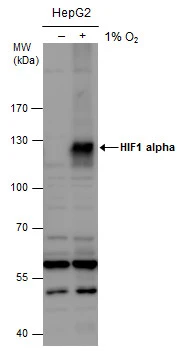
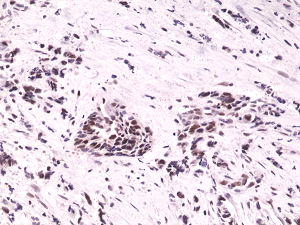
HIF1A Antibody / HIF-1 alpha
ORB1825526
ApplicationsImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetHIF1A
Overview
- SupplierBiorbyt
- Product NameHIF1A Antibody / HIF-1 alpha
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ApplicationsImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- Applications SupplierImmunohistochemistry (FFPE): 1-2ug/ml for 30 minutes at RT IHC-P
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDHIF1A/3248
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID3091
- Target nameHIF1A
- Target descriptionhypoxia inducible factor 1 subunit alpha
- Target synonymsHIF-1-alpha, HIF-1A, HIF-1alpha, HIF1, HIF1-ALPHA, MOP1, PASD8, bHLHe78, hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha, ARNT interacting protein, PAS domain-containing protein 8, basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS protein MOP1, class E basic helix-loop-helix protein 78, hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha subunit, hypoxia inducible factor 1, alpha subunit (basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor), hypoxia-inducible factor1alpha, member of PAS protein 1, member of PAS superfamily 1
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG1
- Protein IDQ16665
- Protein NameHypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha
- Scientific DescriptionHIF1 (hypoxia-inducible factor 1), a heterodimeric transcription factor complex central to cellular response to hypoxia, consists of two subunits (HIF-1 alpha and HIF-1 beta) which are basic helix-loop-helix proteins of the PAS (Per, ARNT, Sim) family. Expression of HIF-1 alpha protein is regulated by cellular oxygen level alterations as well as in oxygen-independent manner via different cytokines (through the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway), growth factors, oncogenic activation, or loss of tumor suppressor function etc. In normoxic cells, HIF-1 alpha is proline hydroxylated leading to a conformational change that promotes its binding to the VLH (von Hippel Lindau) protein E3 ligase complex; ubiquitination and followed by rapid proteasomal degradation. Hypoxia as well as chemical hydroxylase inhibitors (desferrioxamine, cobalt etc.) inhibit HIF-1 alpha degradation and lead to its accumulation in the cells, whereas, contrastingly, HIF-1 beta/ARNT (AhR nuclear translocator) remains stable under both conditions. Besides their critical role in hypoxic response, HIF1s regulates the transcription of genes responsible for angiogenesis, erythropoiesis/iron-metabolism, glucose metabolism, cell proliferation/survival, adipogenesis, carotid body formation, B lymphocyte development and immune reactions.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C
- UNSPSC12352203