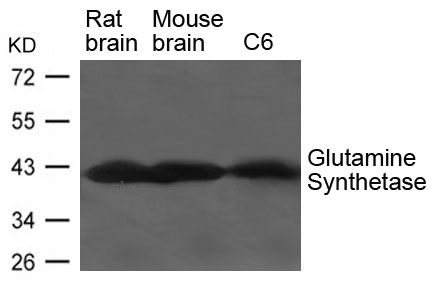
Mouse tissue extract (50 μg) was separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Glutamine synthetase antibody (GTX630657) diluted at 1:1000.
Glutamine synthetase antibody [GT7711]
GTX630657
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetGLUL
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameGlutamine synthetase antibody [GT7711]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. ICC/IF: 1:100-1:1000. IHC-Fr: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDGT7711
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID2752
- Target nameGLUL
- Target descriptionglutamate-ammonia ligase
- Target synonymsDEE116, GLNS, GS, PIG43, PIG59, glutamine synthetase, cell proliferation-inducing protein 59, glutamate decarboxylase, glutamine synthase, palmitoyltransferase GLUL, proliferation-inducing protein 43
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG1
- Protein IDP15104
- Protein NameGlutamine synthetase
- Scientific DescriptionGlutamine is a main source of energy and is involved in cell proliferation, inhibition of apoptosis, and cell signaling (Haberle et al., 2005 [PubMed 16267323]). Fetal glutamine requirements are very high and depend largely on active glutamine synthesis and the release of glutamine into the fetal circulation by the placenta. Glutamine synthetase (EC 6.3.1.2), also called glutamate-ammonia ligase (GLUL), is expressed throughout the body and plays an important role in controlling body pH and in removing ammonia from the circulation. The enzyme clears L-glutamate, the major neurotransmitter in the central nervous system, from neuronal synapses (see references in Clancy et al., 1996 [PubMed 8975719]).[supplied by OMIM]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203

![Glutamine synthetase antibody [GT7711] detects Glutamine synthetase protein by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Frozen sectioned adult mouse retina. Green: Glutamine synthetase protein stained by Glutamine synthetase antibody [GT7711] (GTX630657) diluted at 1:250. Red: PKC alpha protein stained by PKC alpha antibody [GT1876] (GTX130453) diluted at 1:250. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920). Glutamine synthetase antibody [GT7711] detects Glutamine synthetase protein by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Frozen sectioned adult mouse retina. Green: Glutamine synthetase protein stained by Glutamine synthetase antibody [GT7711] (GTX630657) diluted at 1:250. Red: PKC alpha protein stained by PKC alpha antibody [GT1876] (GTX130453) diluted at 1:250. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920).](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX630657/GTX630657_41617_20160824_IHC-Fr_w_23061202_803.webp)
![Various tissue extracts (50 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Glutamine synthetase antibody [GT7711] (GTX630657) diluted at 1:250000. The HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibody (GTX213111-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Various tissue extracts (50 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Glutamine synthetase antibody [GT7711] (GTX630657) diluted at 1:250000. The HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibody (GTX213111-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX630657/GTX630657_44510_20211231_WB_M_R_w_23061202_308.webp)
![Glutamine synthetase antibody [GT7711] detects Glutamine synthetase protein in glial cells by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: DIV10 rat E18 primary cortical neuron & glia cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: Glutamine synthetase stained by Glutamine synthetase antibody [GT7711] (GTX630657) diluted at 1:500. Red: Tau, a Tau marker, stained by Tau antibody (GTX130462) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920). Glutamine synthetase antibody [GT7711] detects Glutamine synthetase protein in glial cells by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: DIV10 rat E18 primary cortical neuron & glia cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: Glutamine synthetase stained by Glutamine synthetase antibody [GT7711] (GTX630657) diluted at 1:500. Red: Tau, a Tau marker, stained by Tau antibody (GTX130462) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920).](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX630657/GTX630657_44510_20220128_ICC_IF_w_23061202_442.webp)
![Non-transfected (–) and transfected (+) 293T whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Glutamine synthetase antibody [GT7711] (GTX630657) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibody (GTX213111-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Non-transfected (–) and transfected (+) 293T whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Glutamine synthetase antibody [GT7711] (GTX630657) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibody (GTX213111-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX630657/GTX630657_41617_20180928_WB_B_w_23061202_816.webp)
![Glutamine synthetase antibody [GT7711] detects Glutamine synthetase protein by western blot analysis. A. 30 μg 293T whole cell lysate/extract B. 30 μg A431 whole cell lysate/extract C. 30 μg HeLa whole cell lysate/extract D. 30 μg HepG2 whole cell lysate/extract 10 % SDS-PAGE Glutamine synthetase antibody [GT7711] (GTX630657) dilution: 1:1000 Glutamine synthetase antibody [GT7711] detects Glutamine synthetase protein by western blot analysis. A. 30 μg 293T whole cell lysate/extract B. 30 μg A431 whole cell lysate/extract C. 30 μg HeLa whole cell lysate/extract D. 30 μg HepG2 whole cell lysate/extract 10 % SDS-PAGE Glutamine synthetase antibody [GT7711] (GTX630657) dilution: 1:1000](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX630657/GTX630657_41617_WB_w_23061202_387.webp)
![Non-transfected (–) and transfected (+) 293T whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Glutamine synthetase antibody [GT7711] (GTX630657) diluted at 1:500. Non-transfected (–) and transfected (+) 293T whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Glutamine synthetase antibody [GT7711] (GTX630657) diluted at 1:500.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX630657/GTX630657_41617_20160630_WB_shRNA_watermark_w_23061202_443.webp)
![Glutamine synthetase antibody [GT7711] detects Glutamine synthetase protein by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse tissues. Glutamine synthetase stained by Glutamine synthetase antibody [GT7711] (GTX630657) diluted at 1:200. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min Glutamine synthetase antibody [GT7711] detects Glutamine synthetase protein by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse tissues. Glutamine synthetase stained by Glutamine synthetase antibody [GT7711] (GTX630657) diluted at 1:200. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX630657/GTX630657_44825_20230609_IHC-P_multiple_M_23062718_255.webp)
![Glutamine synthetase antibody [GT7711] detects Glutamine synthetase protein at cell membrane by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse eye. Green: Glutamine synthetase stained by Glutamine synthetase antibody [GT7711] (GTX630657) diluted at 1:200. Red: beta Tubulin 3/ Tuj1 , a Cytoskeleton marker, stained by beta Tubulin 3/ Tuj1 antibody [GT11710] (GTX631836) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920). Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min Glutamine synthetase antibody [GT7711] detects Glutamine synthetase protein at cell membrane by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded mouse eye. Green: Glutamine synthetase stained by Glutamine synthetase antibody [GT7711] (GTX630657) diluted at 1:200. Red: beta Tubulin 3/ Tuj1 , a Cytoskeleton marker, stained by beta Tubulin 3/ Tuj1 antibody [GT11710] (GTX631836) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Fluoroshield with DAPI (GTX30920). Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX630657/GTX630657_44825_20230609_IHC-P_M_1_23062718_893.webp)
![Glutamine synthetase antibody [GT7711] detects Glutamine synthetase protein at cell membrane and cytoplasm by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded rat stomach. Glutamine synthetase stained by Glutamine synthetase antibody [GT7711] (GTX630657) diluted at 1:200. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min Glutamine synthetase antibody [GT7711] detects Glutamine synthetase protein at cell membrane and cytoplasm by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded rat stomach. Glutamine synthetase stained by Glutamine synthetase antibody [GT7711] (GTX630657) diluted at 1:200. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX630657/GTX630657_44510_20231201_IHC-P_R_24010223_252.webp)

![IHC-P analysis of human liver tissue using GTX04471 Glutamine synthetase antibody [MSVA-750M] HistoMAX?. Glutamine synthetase staining is strong in centrilobular hepatocytes weak to moderate in Kupffer cells but absent in periportal hepatocytes.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX04471/GTX04471_20230728_IHC-P_57_23072722_662.webp)
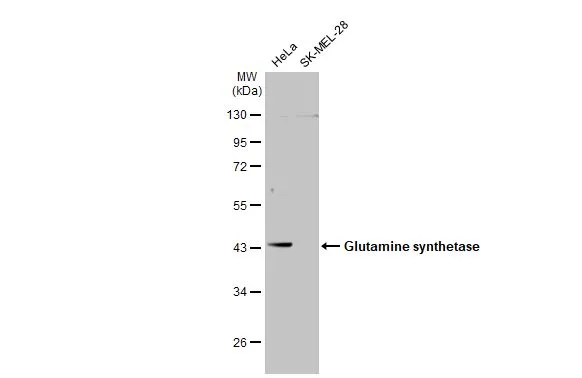
![Rat tissue extract (50 μg) was separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Glutamine synthetase antibody [GT1055] (GTX630654) diluted at 1:5000.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX630654/GTX630654_41603_20160901_WB_R_brain_w_23061202_653.webp)
![Various tissue extracts (50 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Glutamine synthetase antibody [HL2283] (GTX638336) diluted at 1:5000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX638336/GTX638336_T-44977_20230317_WB_M_R_23032022_129.webp)
![IHC-P analysis of human endometrium tissue using GTX84426 Glutamine synthetase antibody [1F4]. Antigen retrieval : Heat-induced epitope retrieval by 10mM citrate buffer, pH6.0, 100oC for 10min.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX84426/GTX84426_2705_IHC-P_w_23061420_245.webp)