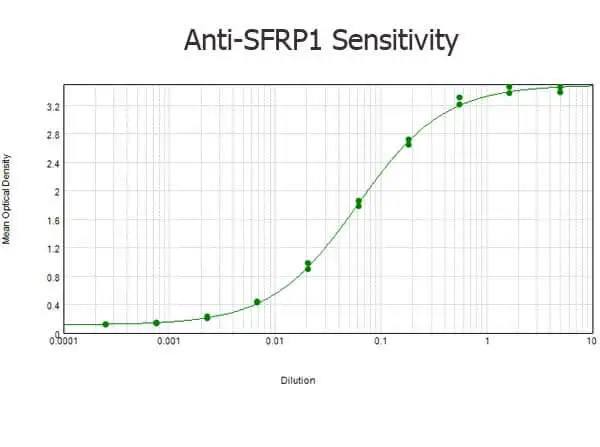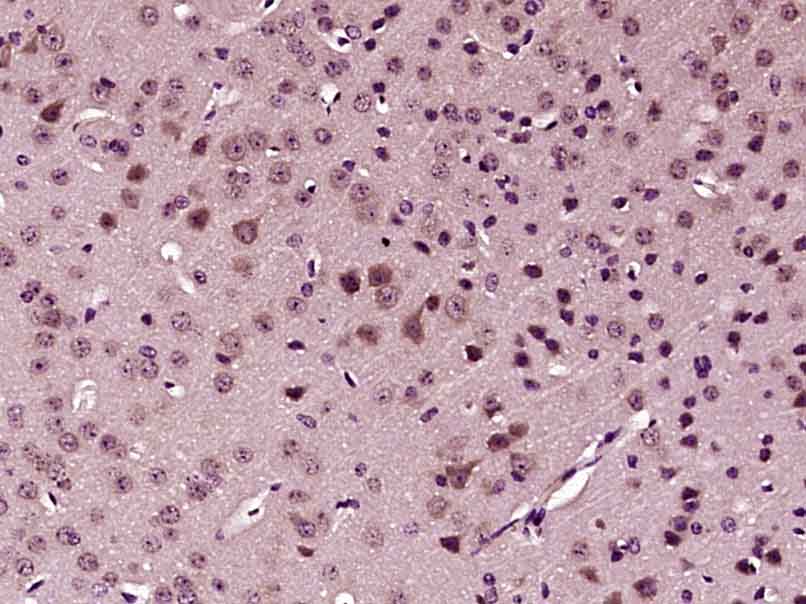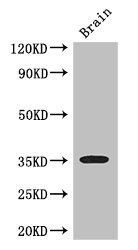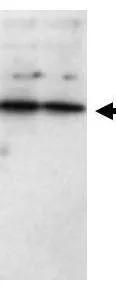
Western blot using GeneTex Affinity Purified anti-SFRP1 antibody (GTX24193) shows detection of a band ~37 kDa (arrowhead) corresponding to SFRP1 in lysates from human cultured airway epithelial cells. Lysates were run on a SDS-PAGE and transferred onto nitrocellulose followed by reaction with a 1:230 dilution of anti-SFRP1 antibody overnight at 4oC. Signal was detected using standard techniques.
SFRP1 antibody
GTX24193
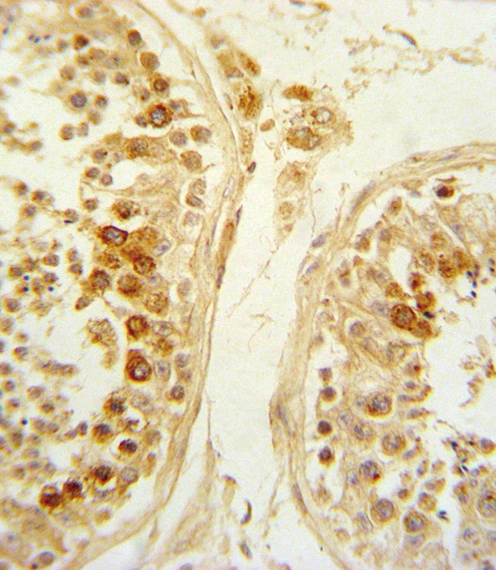
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetSFRP1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameSFRP1 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:200-1:2000. ICC/IF: 5 microg/mL. IHC-P: 1:800. ELISA: 1:5000-1:15000. IHC: 1:800. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID6422
- Target nameSFRP1
- Target descriptionsecreted frizzled related protein 1
- Target synonymsFRP, FRP-1, FRP1, FrzA, SARP2, secreted frizzled-related protein 1, SARP-2, frizzled-related protein, sFRP-1, secreted apoptosis-related protein 2
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ8N474
- Protein NameSecreted frizzled-related protein 1
- Scientific DescriptionSFRP1 is a member of the SFRP family that contains a cysteine-rich domain homologous to the putative Wnt-binding site of Frizzled proteins. SFRPs act as soluble modulators of Wnt signaling. SFRP1 and SFRP5 may be involved in determining the polarity of photoreceptor cells in the retina. SFRP1 is expressed in several human tissues, with the highest levels in heart.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
References
- Increased expression of secreted frizzled related protein 1 (SFRP1) predicts ampullary adenocarcinoma recurrence. Cheng LC et al., 2020 Aug 6, Sci RepRead this paper