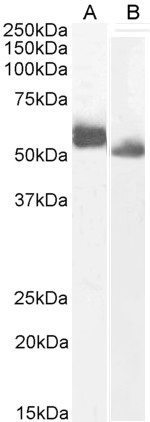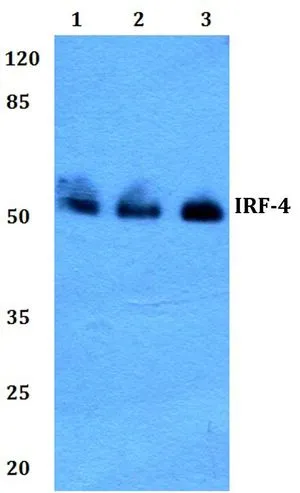
WB analysis of various samples using GTX66692 IRF4 / MUM1 antibody. Lane1 : HEK293T whole cell lysate
Lane2 : Raw264.7 whole cell lysate
Lane3 : PC12 whole cell lysate Dilution : 1:500
IRF4 / MUM1 antibody
GTX66692
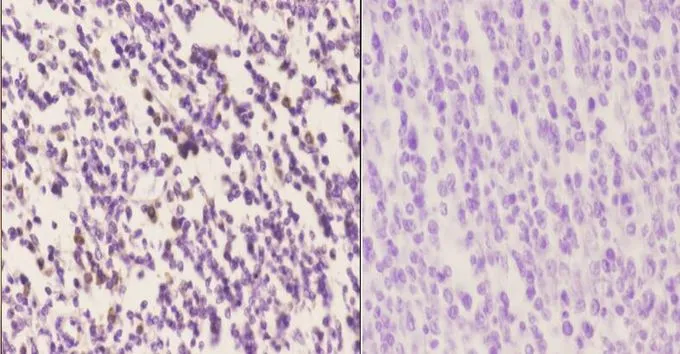
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetIRF4
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameIRF4 / MUM1 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteIHC-P: 1:50-1:200. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID3662
- Target nameIRF4
- Target descriptioninterferon regulatory factor 4
- Target synonymsIMD131, LSIRF, MUM1, NF-EM5, SHEP8, interferon regulatory factor 4, lymphocyte-specific interferon regulatory factor, multiple myeloma oncogene 1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ15306
- Protein NameInterferon regulatory factor 4
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene belongs to the IRF (interferon regulatory factor) family of transcription factors, characterized by an unique tryptophan pentad repeat DNA-binding domain. The IRFs are important in the regulation of interferons in response to infection by virus, and in the regulation of interferon-inducible genes. This family member is lymphocyte specific and negatively regulates Toll-like-receptor (TLR) signaling that is central to the activation of innate and adaptive immune systems. A chromosomal translocation involving this gene and the IgH locus, t(6;14)(p25;q32), may be a cause of multiple myeloma. Alternatively spliced transcript variants have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2010]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161